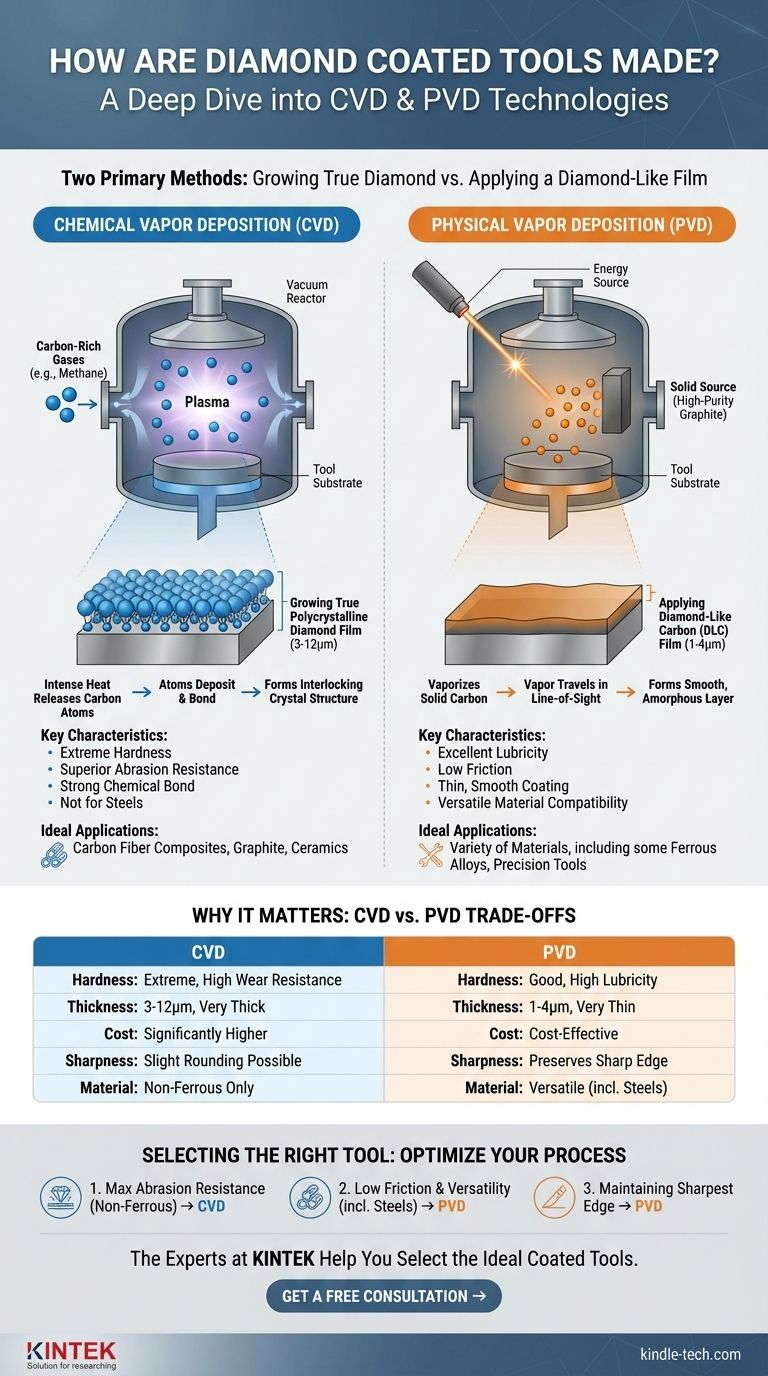
In short, diamond-coated tools are made using one of two primary methods: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The CVD process literally grows a film of true, polycrystalline diamond directly onto the tool's surface. In contrast, the PVD process applies a film of amorphous Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), which mimics diamond's properties but lacks its crystalline structure.
The critical distinction lies in the final product: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) creates a thick, exceptionally hard layer of real diamond for extreme abrasion resistance, while Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) applies a thinner, smoother, diamond-like film prized for its low friction and versatility.

The Two Paths to a Diamond Coating
Understanding the manufacturing process is crucial because it dictates the tool's performance, ideal application, and cost. The terms "diamond coating" and "diamond-like coating" are often used interchangeably, but they result from fundamentally different technologies.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Growing True Diamond
In the CVD process, tools, typically made of tungsten carbide, are placed inside a high-temperature vacuum reactor.
Carbon-rich gases, such as methane, are introduced into the chamber. The intense heat breaks these gases down, releasing carbon atoms.
These carbon atoms then deposit onto the tool's surface, bonding with each other and the carbide substrate to grow a genuine, interlocking polycrystalline diamond film.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Applying a Diamond-Like Film
The PVD process also occurs in a vacuum but operates differently. Instead of a gas, it starts with a solid source of high-purity graphite (a form of carbon).
This solid carbon is vaporized by an energy source, such as an arc or a laser, and the vaporized carbon travels in a line-of-sight path to coat the tool.
The result is a very thin, dense, and smooth film of Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC). This coating is amorphous, meaning its atoms lack the rigid, crystalline structure of true diamond, but it still possesses remarkable hardness and lubricity.
Why the Manufacturing Method Matters
The difference between growing a crystalline structure (CVD) and depositing an amorphous one (PVD) has direct consequences for tool performance.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
CVD diamond is significantly harder and more wear-resistant than any PVD coating. Its true diamond structure makes it the ultimate choice for machining highly abrasive, non-ferrous materials like carbon fiber composites, graphite, and high-silicon aluminum.
Coating Thickness and Adhesion
CVD coatings are generally much thicker (typically 3 to 12 microns) and form an incredibly strong chemical bond with the carbide substrate, making them highly resistant to flaking.
PVD (DLC) coatings are much thinner (typically 1 to 4 microns). This can be an advantage, as it does a better job of preserving the original tool's razor-sharp cutting edge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies is not about which is "better" overall, but which is correct for a specific task. Each process involves clear compromises.
The Cost Factor
The CVD process is more complex, time-consuming, and energy-intensive. Consequently, CVD diamond tools are significantly more expensive than tools with a PVD (DLC) coating.
Impact on Tool Sharpness
The high temperatures required for the CVD process can cause a very slight rounding or blunting of an extremely sharp cutting edge. For applications where the absolute sharpest edge is paramount, the lower-temperature PVD process often has an advantage.
Material Compatibility
True diamond reacts chemically with iron at high temperatures, causing rapid tool failure. Therefore, CVD diamond tools cannot be used to machine steels. PVD (DLC) coatings, however, are often formulated to work effectively on a wider range of materials, including some ferrous alloys.
Selecting the Right Tool for the Job
Your choice should always be driven by your material and your primary performance goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance for machining abrasive non-ferrous materials (composites, graphite, ceramics): CVD diamond tools provide the longest life and best performance.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and moderate wear across a variety of materials, including some steels: A PVD (DLC) coating offers a versatile and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the sharpest possible cutting edge on a precision tool: The thin, smooth nature of a PVD (DLC) coating is often the superior choice.
Ultimately, understanding how a tool is made is the key to unlocking its intended performance in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Method | Coating Type | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | True Polycrystalline Diamond | Extreme hardness, thick coating (3-12µm), superior abrasion resistance | Machining abrasive non-ferrous materials (e.g., composites, graphite, ceramics) |
| Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Excellent lubricity, thin coating (1-4µm), versatile, cost-effective | Reducing friction on a variety of materials, including some steels |
Optimize Your Machining Process with the Right Coating
Choosing between CVD and PVD diamond coatings is critical for maximizing tool life and performance in your specific application. The experts at KINTEK specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables for advanced material analysis and processing. We can help you select the ideal coated tools for your needs, whether you require the ultimate wear resistance of CVD diamond or the versatile low-friction properties of PVD DLC.
Contact our specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















