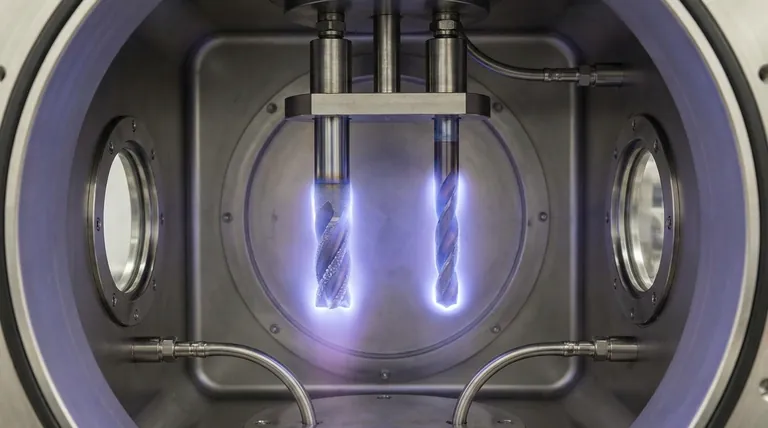
In essence, diamond coatings are grown onto a tool's surface using a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In a vacuum chamber, carbon-containing gases like methane are energized, causing carbon atoms to break free and meticulously arrange themselves into a diamond crystal lattice on the tool. This transforms a standard tool into one with the extreme hardness and low friction of diamond.
The core challenge of diamond coating is not the deposition process itself, but ensuring the diamond film permanently adheres to the tool's base material. Without solving this adhesion problem, the coating will quickly fail in service.
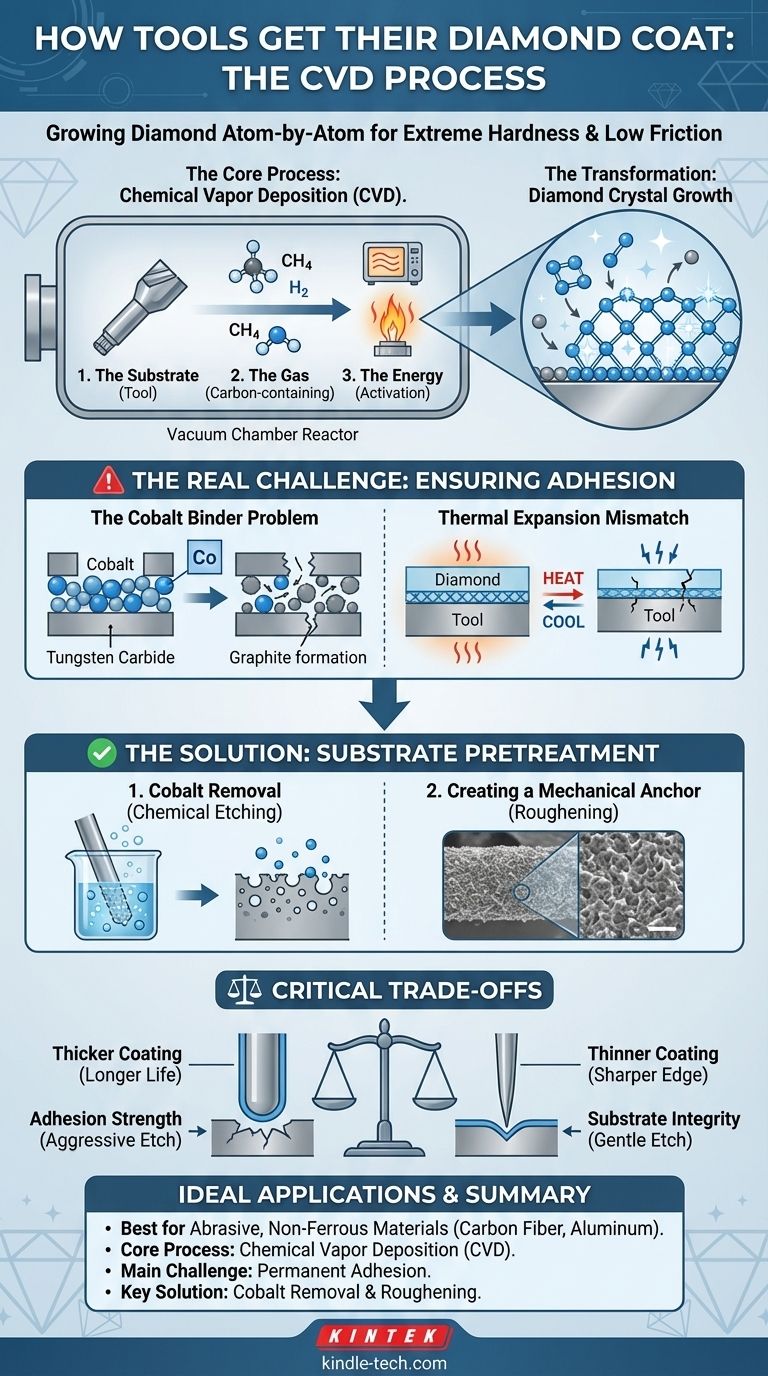
The Core Process: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
To understand the challenges, you first need to understand the fundamental process. CVD is less like painting and more like growing crystals atom-by-atom.
The Principle of Deposition
Imagine water vapor condensing into intricate frost patterns on a cold windowpane. CVD operates on a similar principle but under far more controlled conditions. Carbon atoms from a gas phase are encouraged to settle and bond onto a solid surface—the tool—in a specific crystalline structure: diamond.
The Key Ingredients
The process takes place inside a sealed reactor chamber. Three things are required:
- The Substrate: The tool itself, typically made of cemented carbide.
- The Gas: A source of carbon, most commonly methane (CH₄), mixed with hydrogen.
- The Energy: An activation method, such as microwaves or a hot filament, to break apart the gas molecules and create a reactive plasma.
The Transformation to Diamond
The intense energy breaks down the methane and hydrogen molecules. The hydrogen plays a critical role in scavenging any carbon that tries to form weaker graphite bonds, ensuring only the strong, diamond-structured carbon is deposited onto the heated tool surface. Over hours, these atoms build up into a continuous, pure diamond film.
The Real Challenge: Ensuring Adhesion
The references are correct: the most significant point of failure is the bond between the diamond film and the tool. If the coating doesn't stick, its hardness is irrelevant.
The Cobalt Binder Problem
Most cutting tools are made of cemented carbide, which consists of hard tungsten carbide grains held together by a metallic cobalt binder. During the high temperatures of CVD, this cobalt binder becomes a major problem. It acts as a catalyst that promotes the formation of soft graphite instead of hard diamond, poisoning the interface and creating a weak bond.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch
Diamond and cemented carbide expand and contract at very different rates when heated and cooled. As the tool cools after the coating process, this mismatch creates immense stress at the boundary layer, which can cause the diamond film to crack, peel, or flake off.
The Solution: Substrate Pretreatment
Because of these challenges, simply placing a tool in a CVD reactor will produce a useless coating. The surface of the tool must be meticulously prepared, or "pretreated," to make it receptive to a strong diamond bond.
Removing the Problematic Cobalt
The most critical pretreatment step is removing the cobalt from the surface of the tool. This is typically done through chemical etching processes that selectively dissolve the cobalt binder from the top few microns of the substrate, leaving a cobalt-free surface of tungsten carbide for the diamond to grow on.
Creating a Mechanical Anchor
After chemical etching, the surface is often physically roughened on a microscopic scale. This creates a more complex surface topography with more area for the diamond film to "grip," establishing a stronger mechanical interlock in addition to the chemical bond.
The Complexity Factor
As your reference notes, these pretreatment steps are difficult to perform uniformly on tools with complex shapes, like the flutes of a drill or an end mill. Uneven etching or roughening can lead to areas of poor adhesion, creating weak points where the coating will fail first under the stress of machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Diamond coating is not a magic bullet, and the process involves critical engineering compromises.
Coating Thickness vs. Edge Sharpness
A thicker coating (e.g., 10-15 microns) offers longer life in abrasive materials but can round a sharp cutting edge, making it less effective for high-precision finishing. A thinner coating (e.g., 2-5 microns) preserves the sharp edge but wears out faster.
Adhesion Strength vs. Substrate Integrity
Aggressive chemical etching is excellent for removing cobalt and promoting adhesion, but if overdone, it can weaken the underlying cemented carbide substrate. This can make the cutting edge brittle and prone to chipping, trading one failure mode for another.
Cost vs. Performance
The multi-step process of pretreatment and long CVD cycles makes diamond-coated tools significantly more expensive. The performance gain must be substantial enough to justify the investment over other advanced coatings like TiAlN or AlCrN, especially for materials that don't strictly require diamond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right tool requires looking beyond the "diamond coated" label and considering the specifics of the process in relation to your goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum tool life in highly abrasive, non-ferrous materials (like carbon fiber composites or high-silicon aluminum): Prioritize a thicker coating from a supplier who details their cobalt-leaching pretreatment process, as this indicates a focus on robust adhesion.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight tolerances and sharp features on complex parts: Opt for a thinner, highly conformal coating and verify the coater's specific experience with complex geometries to ensure uniform adhesion.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining or cost-effectiveness: Carefully evaluate if the performance gains of diamond justify the cost over less expensive but highly effective PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coatings.
Understanding the interplay between deposition and adhesion is the key to selecting a tool that truly delivers on the promise of diamond.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
| Main Challenge | Ensuring permanent adhesion to the tool substrate |
| Key Pretreatment | Cobalt removal and surface roughening |
| Critical Trade-off | Coating thickness vs. edge sharpness |
| Ideal For | Machining abrasive, non-ferrous materials (e.g., carbon fiber, aluminum) |
Ready to enhance your machining performance with diamond-coated tools?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating technologies. Our expertise ensures you get tools with superior adhesion and durability, tailored for your specific laboratory or industrial needs.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how our diamond-coated solutions can extend tool life and improve your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
People Also Ask
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers



















