At its core, a material's heat capacity is determined by the number of ways it can store thermal energy at the microscopic level. When you add heat, that energy doesn't just make atoms move faster; it gets distributed into various "storage bins," such as molecular rotations and vibrations. Materials with more complex structures have more of these storage bins, so they require more energy to achieve the same increase in temperature.
The key takeaway is this: heat capacity is a measure of molecular complexity and freedom. Materials with simple atoms (like noble gases) have low heat capacity, while materials with complex molecules and strong intermolecular forces (like water) have high heat capacity because they have many more ways to absorb energy beyond simple movement.

What is Heat Capacity, Really?
To understand the differences between materials, we must first separate the concepts of heat and temperature.
Temperature vs. Heat
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Think of it as the average speed of the atoms or molecules as they move, wiggle, and jiggle.
Heat, on the other hand, is the total thermal energy transferred into or out of a substance. When you add heat, you are adding energy. That energy's job is to raise the substance's total internal energy.
The "Energy Storage" Analogy
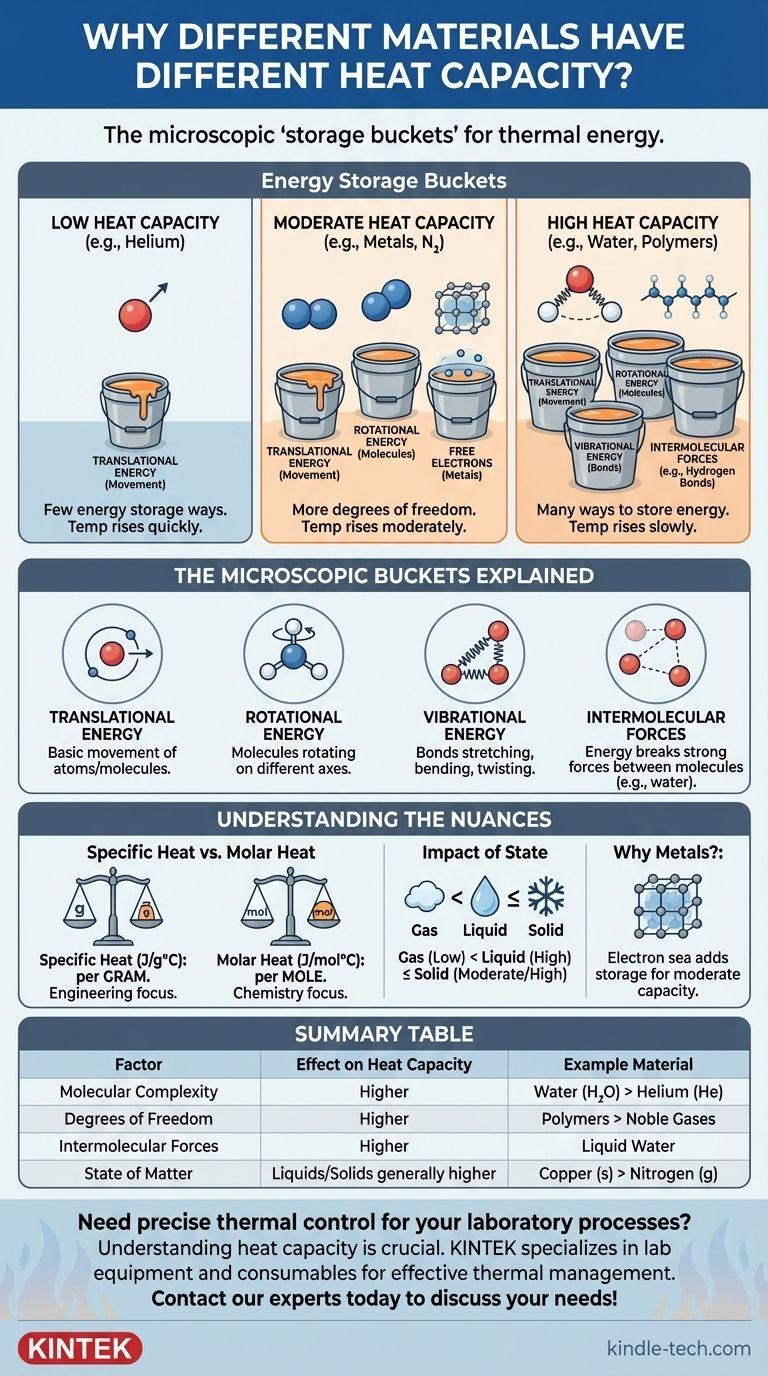
Imagine you have several empty buckets. Adding heat is like pouring water into them. The temperature is like the water level in just one of those buckets, the one labeled "Movement" (kinetic energy).
A material's heat capacity is determined by how many total buckets it has. If a material only has one bucket ("Movement"), all the water you pour in goes there, and the level rises quickly. If a material has many buckets, you have to pour in a lot more water to raise the level in that one specific "Movement" bucket.
The Microscopic Buckets: Where Energy is Stored
Different materials have different types of microscopic "buckets," formally known as degrees of freedom. Each one provides a different way to store thermal energy.
1. Translational Energy (The Basic Bucket)
This is the energy of an atom or molecule moving from one place to another. All materials have this. It is the primary contributor to what we measure as temperature.
For a simple substance like helium gas, whose atoms are individual spheres, this is almost the only way to store energy. Its heat capacity is very low.
2. Rotational Energy (For Molecules)
A single atom cannot meaningfully rotate to store energy, but a molecule can. A simple two-atom molecule like nitrogen (N₂) can spin on two different axes, like a baton twirling.
A more complex, non-linear molecule like water (H₂O) can rotate on three different axes. Each axis of rotation is another "bucket" for storing energy, increasing its heat capacity.
3. Vibrational Energy (A Key Differentiator)
The bonds holding atoms together in a molecule are not rigid rods; they are more like springs. They can stretch, bend, and twist. Each of these vibrational modes is another highly effective energy bucket.
A simple diatomic molecule has one vibrational mode. A complex molecule with many atoms and bonds has dozens. This is a primary reason why complex substances like oils and polymers have higher heat capacities than simple gases.
4. Intermolecular Forces (The Water Example)
In liquids and solids, energy is also used to work against the forces between molecules. Water is the ultimate example of this. Its molecules are linked by strong hydrogen bonds.
Before the water molecules can significantly speed up (increase temperature), a large portion of the added heat energy must first go into jostling and breaking these powerful bonds. This acts as a massive energy sink, giving water one of the highest specific heat capacities of any common substance.
Understanding the Nuances
When comparing materials, context is critical. Simply looking at a number can be misleading without understanding what it represents.
Specific Heat vs. Molar Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the energy required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius (J/g°C). This is useful for engineering and real-world applications where mass is the primary concern.
Molar heat capacity is the energy needed to raise one mole of a substance by one degree (J/mol°C). This is often more useful for physicists and chemists, as it compares an equal number of molecules, providing a fairer comparison of molecular complexity. For instance, water's specific heat is over four times that of copper, but its molar heat capacity is only about three times greater.
The Impact of State (Gas, Liquid, Solid)
A substance's heat capacity changes depending on its state.
- Gases have lower heat capacities because their molecules are far apart and don't interact much.
- Liquids have higher capacities because of the energy needed to overcome intermolecular forces.
- Solids store energy in a collective lattice of vibrations (called phonons). Their capacity is often similar to their liquid form but can be lower at very cold temperatures.
Why Metals Have Moderate Heat Capacity
You might expect metals, being simple atoms, to have low heat capacity. Their capacity is moderate because of their unique structure: a rigid lattice of ions within a "sea" of free-moving electrons. This electron sea can also absorb thermal energy, acting as an additional energy storage bucket that simple atomic gases lack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
How you interpret heat capacity data depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is engineering or thermal management: Use specific heat capacity (per gram), as it directly informs how much a given mass of material will heat up in a real-world design.
- If your primary focus is fundamental chemistry or physics: Compare molar heat capacity (per mole) to isolate the effects of molecular structure, degrees of freedom, and bonding on energy storage.
- If your primary focus is climate science or biology: Recognize that water's exceptionally high specific heat capacity, driven by hydrogen bonding, is the single most important factor in stabilizing Earth's climate and moderating body temperature in living organisms.
Ultimately, a material's heat capacity is the macroscopic signature of its microscopic world.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Heat Capacity | Example Material |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Complexity | More complex molecules = higher capacity | Water (H₂O) vs. Helium (He) |
| Degrees of Freedom | More ways to store energy (rotation, vibration) = higher capacity | Polymers vs. Noble Gases |
| Intermolecular Forces | Stronger forces (e.g., hydrogen bonds) = higher capacity | Liquid Water |
| State of Matter | Liquids/Solids generally higher than Gases | Copper (solid) vs. Nitrogen (gas) |
| Free Electrons | Electron sea in metals adds moderate capacity | Metals like Aluminum |
Need precise thermal control for your laboratory processes? Understanding heat capacity is crucial for applications like chemical synthesis, materials testing, and thermal analysis. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools you need to manage thermal energy effectively. Whether you require furnaces, heaters, or temperature monitoring systems, our solutions are designed for accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and enhance your research outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Flat Corrugated Heat Sink for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Copper Foam
People Also Ask
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained













