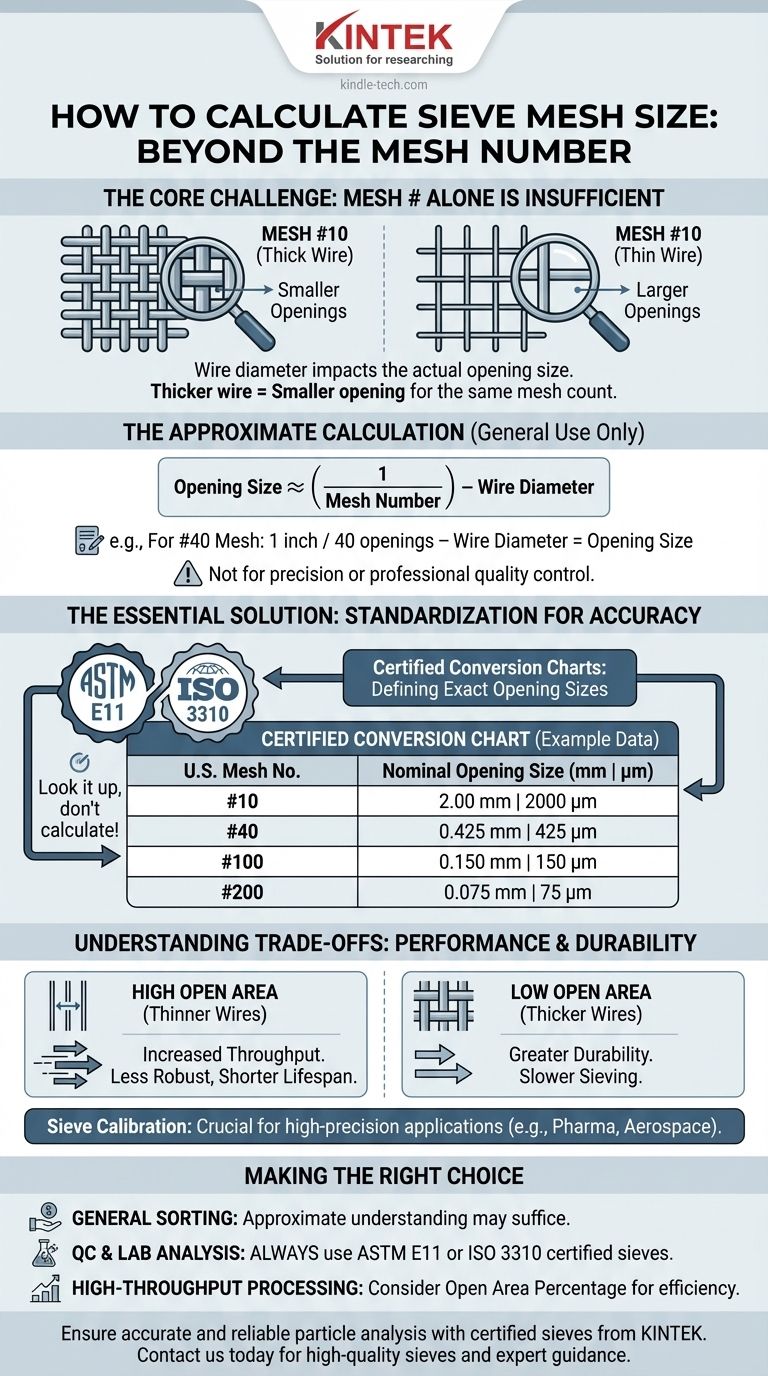
Calculating sieve mesh size is not done with a single, universal formula because the mesh number alone is insufficient. The mesh number tells you the number of openings per linear inch, but the actual size of each opening depends on the diameter of the wire used to weave the sieve. A thicker wire results in a smaller opening for the same mesh number.
The core principle is that a sieve's opening size is determined by the inverse of its mesh number, minus the space taken up by the wires. For any precise or professional work, you do not calculate this; you refer to official conversion charts from standards like ASTM E11 or ISO 3310, which specify the exact opening size for each certified mesh designation.

The Fundamentals of Sieve Mesh
To select the correct sieve, you must understand the relationship between its three core properties: the mesh number, the wire diameter, and the resulting opening size.
What is "Mesh Number"?
The mesh number (or mesh count) is a simple measure of how fine a woven wire mesh is. It represents the number of openings you can count across one linear inch of the screen.
For example, a sieve with a #10 mesh has 10 openings per inch. A much finer #200 mesh sieve has 200 openings per inch.
The Critical Role of Wire Diameter
The wires themselves take up space. For a given mesh number, using a thicker, more durable wire will necessarily create smaller openings. Conversely, a thinner wire will create larger openings.
This is why you cannot accurately determine the opening size from the mesh number alone.
The Approximate Calculation
If you know the wire diameter, you can estimate the opening size with a simple formula:
Opening Size ≈ (1 / Mesh Number) - Wire Diameter
For example, for a #40 mesh sieve, there are 40 openings and 40 wires per inch. If you do not know the wire diameter, you cannot solve for the opening size. This approximation is useful for general understanding but not for scientific or quality control applications.
Why Standardization is Essential
In any technical field, repeatable results are paramount. Relying on an approximate calculation introduces unacceptable variability, which is solved by using internationally recognized standards.
The Problem with Uncertified Sieves
If two #100 mesh sieves from different manufacturers use different wire diameters, they will separate particles differently. This makes it impossible to compare test results or ensure consistent product quality.
Introducing ASTM E11 and ISO 3310
To solve this, organizations developed standards that rigidly define sieve specifications. The most common are ASTM E11 (in the United States) and ISO 3310 (internationally).
These standards prescribe the nominal opening size for each standard mesh number. They also specify the required wire diameter and the permissible manufacturing tolerances to ensure global uniformity.
How to Use a Standard Conversion Chart
For any professional application, you do not calculate the opening size—you look it up on a certified conversion chart. These charts directly link the mesh number to its official opening size in millimeters (mm) or micrometers (microns).
| U.S. Mesh No. | Nominal Sieve Opening (mm) | Nominal Sieve Opening (microns, μm) |
|---|---|---|
| #10 | 2.00 | 2000 |
| #40 | 0.425 | 425 |
| #100 | 0.150 | 150 |
| #200 | 0.075 | 75 |
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sieve involves more than just the opening size. The physical construction of the mesh creates important performance trade-offs.
Open Area Percentage
The open area is the ratio of the area of the openings to the total area of the sieve. It is influenced by the wire diameter.
A sieve with a higher open area (thinner wires) allows particles to pass through more quickly, increasing throughput. However, it may be less robust and have a shorter lifespan. A lower open area offers greater durability at the cost of slower sieving.
Woven Wire vs. Perforated Plate
While woven wire mesh is most common, some sieves are made from a perforated plate—a solid sheet of metal with fixed-size holes. These are typically used for larger particle sizes (>4 mm) and offer superior durability, but they cannot achieve the fine separations of a woven wire sieve.
The Importance of Sieve Calibration
Even certified sieves have manufacturing tolerances. For high-precision applications, such as in the pharmaceutical or aerospace industries, sieves must be periodically calibrated using traceable glass beads or an optical comparator to verify that the openings remain within specification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates how you should approach sieve selection. Use the official standards as your definitive guide for any task that requires accuracy and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is general, non-critical sorting: An approximate understanding of the relationship between mesh number and opening size may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is quality control, lab analysis, or scientific research: Always use sieves certified to ASTM E11 or ISO 3310 and refer to their official conversion charts for opening sizes.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial processing: Pay close attention to the open area percentage, as it directly impacts sieving efficiency and equipment wear.
By moving beyond simple calculation and leveraging industry standards, you ensure your particle analysis is both accurate and reliable.
Summary Table:
| U.S. Mesh No. | Nominal Opening (mm) | Nominal Opening (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| #10 | 2.00 | 2000 |
| #40 | 0.425 | 425 |
| #100 | 0.150 | 150 |
| #200 | 0.075 | 75 |
Ensure your particle analysis is accurate and reliable with certified sieves from KINTEK.
As a leading supplier of laboratory equipment, KINTEK provides high-quality sieves that meet ASTM E11 and ISO 3310 standards, guaranteeing precise opening sizes and consistent results for your quality control, research, or industrial processes. Our experts can help you select the right sieves for your specific application, whether you're in pharmaceuticals, materials science, or food processing.
Contact our team today to discuss your sieve requirements and elevate your particle analysis workflow. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum sieving deviation permitted? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Precision Limits
- What is the process of sieve analysis? A Step-by-Step Guide to Particle Size Distribution
- What is sieving filtering? Master the Key Differences for Accurate Material Separation
- What is a laboratory sieve? A Guide to Precise Particle Size Analysis
- How does using a standard analytical sieve affect phenol photocatalytic degradation? Control Particle Size for Accuracy
- What are the precautions for sieving method? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Analysis
- Why are industrial standard sieves necessary for controlling the physical properties of dense refractory bricks?
- What are the sieve sizes available? Choose the Right Sieve for Accurate Particle Analysis



















