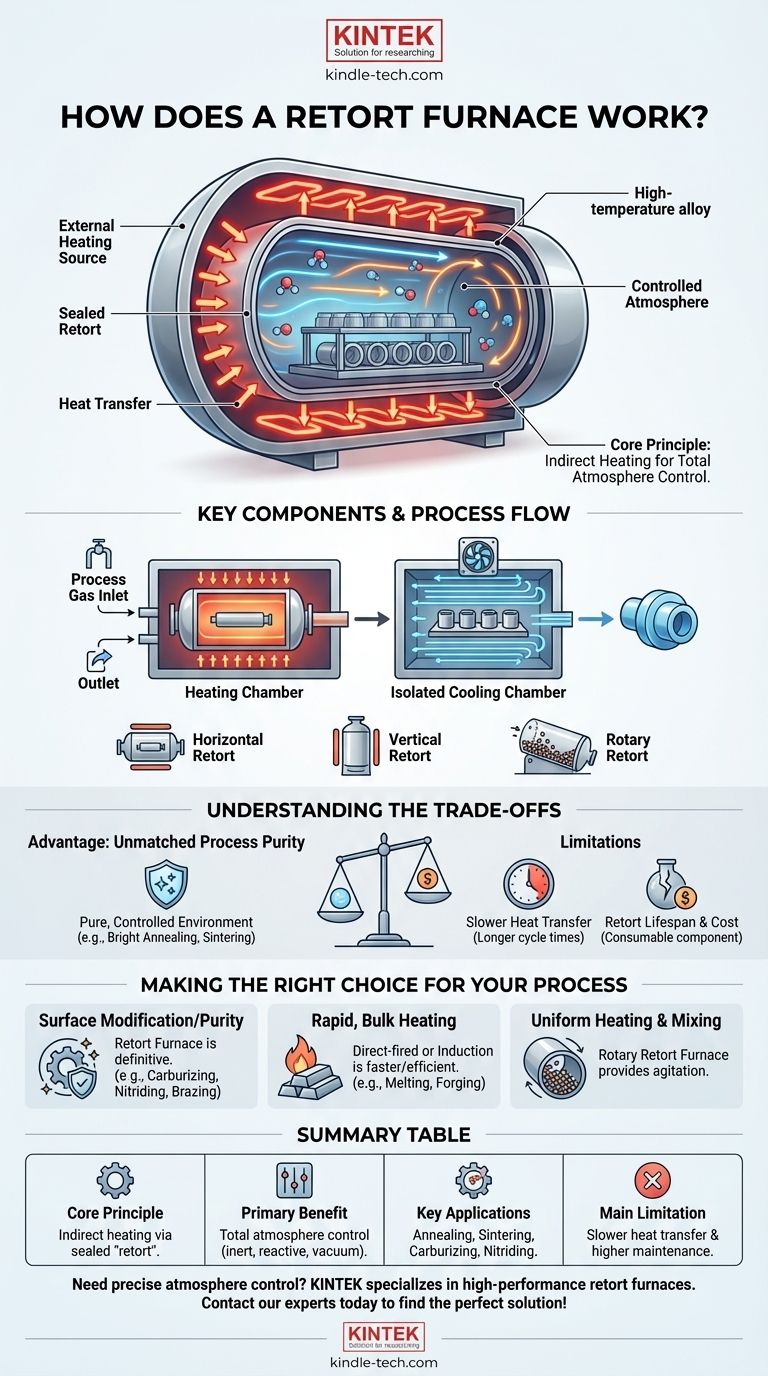
In essence, a retort furnace works by heating a sealed, gas-tight vessel—the retort—from the outside. This design isolates the material being processed from the external heating source and its combustion byproducts. This separation is the key, as it allows for precise control over the gaseous atmosphere inside the retort, which is critical for many advanced heat-treating processes.
The fundamental purpose of a retort furnace is not just to heat a material, but to do so within a perfectly controlled atmosphere. This indirect heating method prevents contamination and enables chemical changes to the material's surface that would be impossible in an open-air or direct-fired furnace.

The Core Principle: Indirect Heating and Atmosphere Control
Understanding a retort furnace begins with the concept of separation. Unlike a simple oven where the heating elements and the workpiece share the same space, a retort furnace uses a chamber-within-a-chamber design.
The Sealed Retort
The "retort" is the heart of the system. It is a sealed container, often made from a high-temperature metal alloy or ceramic, that holds the parts to be treated.
This vessel is completely isolated from the furnace's heating elements. It includes ports that allow specific process gases to be introduced and purged.
The External Heating Source
The furnace itself is an insulated box that contains the heating system. This system heats the outside of the retort to the required temperature.
Heating is typically accomplished in one of two ways: through electrical resistance heaters that surround the retort or with high-power gas burners that fire into the chamber around the retort.
Why This Separation Matters
This design provides one primary benefit: total atmosphere control. Because the workpiece is sealed inside the retort, the environment can be meticulously managed.
Combustion gases from a gas burner never touch the workpiece, preventing oxidation or contamination. This allows for processes that require a specific environment, such as an inert argon atmosphere, a reactive ammonia atmosphere for nitriding, or a vacuum.
Key Components and Process Flow
While designs vary, most retort furnaces share a common set of components that facilitate the controlled heating and cooling cycle.
The Heating Chamber
This is the main insulated body of the furnace. It houses the heating elements and the retort itself. The design focuses on providing uniform, consistent heat to the exterior of the retort wall.
The Cooling Chamber
Many retort furnaces are built with an attached, isolated cooling chamber. After the heating cycle is complete, the workpiece can be transferred into this chamber without ever leaving the controlled atmosphere.
This rapid, controlled cooling is crucial for locking in the desired material properties and preventing oxidation that would occur if the hot part were exposed to air.
Design and Orientation
Retort furnaces can be built in various configurations to suit the application. Horizontal and vertical orientations are common for processing batches of parts.
For continuous processing of powders or small parts, a rotary retort furnace is used. This is a slowly rotating tube that tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is heated evenly as it moves through the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every application. The unique design of a retort furnace presents clear advantages but also specific limitations.
Advantage: Unmatched Process Purity
The ability to maintain a pure, controlled atmosphere is the retort furnace's greatest strength. It is essential for sensitive processes like bright annealing, sintering, and case hardening.
Limitation: Slower Heat Transfer
Because the heat must travel through the retort wall to reach the workpiece, the heating process is inherently less efficient than direct heating methods. This can result in longer cycle times compared to other furnace types.
Limitation: Retort Lifespan and Cost
The retort itself is a consumable component. It is constantly subjected to extreme thermal stress and will eventually warp, crack, or fail. Replacing a large industrial retort is a significant maintenance expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your material and the desired outcome. The retort furnace excels in applications where the process environment is as important as the temperature.
- If your primary focus is surface modification or purity: The retort furnace is the definitive choice for processes like carburizing, nitriding, or bright brazing that demand a specific, clean atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating: A direct-fired furnace or an electric induction heater will often be a faster and more energy-efficient solution for simple melting or forging.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating and mixing of granules: A rotary retort furnace is specifically designed to provide the necessary agitation within a controlled environment.
Ultimately, choosing a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize precision and atmospheric control over raw heating speed and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Indirect heating via a sealed 'retort' vessel, isolating the workpiece from the heating source. |
| Primary Benefit | Total control over the internal atmosphere (e.g., inert, reactive, vacuum). |
| Key Applications | Bright Annealing, Sintering, Carburizing, Nitriding, Brazing. |
| Main Limitation | Slower heat transfer and higher maintenance due to the retort vessel. |
Need precise atmosphere control for your heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance retort furnaces and lab equipment, delivering the purity and reliability your laboratory demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is an inert condition? A Guide to Preventing Fires and Explosions
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety



















