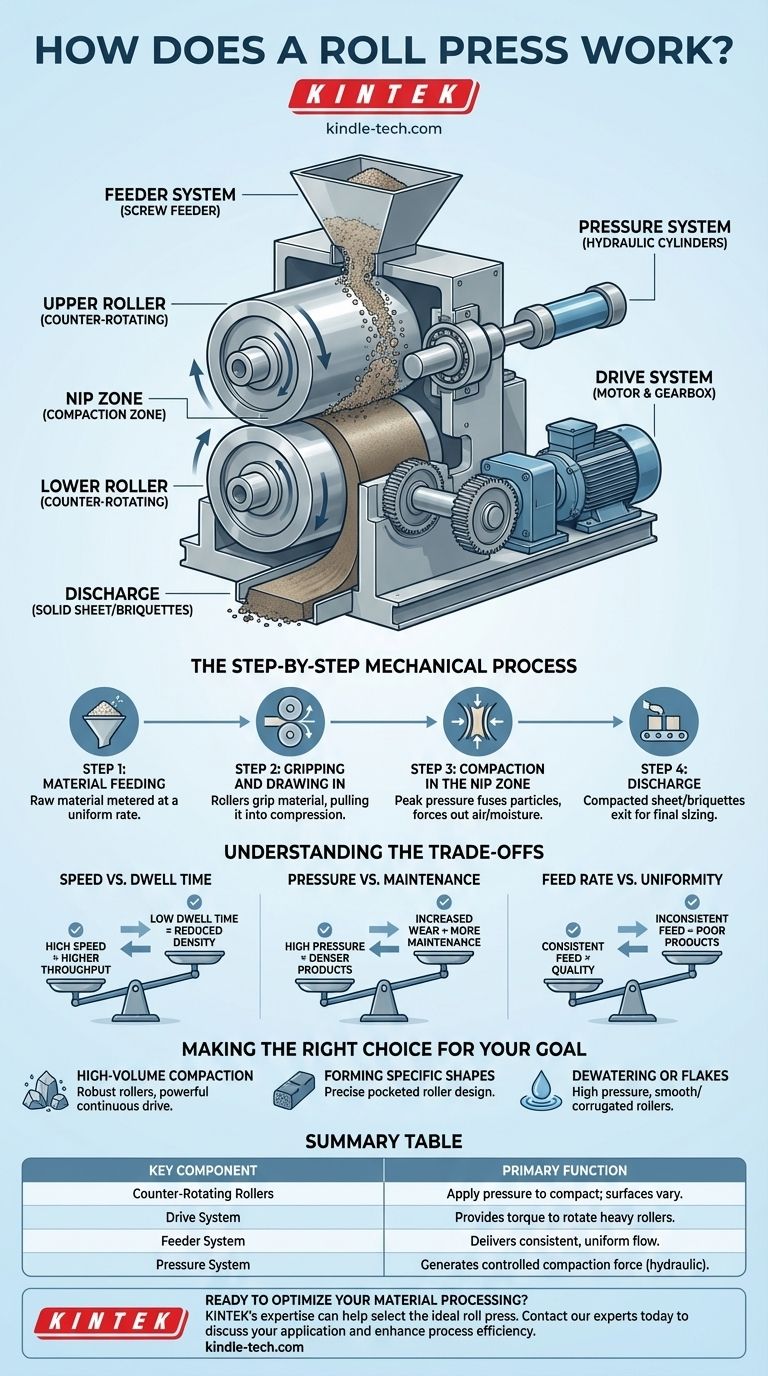
At its core, a roll press is a machine of continuous mechanical pressure. It functions by drawing material between two large, counter-rotating rollers. As the material passes through the narrowing gap between them—a zone known as the nip—it is subjected to immense force, compacting it into a denser, solid form.
The essential principle of a roll press is its ability to transform a continuous flow of loose material into a compacted sheet or briquette. Unlike a press that operates in cycles, the roll press works constantly, making it a highly efficient solution for high-throughput industrial processes.

The Core Components of a Roll Press
To understand the process, it's essential to recognize the key components that work in unison.
The Counter-Rotating Rollers
These are the heart of the machine. Their surfaces can be smooth for creating dense sheets, corrugated for flakes, or pocketed (indented) for producing precisely shaped briquettes.
The Drive System
A powerful motor and gearbox assembly provides the torque needed to turn the heavy rollers against the immense resistance of the material being compacted. The synchronization of these rollers is critical.
The Feeder System
This mechanism, often a screw feeder, is responsible for delivering a consistent and even flow of raw material into the gap above the rollers. The quality of the final product is highly dependent on the feeder's performance.
The Pressure System
While the rollers provide the mechanical action, the compressive force itself is typically generated by a hydraulic system. Hydraulic cylinders push one of the roller bearings, forcing the rollers together with a controlled, consistent pressure.
The Step-by-Step Mechanical Process
The operation is a seamless, four-stage flow that repeats continuously as long as material is supplied.
Step 1: Material Feeding
Raw material is loaded into a hopper and the feeder system meters it, ensuring it is introduced to the rollers at a predictable and uniform rate.
Step 2: Gripping and Drawing In
As the rollers turn inward, they grip the loose material and pull it down into the compression zone. The angle at which this happens is known as the "nip angle."
Step 3: Compaction in the Nip Zone
The gap between the rollers narrows to its minimum point. Here, the pressure peaks, forcing air or moisture out of the material and fusing the individual particles together into a solid, densified mass.
Step 4: Discharge
The newly formed solid sheet or stream of briquettes exits from the bottom of the rollers. It may then fall onto a conveyor or into a breaker to be sized for its final application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The efficiency of a roll press is not absolute; it's a balance of competing factors that must be managed.
Speed vs. Dwell Time
Increasing the rotational speed of the rollers increases throughput, which is often desirable. However, this reduces the "dwell time"—the duration the material is under maximum pressure—which can negatively impact the final density and strength of the product.
Pressure vs. Maintenance
Higher hydraulic pressure leads to denser, stronger products. But this elevated force dramatically increases the rate of wear on the roller surfaces and bearings, leading to more frequent and costly maintenance cycles.
Feed Rate vs. Uniformity
An inconsistent feed is the most common cause of poor results. Over-feeding can choke the press and strain the drive motor, while under-feeding results in poorly formed, low-density products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal setup for a roll press depends entirely on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume compaction (e.g., minerals, fertilizers): You need robust, wear-resistant roller surfaces and a powerful, reliable drive system capable of continuous, high-pressure operation.
- If your primary focus is forming specific shapes (briquetting coal or charcoal): The design and precision of the roller pockets are paramount, as they directly define the shape, size, and quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is dewatering or creating flakes: A combination of high pressure with smooth or corrugated rollers is essential to squeeze out liquid efficiently or shear the material into the desired form.
Ultimately, mastering a roll press application is about achieving the perfect equilibrium between feed rate, roller speed, and applied pressure.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Counter-Rotating Rollers | Apply pressure to compact material; surfaces can be smooth, corrugated, or pocketed. |
| Drive System | Provides the torque to rotate the heavy rollers against material resistance. |
| Feeder System | Delivers a consistent and uniform flow of raw material into the press. |
| Pressure System | Typically hydraulic, it generates the controlled force needed for compaction. |
Ready to Optimize Your Material Processing?
Understanding the mechanics of a roll press is the first step. Implementing the right one for your specific material and throughput goals is what delivers real results. Whether you need high-volume compaction, precise briquetting, or efficient dewatering, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you select and maintain the ideal roll press for your laboratory or industrial needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What are the two classifications of press machines? Single Punch vs. Rotary Presses Explained
- What is a punch tablet press? Precision Tableting for R&D and Small Batches
- What is the difference between single punch and rotary tablet press? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production
- What are advantages of single punch tablet press machine? Maximize R&D Efficiency with Minimal Material
- What is the advantage of a single punch tablet machine? Ideal for Low-Waste R&D and Formulation Testing



















