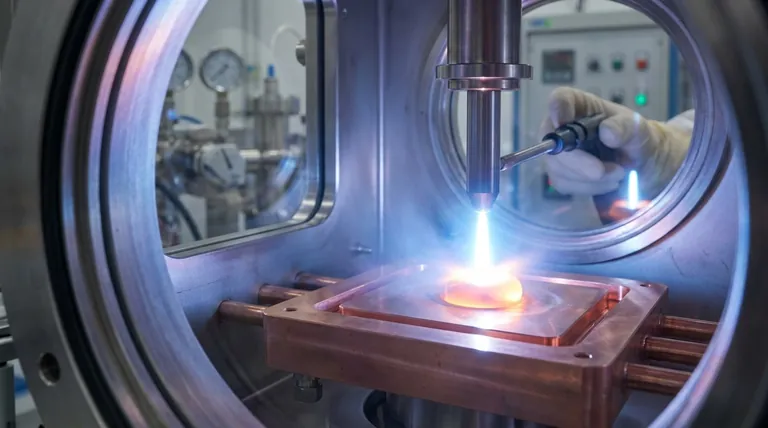
Arc melting is a metallurgical process that uses a high-current, low-voltage electric arc to melt metals and create alloys. It functions like a controlled, miniature bolt of lightning, generating intense and localized heat to melt materials with extremely high melting points in a highly controlled environment.
The core principle of arc melting is to use the intense heat of an electric plasma arc to melt materials on a water-cooled copper hearth. This "containerless" melting in an inert gas atmosphere prevents contamination, making it a benchmark method for producing high-purity, refractory, and novel research-grade alloys.
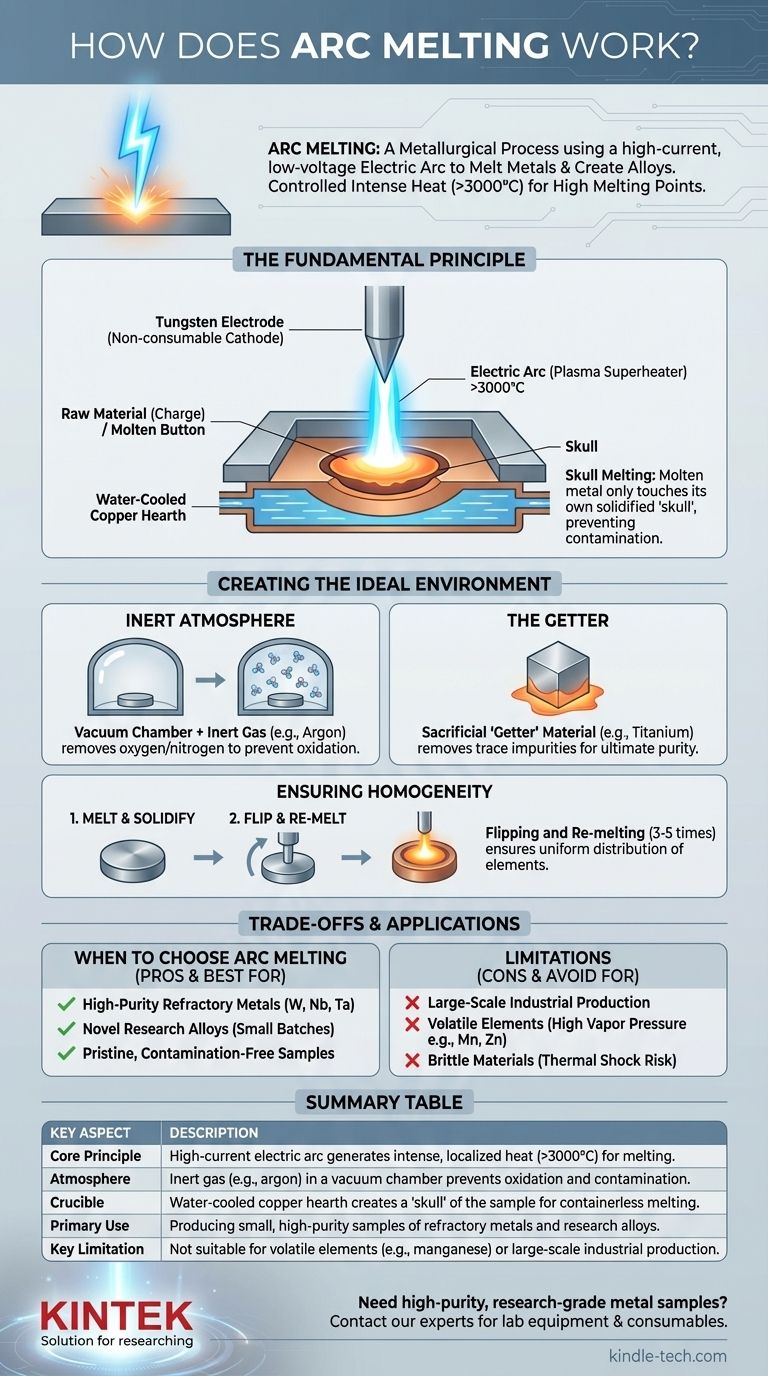
The Fundamental Principle: Generating Intense Heat
Arc melting's effectiveness comes from its ability to generate and control temperatures exceeding 3000°C in a very small area.
The Electric Arc as a Plasma Superheater
The process begins by striking an electric arc between a sharp, non-consumable electrode and the raw material (the charge) resting below it. This arc is a channel of plasma—an ionized gas—through which a high-current direct current (DC) flows. This plasma channel concentrates immense energy, rapidly heating and melting the material directly beneath it.
The Non-Consumable Tungsten Electrode
The electrode serving as the cathode (negative terminal) must withstand these extreme temperatures without melting or contaminating the sample. For this reason, it is almost always made of tungsten, which has one of the highest melting points of any element (3422°C).
The Water-Cooled Copper Hearth
The material to be melted sits in a crucible known as a hearth. This hearth is made of high-purity copper and is aggressively water-cooled. This design is critical.
When the arc melts the sample, the portion of the sample in direct contact with the cold copper hearth freezes instantly. This thin, solidified layer of the sample material, known as a "skull," forms a self-containing crucible. This phenomenon of "skull melting" ensures the molten metal only ever touches solid metal of its own kind, preventing any contamination from the copper hearth.
Creating the Ideal Melting Environment
Controlling the atmosphere is just as important as generating the heat. The goal is to eliminate unwanted chemical reactions, primarily oxidation.
The Inert Atmosphere
Before melting, the sealed chamber is placed under a high vacuum to remove atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. The chamber is then backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, most commonly argon. This argon atmosphere prevents the hot, highly reactive molten metal from oxidizing.
The "Getter" for Ultimate Purity
For applications requiring the highest purity, a small, sacrificial piece of a highly reactive metal like titanium or zirconium is often melted first. This "getter" material chemically combines with any trace residual oxygen or nitrogen left in the chamber, effectively cleaning the atmosphere before the primary sample is melted.
Ensuring Homogeneity: Flipping and Re-melting
To create a homogenous alloy, the initial "button" of melted material must be thoroughly mixed. Since there is no stirring mechanism, the operator uses the electrode stinger to flip the button over after it solidifies. The button is then re-melted several times (typically 3-5) to ensure all constituent elements are evenly distributed throughout the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, arc melting is not a universal solution. It has specific constraints that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Sample Size and Geometry
Arc melting is primarily a laboratory-scale technique used to produce small samples, typically weighing from a few grams to a hundred grams. The resulting "buttons" are excellent for research and analysis but the process is not suited for large-scale industrial production.
High Vapor Pressure Elements
A significant limitation arises when alloying elements with vastly different boiling points. Elements with high vapor pressure (i.e., those that evaporate easily), such as manganese, zinc, or magnesium, can boil off from the melt. This leads to a final composition that does not match the intended stoichiometry, a problem known as compositional control loss.
Thermal Shock
The extremely rapid heating and cooling cycles can induce significant thermal stress. This can cause brittle materials, such as ceramics or intermetallics, to crack or shatter during the process.
When to Choose Arc Melting
Based on these principles, the decision to use arc melting becomes clear when framed by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity samples of refractory metals (e.g., tungsten, niobium, tantalum): Arc melting is the ideal choice due to its non-contaminating skull melting and inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is developing novel, homogenous alloys for research: The ability to flip and re-melt small batches provides excellent compositional uniformity for analysis and testing.
- If your primary focus is alloying with volatile elements (e.g., creating a high-manganese steel): You must account for evaporative losses or choose an alternative method like induction melting in a sealed crucible.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: Arc melting is unsuitable; you should consider techniques like Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) or Electroslag Remelting (ESR).
Arc melting remains an indispensable tool in materials science for its unparalleled ability to produce pristine, research-quality samples of the world's most demanding materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses a high-current electric arc to generate intense, localized heat (>3000°C) for melting. |
| Atmosphere | Inert gas (e.g., argon) in a vacuum chamber prevents oxidation and contamination. |
| Crucible | Water-cooled copper hearth creates a 'skull' of the sample for containerless melting. |
| Primary Use | Producing small, high-purity samples of refractory metals and research alloys. |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for volatile elements (e.g., manganese) or large-scale industrial production. |
Need to produce high-purity, research-grade metal samples?
Arc melting is the benchmark method for creating pristine alloys of refractory metals like tungsten and tantalum. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to achieve reliable, contamination-free results in your materials research.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and support your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity



















