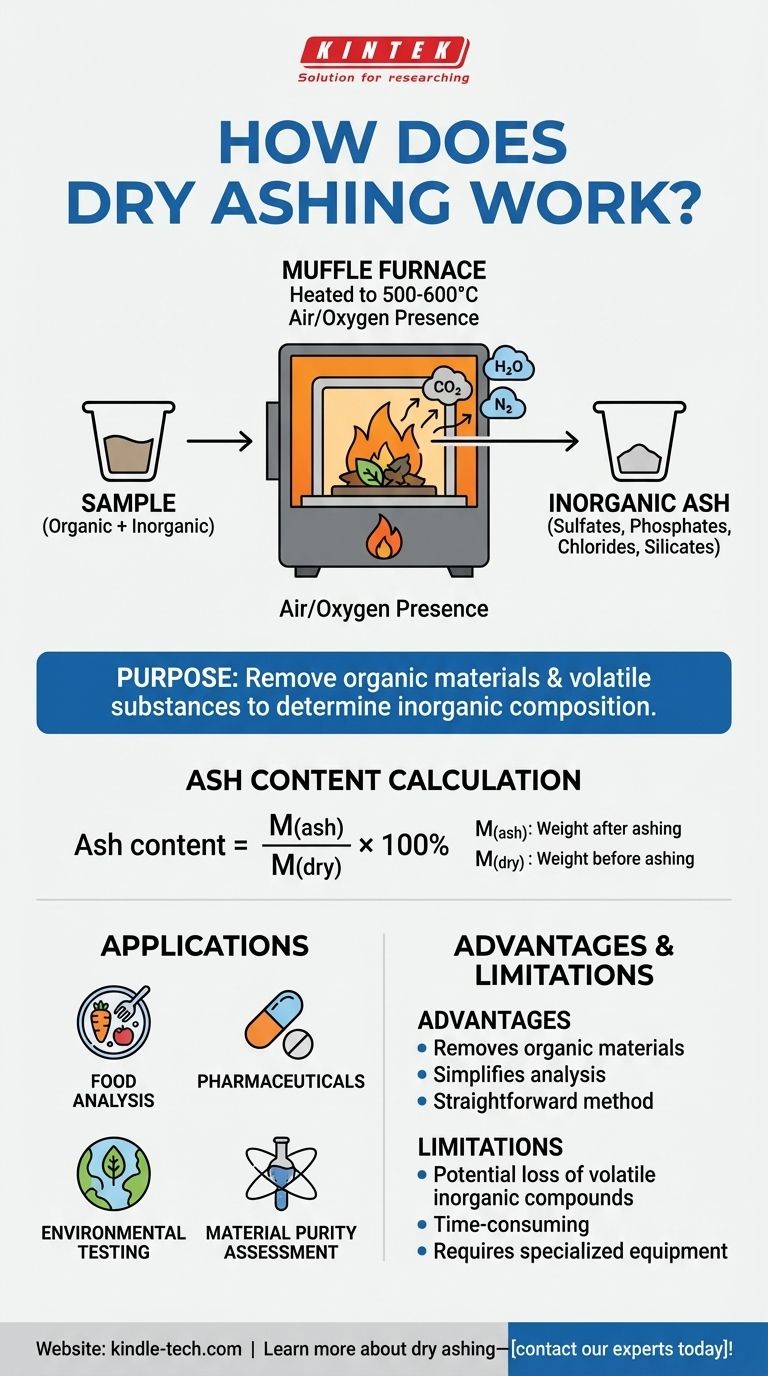
Dry ashing is a method used to analyze the inorganic composition of a sample by heating it in a high-temperature muffle furnace. This process removes water, volatile substances, and organic materials through combustion, leaving behind inorganic residues like sulfates, phosphates, chlorides, and silicates. The ash content is calculated by comparing the weight of the sample before and after ashing. The technique is governed by international standards and is widely used in analytical chemistry for elemental analysis and determining mass reduction.

Key Points Explained:
-
Purpose of Dry Ashing:
- Dry ashing is primarily used to determine the inorganic composition of a sample by removing organic materials and volatile components. This leaves behind non-combustible residues, which can be analyzed for their elemental composition.
-
Process Overview:
- The sample is placed in a muffle furnace and heated to temperatures between 500-600°C in the presence of air or oxygen.
- During heating, water and volatile materials are vaporized, and organic matter undergoes combustion, producing gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and nitrogen gas.
- The remaining inorganic compounds, such as sulfates, phosphates, chlorides, and silicates, form the residual ash.
-
Equipment Used:
- A muffle furnace is the primary equipment for dry ashing. It is designed to handle high temperatures and provide controlled heating in an oxygen-rich environment.
-
Chemical Reactions:
- Organic compounds in the sample react with oxygen during combustion, breaking down into simpler gases.
- Inorganic minerals are converted into stable compounds like sulfates, phosphates, chlorides, and silicates, which remain as ash.
-
Calculation of Ash Content:
- The ash content is calculated using the formula:
[ \text{Ash content} = \frac{M(\text{ash})}{M(\text{dry})} \times 100% ] where:- ( M(\text{ash}) ) is the weight of the sample after ashing.
- ( M(\text{dry}) ) is the weight of the sample before ashing.
- The ash content is calculated using the formula:
-
Applications:
- Dry ashing is widely used in analytical chemistry for determining the elemental composition of samples.
- It is also used in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing to measure ash content and assess material purity.
-
Standards and Protocols:
- The process is often governed by international standards such as ISO, EN, or ASTM, ensuring consistency and accuracy in results.
- Specific objectives, like Loss on Ignition (LOI), may also be incorporated to measure mass reduction during the ashing process.
-
Advantages:
- Removes unwanted organic materials, simplifying the analysis of inorganic residues.
- Provides a straightforward method for determining ash content and elemental composition.
-
Limitations:
- High temperatures may cause the loss of certain volatile inorganic compounds.
- The process is time-consuming and requires specialized equipment.
-
Practical Considerations:
- Samples must be prepared carefully to ensure accurate results.
- The furnace temperature and heating duration must be controlled to avoid incomplete combustion or excessive loss of volatile components.
By following these steps and principles, dry ashing provides a reliable method for analyzing the inorganic composition of various materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Determines inorganic composition by removing organic materials. |
| Process | Heated in a muffle furnace at 500-600°C, leaving inorganic residues. |
| Equipment | Muffle furnace for controlled, high-temperature heating. |
| Chemical Reactions | Organic compounds combust into gases; inorganic minerals form stable ash. |
| Ash Content Formula | Ash content = (Weight after ashing / Weight before ashing) × 100%. |
| Applications | Elemental analysis in food, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing. |
| Standards | Governed by ISO, EN, or ASTM for consistency and accuracy. |
| Advantages | Removes organic materials, simplifies inorganic residue analysis. |
| Limitations | May lose volatile inorganic compounds; time-consuming and equipment-heavy. |
| Practical Tips | Control temperature and duration; prepare samples carefully for accuracy. |
Learn more about dry ashing and how it can benefit your lab—contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is the annealing treatment in a high-temperature muffle furnace critical for the preparation of an Sb-SnO2 interlayer?
- What is the function of muffle furnace in food industry? Ensure Accurate Ash Determination for Quality Control
- How do high-vacuum sealed tubes and muffle furnaces collaborate for LBE corrosion tests? Master Nuclear Material Testing
- What contributes to ash content in food? A Guide to Mineral Content and Food Quality
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- What would a high ash content indicates? A Key Indicator of Material Composition and Quality
- What is the role of a high-temperature box furnace in BZY20 densification? Achieve 94% Density with Precision
- What are the functions of a high-temperature muffle furnace and alumina ceramic crucibles? Clean Alloy Oil Residues



















