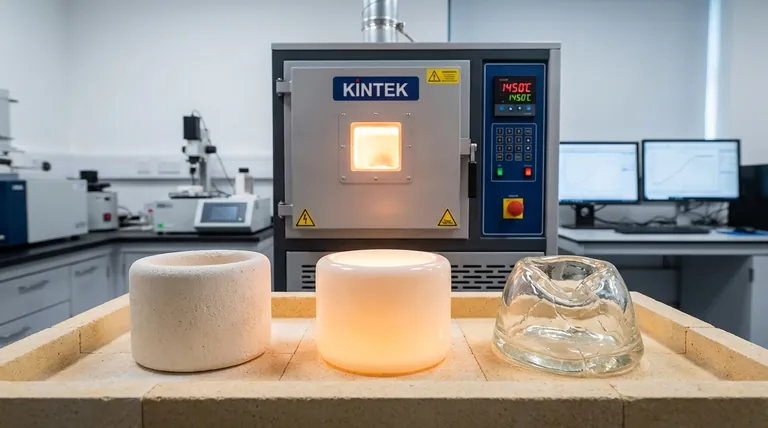
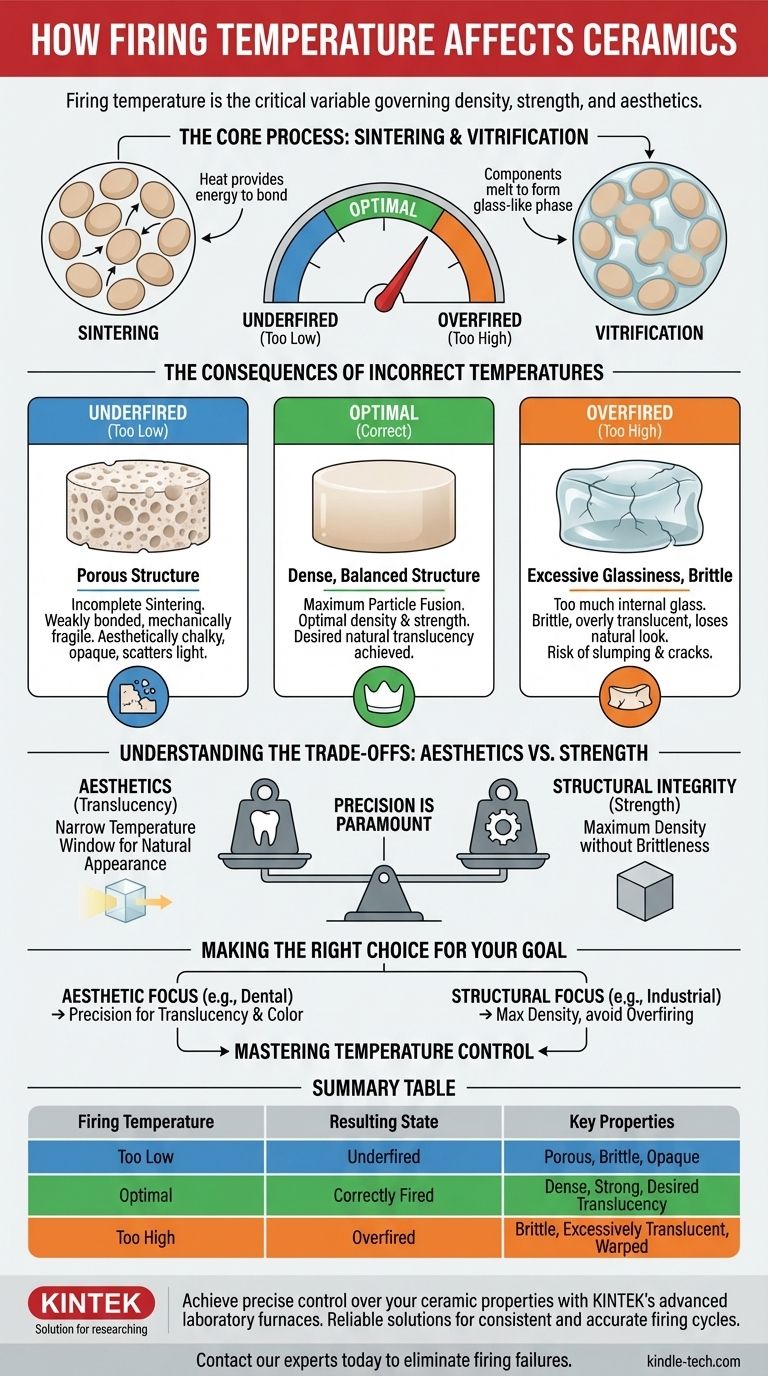
Firing temperature is the single most critical variable in creating ceramics, directly governing their final aesthetic and functional properties. The heat applied during this process dictates the material's density, strength, and optical characteristics, such as translucency. Getting the temperature wrong results in a fundamentally flawed product, while precision yields a successful, reliable outcome.
Firing temperature isn't just about making ceramics hard; it's a precise balancing act. Too high a temperature creates excessive glassiness and structural weakness, while too low a temperature results in a porous, opaque, and brittle product. The correct temperature achieves the optimal fusion of particles for both strength and appearance.

The Core Process: Sintering and Vitrification
What Happens During Firing?
During firing, ceramic particles undergo a process called sintering. Heat provides the energy for individual grains to bond and fuse, eliminating the pores between them.
This densification process is often accompanied by vitrification, where some components melt to form a glass-like phase. This glassy matrix fills the remaining voids, binding the crystalline particles into a strong, coherent mass.
Why Temperature Governs This Process
Temperature is the catalyst for this transformation. It directly controls the rate and extent of atomic diffusion, which allows the ceramic particles to join.
The final ratio of crystalline particles to the glassy phase is determined by the peak temperature and the duration of the firing cycle. This balance is what defines the ceramic's final properties.
The Consequences of Incorrect Temperatures
The Problem of Underfiring
If the firing temperature is too low, the ceramic is underfired. There isn't enough thermal energy to complete the sintering process.
This results in a porous, weakly bonded structure that is mechanically fragile. Aesthetically, underfired ceramics often appear chalky, opaque, and overly reflective because the voids and un-fused particles scatter light instead of transmitting it.
The Dangers of Overfiring
Conversely, if the temperature is too high, the ceramic becomes overfired. This causes excessive vitrification, creating too much internal glass.
While this may increase density, it can also make the material brittle. Visually, an overfired ceramic becomes too translucent, losing its aesthetic appeal and natural appearance. In extreme cases, the material can slump, warp, or develop internal stresses that lead to crack propagation and failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Aesthetics vs. Strength
The Quest for Translucency
Achieving the desired level of translucency is a primary goal, especially in applications like dental ceramics. This optical property is dictated by a very narrow temperature window.
A slight deviation can dramatically alter how light passes through the material, shifting it from a natural appearance to either opaque or glassy. Accurate furnace temperature is therefore essential for aesthetic success.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The functional properties of strength and fracture resistance are just as sensitive to temperature. The objective is to create a dense, non-porous body without introducing the stresses or brittleness associated with overfiring.
The optimal temperature achieves maximum particle fusion and minimal porosity, creating a material that can withstand functional stress without failing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calibrating your approach to the specific material and desired outcome is essential. The "correct" temperature is not a single number but a precise target based on your objective.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (e.g., dental restorations): Precision is paramount, as even minor temperature deviations will visibly alter translucency and color.
- If your primary focus is structural performance (e.g., industrial components): Your goal is maximum density and strength, which requires reaching the full sintering temperature without overshooting into a phase that introduces brittleness.
- If you are experiencing failures like cracking or poor appearance: The first variable to investigate and calibrate is your furnace's firing temperature and cycle.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is mastering the final properties of your ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Firing Temperature | Resulting State | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Too Low | Underfired | Porous, Brittle, Opaque |
| Optimal | Correctly Fired | Dense, Strong, Desired Translucency |
| Too High | Overfired | Brittle, Excessively Translucent, Warped |
Achieve precise control over your ceramic properties with KINTEK's advanced laboratory furnaces.
Whether you are developing dental restorations that demand perfect aesthetics or industrial components that require maximum strength, the right furnace is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab equipment, offering reliable solutions for consistent and accurate firing cycles.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific ceramic application and discover how our equipment can help you eliminate firing failures and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















