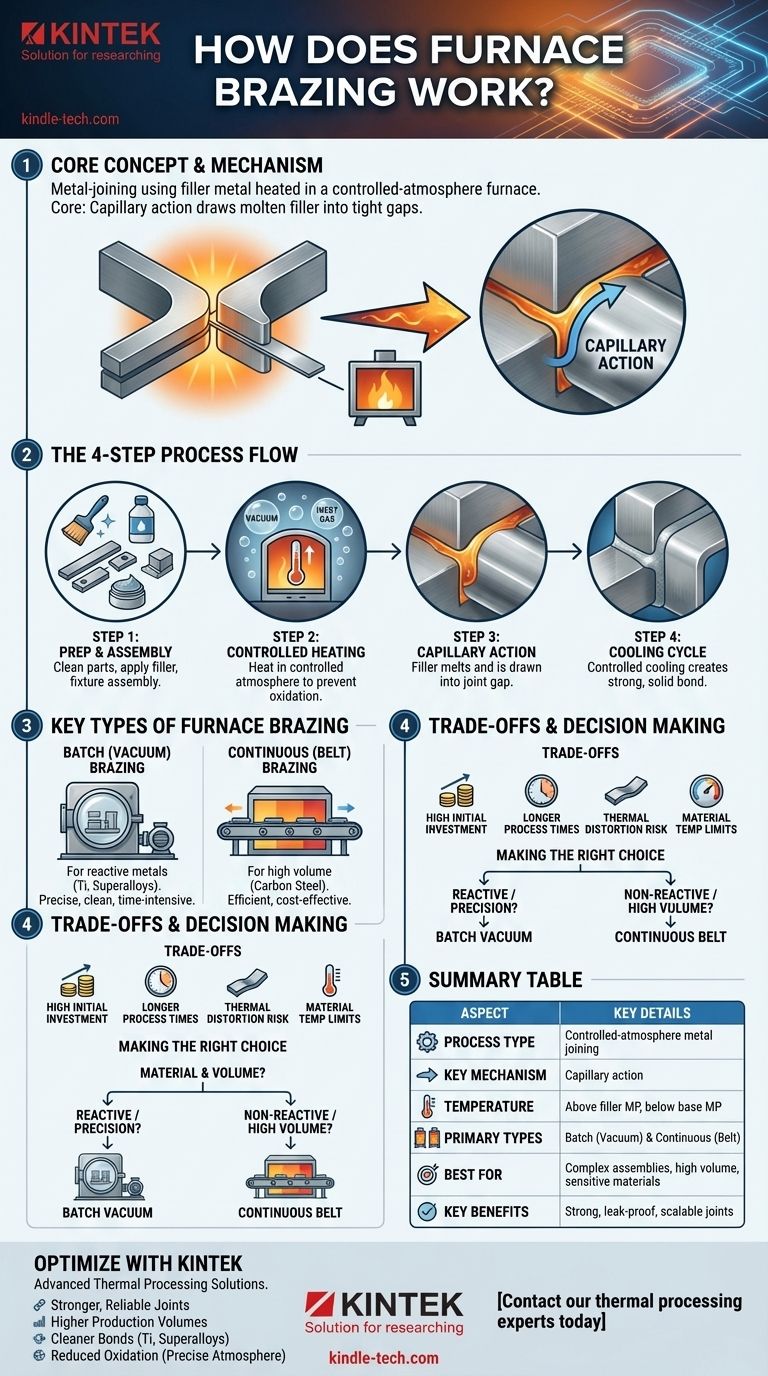
At its core, furnace brazing is a metal-joining process where components are assembled with a filler metal and heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The furnace heats the entire assembly to a temperature that melts the filler metal, but not the base components. The molten filler is drawn into the tight gaps between the parts through capillary action, and upon cooling, it solidifies to form a strong, permanent, and often leak-proof metallurgical bond.
Furnace brazing is not simply about heating metal. It is a highly controlled, semi-automated process designed for scalability and precision, enabling the creation of thousands of strong, clean joints simultaneously, especially for complex assemblies or materials that are sensitive to oxygen.

The Furnace Brazing Process Step-by-Step
To understand how furnace brazing achieves its results, it is best to break it down into its distinct phases. Each step is critical for the integrity of the final bond.
Step 1: Component Preparation and Assembly
Before heating, the components must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any oils, oxides, or contaminants that could interfere with the bond.
The brazing filler metal, often in the form of a paste, wire, or pre-formed shim, is then applied to the joint area. The parts are then fixtured together to maintain their position and ensure tight, consistent gaps.
Step 2: The Controlled Heating Cycle
The assembled parts are placed inside the furnace. The furnace atmosphere is then controlled—either by creating a vacuum or introducing a specific gas—to prevent oxidation of the base metals as they heat up.
The furnace then heats the entire assembly uniformly to the specified brazing temperature. This temperature is above the melting point of the filler metal but below the melting point of the components being joined.
Step 3: Filler Metal Flow (Capillary Action)
Once the brazing temperature is reached, the filler metal melts and becomes a liquid. Because of the tight clearance between the components, a phenomenon called capillary action automatically draws the molten filler into the joint.
This action ensures the gap is completely filled, creating a full, continuous bond between the surfaces.
Step 4: The Cooling Cycle
After a set time at temperature, the assembly is cooled in a controlled manner. This allows the filler metal to solidify, creating the final, strong brazed joint.
The cooling rate can be adjusted to achieve specific material properties, such as hardness, in the finished assembly. Once cooled to a safe temperature, the parts are removed from the furnace.
Key Types of Furnace Brazing
Not all furnace brazing is the same. The choice of furnace depends entirely on the materials being joined and the production volume required.
Batch Furnace (Vacuum) Brazing
This method involves loading a batch of parts into a furnace, sealing the chamber, and then pumping out the air to create a vacuum. This is the ultimate way to prevent oxidation.
Vacuum brazing is essential for joining highly reactive materials like stainless steel, titanium, and superalloys. The process is time-intensive due to the pump-down and cooling cycles but results in exceptionally clean and strong joints.
Continuous (Belt) Furnace Brazing
A continuous furnace operates with a conveyor belt that moves parts through different temperature zones. Parts are loaded at one end, pass through a pre-heat zone, a high-heat brazing zone, and a cooling zone before exiting at the other end.
This method is ideal for high-volume production of less-reactive materials like carbon steel. It is a highly efficient and cost-effective process for mass-producing brazed components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing is a specific tool with its own set of limitations that must be weighed against its benefits.
High Initial Investment
Brazing furnaces, particularly large vacuum furnaces, represent a significant capital expenditure. This makes the process better suited for established production lines rather than one-off prototypes.
Longer Process Times
Batch-type furnace brazing is not an instantaneous process. The heating, soaking, and cooling cycles can take several hours, making it slower than other joining methods like welding for single parts.
Potential for Thermal Distortion
Because the entire assembly is heated and cooled, there is a risk of thermal expansion and contraction causing distortion. This must be managed with proper part design and fixturing.
Material Temperature Limits
The base materials must be able to withstand the brazing temperature without being damaged. This makes furnace brazing unsuitable for metals with low melting points or those that undergo undesirable changes at the required heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing approach is critical for project success. Your choice should be driven by your materials, production volume, and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is mass production of non-reactive parts: Continuous belt furnace brazing offers the most cost-effective and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is joining oxygen-sensitive materials (like titanium or superalloys): Vacuum furnace brazing is non-negotiable to prevent oxidation and ensure a high-integrity bond.
- If your primary focus is maintaining extremely tight dimensional tolerances on complex assemblies: Furnace brazing is an excellent choice because it joins components without melting and warping the base metals.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently determine if furnace brazing is the precise thermal joining process that aligns with your material, volume, and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Controlled-atmosphere metal joining using filler metal |
| Key Mechanism | Capillary action draws molten filler into tight gaps |
| Temperature | Above filler metal melting point, below base metal melting point |
| Primary Types | Batch (Vacuum) Brazing & Continuous (Belt) Furnace Brazing |
| Best For | Complex assemblies, high-volume production, oxygen-sensitive materials |
| Key Benefits | Strong, permanent bonds; leak-proof joints; semi-automated scalability |
Ready to Optimize Your Metal Joining Process?
KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions for laboratory and industrial applications. Our expertise in furnace brazing technology can help you achieve:
- Stronger, more reliable joints for complex assemblies
- Higher production volumes with consistent, repeatable results
- Cleaner bonds for oxygen-sensitive materials like titanium and superalloys
- Reduced oxidation through precise atmosphere control
Whether you need batch vacuum brazing for precision components or continuous belt furnace solutions for mass production, KINTEK has the equipment and knowledge to meet your specific metal joining requirements.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how furnace brazing can enhance your manufacturing capabilities and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















