In short, heat treatment fundamentally changes the strength of a material by altering its internal microstructure. It is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling that allows you to purposefully increase hardness and strength, relieve internal stress, or improve ductility depending on the desired outcome for the component.
The core principle to understand is that heat treatment isn't just about making a material "stronger"—it's about achieving a specific balance of mechanical properties. You are often trading one property, like ductility, to gain another, like hardness.
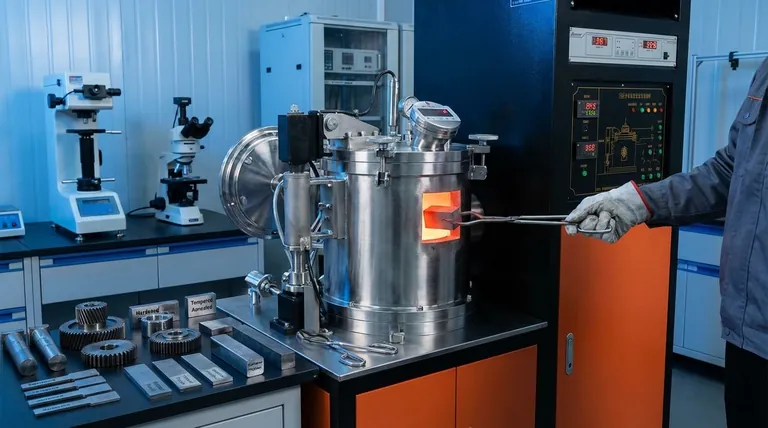

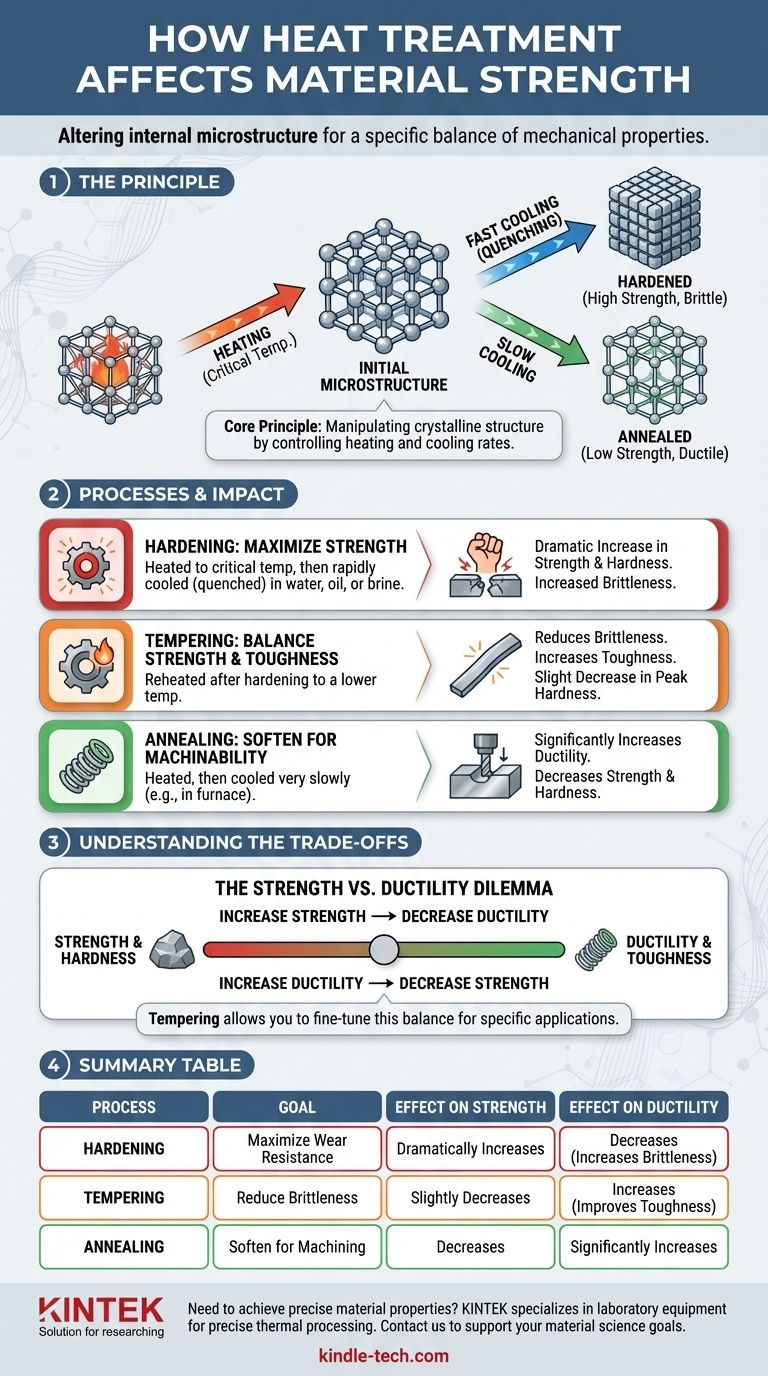
The Principle: How Heating and Cooling Change a Material
Heat treatment works by manipulating the crystalline structure, or microstructure, inside a metallic component. This internal arrangement of atoms is what ultimately dictates its mechanical properties, including strength, hardness, and brittleness.
The Role of Heating
When a metal like steel is heated to a specific critical temperature, its internal crystal structure transforms. In this heated state, the structure becomes more uniform and is primed for change.
This phase is essential for dissolving elements within the metal and "erasing" the previous microstructure, preparing it for a new one to be formed upon cooling.
The Critical Role of Cooling
The rate at which the material is cooled from this high temperature is the most critical factor. This cooling rate "locks in" a specific microstructure, which directly determines the final strength.
A very fast cooling rate, known as quenching, traps the atoms in a hard, highly-stressed structure, dramatically increasing strength and hardness. Conversely, a very slow cooling rate allows the atoms to rearrange into a softer, less-stressed structure, which reduces strength but increases ductility.
Common Processes and Their Impact on Strength
Different combinations of heating and cooling rates define specific heat treatment processes, each designed to achieve a different set of mechanical properties.
Hardening: Maximizing Strength
Hardening is the process used to achieve maximum strength and wear resistance. It involves heating the steel to a critical temperature and then cooling it very rapidly, often by plunging it into water, oil, or brine.
This process creates a very hard, strong, but also brittle material. It is ideal for applications where wear resistance and the ability to withstand high loads without deforming are paramount.
Tempering: Balancing Strength with Toughness
A hardened part is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary treatment applied after hardening to reduce this brittleness and increase toughness.
The part is reheated to a lower temperature and held for a specific time. This process relieves some of the internal stress from the hardening process, resulting in a slight reduction in peak hardness but a significant gain in toughness, making the material less likely to fracture.
Annealing: Softening for Machinability
Annealing is the opposite of hardening. The goal is to make the material as soft and ductile as possible, which relieves internal stresses and improves its ability to be machined or formed.
This is achieved by heating the material and then cooling it very slowly, often by letting it cool down inside the furnace. This results in a material with lower strength and hardness but high ductility and machinability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heat treatment process is always an exercise in balancing competing properties. It is impossible to maximize all desirable characteristics simultaneously.
The Strength vs. Ductility Dilemma
The most fundamental trade-off is between strength and ductility. As you increase a material's strength and hardness through a process like quenching, you almost always decrease its ductility, making it more brittle.
Tempering is the primary method for navigating this trade-off, allowing you to fine-tune the balance between hardness and toughness for a specific application.
The Impact on Manufacturing
A key consideration is when to perform the heat treatment. An annealed, softer part is much easier and cheaper to machine, but it lacks the final required strength.
Therefore, a common manufacturing sequence is to machine the part in its soft, annealed state and then heat treat it to achieve the final desired strength and hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the end-use requirements of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and hardness: A hardening process followed by a low-temperature temper is the most effective approach.
- If your primary focus is durability and toughness under impact: A hardening process followed by a higher-temperature temper will provide the best balance of strength and fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is ease of manufacturing (machining or forming): An annealing process is necessary to put the material in its softest, most ductile state.
Ultimately, understanding heat treatment empowers you to specify not just a material, but the precise properties required for its successful application.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Effect on Strength | Effect on Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardening | Maximize wear resistance | Dramatically Increases | Decreases (Increases Brittleness) |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness | Slightly Decreases | Increases (Improves Toughness) |
| Annealing | Soften for machining | Decreases | Significantly Increases |
Need to achieve precise material properties for your components? The right heat treatment process is critical for performance and durability. KINTEK specializes in providing the laboratory equipment and consumables needed for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you select the right furnaces and ovens to harden, temper, or anneal your materials to exact specifications. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's material science and manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is argon gas used for? Unlock the Power of Inertness for Welding, Lighting & More
- What are the steps in additive manufacturing process? A Complete Guide to the Digital-to-Physical Workflow
- What are the key features of slow pyrolysis and fast pyrolysis? Choose the Right Process for Bio-Oil or Biochar
- What are the components of pyrolysis oil? A Guide to Its Complex Bio-Crude Composition
- Are electric arc furnaces efficient? Unlocking Modern Steelmaking's Power and Flexibility
- What type of samples can be characterized with IR spectroscopy? Analyze Solids, Liquids, and Gases
- Why does melting require energy? Unlock the Science of Latent Heat and Phase Changes
- Why do intrinsic self-healing polymers require heating? Unlock Repeatable Repair with Thermal Activation



















