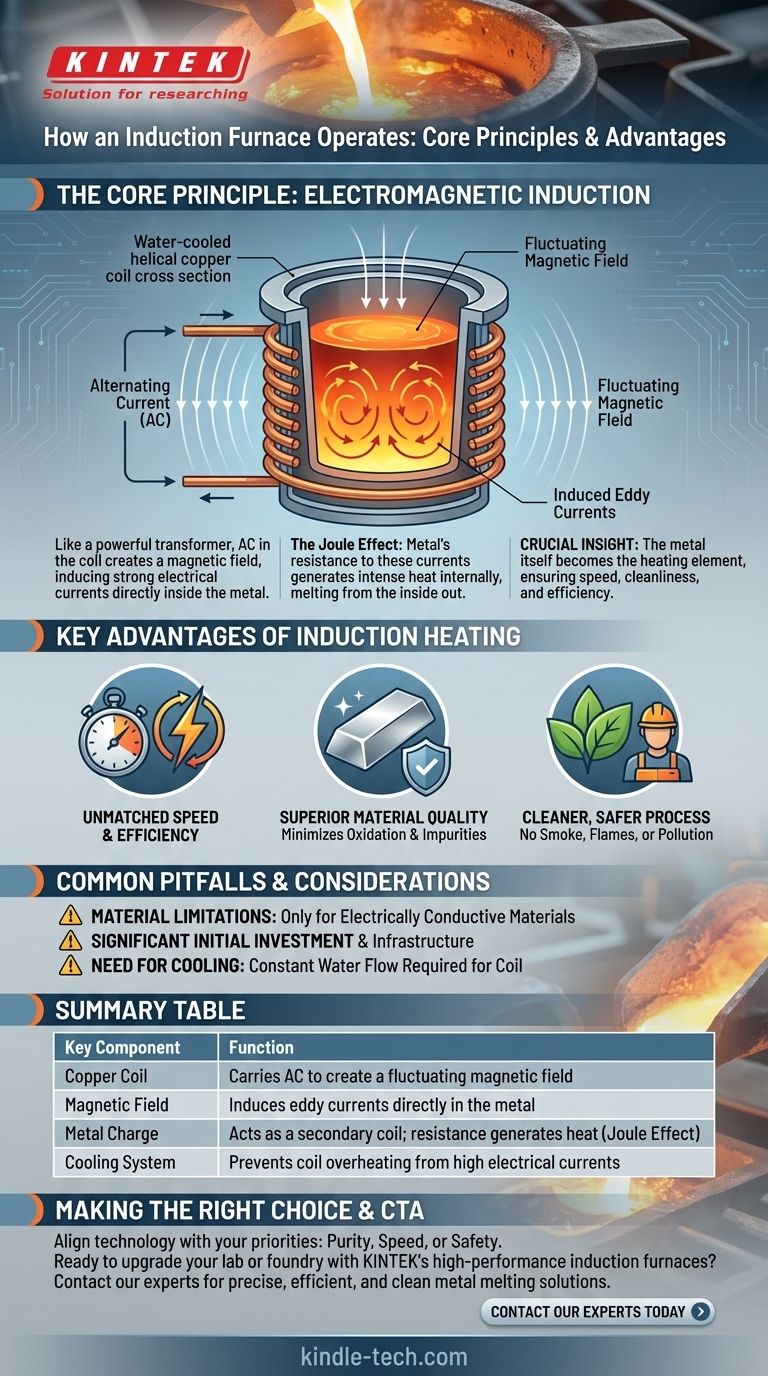
At its core, an induction furnace operates like a powerful transformer. It uses an alternating current flowing through a copper coil to create a fluctuating magnetic field. This field induces a strong electrical current directly within the metal to be melted, and the metal's own resistance to this current generates intense, rapid heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The crucial insight is that an induction furnace turns the metal itself into the heating element. This shift from external to internal heating provides a level of speed, cleanliness, and efficiency that traditional combustion-based methods cannot match.

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
The operation of an induction furnace is a direct application of Faraday's Law of Induction and the Joule Effect. The process can be broken down into a few distinct steps.
The Coil and the Magnetic Field
The heart of the furnace is a helical coil, typically made of water-cooled copper tubing. A powerful alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
Because the current is constantly and rapidly changing direction, it generates a powerful and fluctuating magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Inducing a Current in the Metal
When an electrically conductive material, like steel or gold, is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces strong, swirling electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Think of the furnace's primary coil as one side of a transformer and the piece of metal as a single-turn secondary coil. The energy is transferred wirelessly through the magnetic field.
Resistance and the Joule Effect
Every metal has some natural electrical resistance. As the powerful eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter this resistance, which generates immense heat.
This phenomenon is known as the Joule Effect or resistive heating. The heat is generated inside the metal itself, leading to extremely fast and uniform melting without any external flame or heating element making contact.
Key Advantages of Induction Heating
This unique method of heating provides significant operational benefits, making it a preferred choice in modern foundries and industrial settings.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because the heat is generated directly within the material, heating cycles are incredibly fast. Power is transferred with very high efficiency—up to 98% in some designs—minimizing wasted energy.
Superior Material Quality
Traditional furnaces burn fuel, introducing impurities and promoting oxidation (material loss) on the metal's surface. Induction heating is a clean process with no combustion.
The rapid heating also minimizes the time the metal is at a high temperature, significantly reducing oxidation and decarburization. This saves material and preserves the integrity of the alloy.
A Cleaner, Safer Process
Induction furnaces produce no smoke, waste heat, or noxious emissions, contributing to a safer and cleaner working environment and eliminating process pollution.
The absence of open flames and molten metal splashes, common in older methods, dramatically improves operational safety. The process is more contained and creates less mess.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While highly effective, the technology is not without its specific requirements and limitations. Objectively weighing these factors is critical.
Material Limitations
Induction heating only works on materials that are electrically conductive. It cannot be used to directly heat non-conductive materials like ceramics or glass, though a conductive crucible can be heated to transfer heat indirectly.
Initial Investment and Infrastructure
Induction furnace systems represent a significant capital investment. They also require a robust electrical infrastructure to supply the high levels of power needed for operation.
The Need for Cooling
The massive currents flowing through the primary coil generate their own heat. A constant flow of cooling water is required to prevent the copper coil from overheating and melting, adding a layer of complexity and a potential point of failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is material purity and quality: The clean, non-contact nature of induction heating prevents contamination and minimizes oxidation, making it a superior choice.
- If your primary focus is production speed: The rapid heating cycles inherent to induction furnaces allow for significantly higher throughput compared to traditional methods.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and worker safety: The pollution-free and contained operation of an induction furnace is the ideal solution for meeting modern standards.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of induction heating empowers you to select a technology that aligns perfectly with the demands of modern, high-efficiency manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Copper Coil | Carries AC to create a fluctuating magnetic field |
| Magnetic Field | Induces eddy currents directly in the metal |
| Metal Charge | Acts as a secondary coil; resistance generates heat (Joule Effect) |
| Cooling System | Prevents coil overheating from high electrical currents |
Ready to upgrade your lab or foundry with the speed and purity of induction heating? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for precise, efficient, and clean metal melting. Whether you're focused on material quality, production speed, or a safer work environment, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect induction furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















