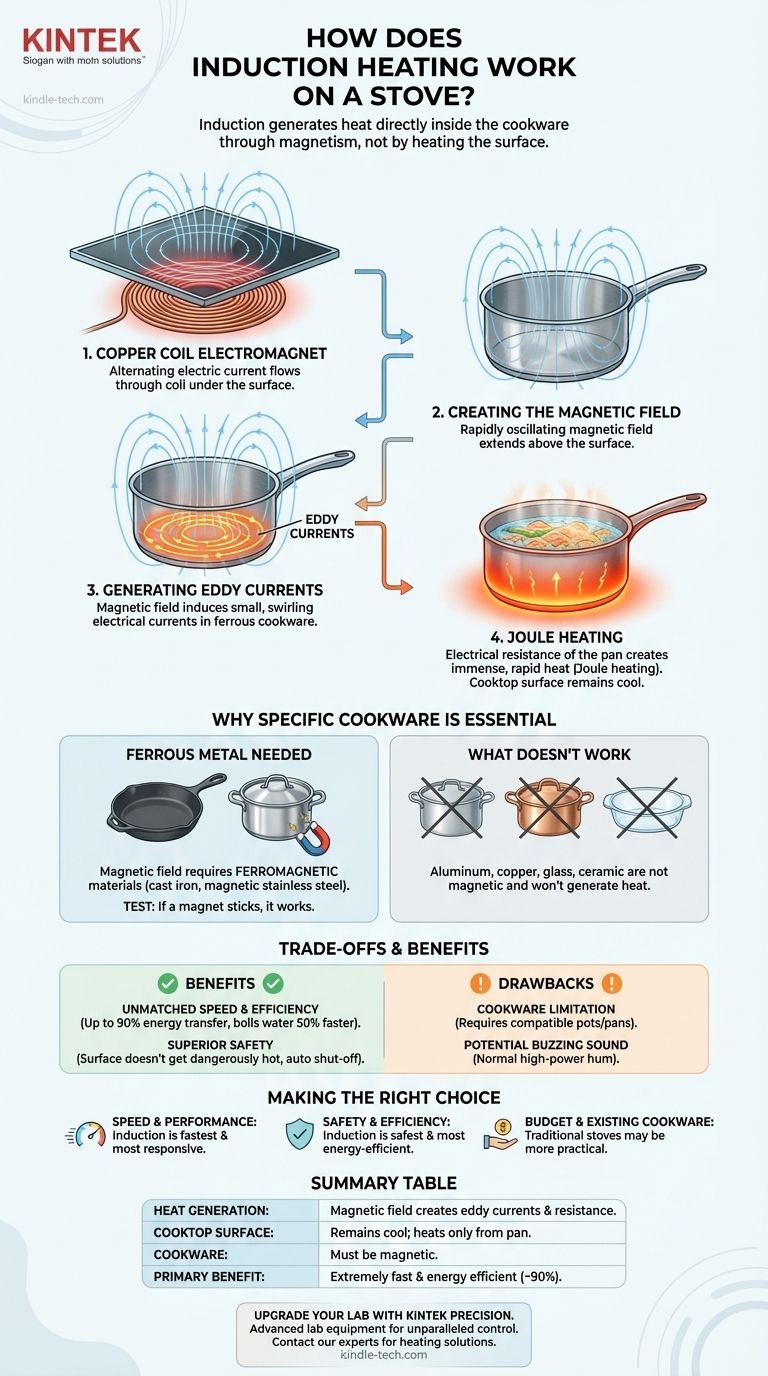
Induction heating is a process of generating heat through magnetism. Unlike traditional stoves that create heat on a surface and then transfer it to a pot, an induction cooktop uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnet to generate heat directly inside the cookware itself. This "non-contact" method is what makes induction so fast and efficient.
The key to understanding induction is that the cooktop surface does not become the primary heat source. Instead, it creates a magnetic field that turns your cookware into its own heater, resulting in faster cooking, precise temperature control, and unmatched energy efficiency.
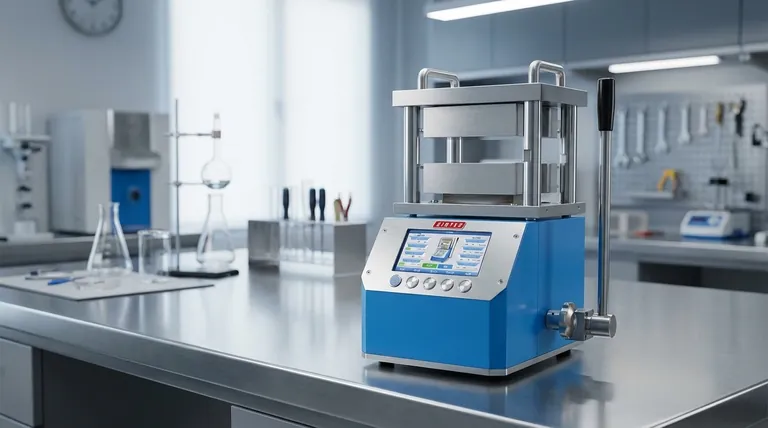

The Core Mechanism: From Magnetism to Heat
The process of turning electricity into heat within your pan involves a few key steps rooted in fundamental physics. It's a seamless and nearly instantaneous chain reaction.
The Copper Coil Electromagnet
Beneath the smooth glass-ceramic surface of an induction cooktop lies a tightly wound coil of copper wire. When you turn the cooktop on, an alternating electric current flows through this coil.
Creating the Magnetic Field
This flow of electricity through the copper coil generates a powerful and rapidly oscillating magnetic field that extends a few millimeters above the cooktop's surface. This is the first step: converting electrical energy into magnetic energy.
Generating Eddy Currents in the Pan
When you place a piece of magnetic cookware on the surface, this oscillating magnetic field penetrates the metal base of the pan. The field induces small, swirling electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The Role of Resistance (Joule Heating)
The metal of your pan naturally resists the flow of these eddy currents. This electrical resistance creates friction on a molecular level, which in turn generates immense and rapid heat. This principle is called Joule heating. The pan gets hot, but the cooktop surface does not.
Why Specific Cookware Is Essential
The reliance on magnetism is precisely why you cannot use just any pot or pan on an induction cooktop. The material of the cookware is a critical part of the heating circuit.
The Need for Ferrous Metal
The magnetic field can only induce strong, heat-generating eddy currents in materials that are ferromagnetic (magnetic). This includes materials like cast iron and many, but not all, types of stainless steel.
How to Test Your Cookware
The test for compatibility is simple: if a refrigerator magnet sticks firmly to the bottom of your pot or pan, it will work with an induction cooktop.
What Doesn't Work
Cookware made from materials like aluminum, all-copper, glass, or ceramic will not work. These materials are not magnetic, so the magnetic field passes through them without inducing the necessary eddy currents to generate heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Benefits
The unique heating method of induction creates a distinct set of advantages and considerations compared to traditional gas or electric stoves.
The Benefit: Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Because heat is generated directly in the pan, very little energy is wasted heating the surrounding air or the cooktop surface. This translates to boiling water up to 50% faster than other methods and means nearly 90% of the energy is transferred to the food, compared to roughly 40% for gas.
The Benefit: Superior Safety
The glass surface itself does not get dangerously hot. It only warms up from residual heat transferred back from the hot pan. The element also automatically shuts off when the cookware is removed, making it significantly safer, especially in homes with children.
The Drawback: The Cookware Limitation
The most significant hurdle for many is the need for compatible cookware. If your current set is aluminum or another non-magnetic material, you will need to invest in new pots and pans.
The Drawback: Potential for a Buzzing Sound
Some users notice a faint buzzing or humming sound, especially at high power settings. This is a normal result of the magnetic field interacting with the cookware and is not a sign of a defect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Kitchen
Understanding the core principle of induction allows you to decide if it aligns with your cooking priorities.
- If your primary focus is speed and performance: Induction is the undisputed leader, offering the fastest heating times and most responsive temperature control available.
- If your primary focus is safety and energy efficiency: The cool-to-the-touch surface and direct-heating method make induction the safest and most efficient choice on the market.
- If your primary focus is budget and using existing cookware: A traditional electric or gas stove may be more practical, as induction has a higher upfront cost and strict cookware requirements.
By understanding that induction makes the cookware the source of the heat, you can fully leverage its power for a faster, safer, and more controlled cooking experience.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | How Induction Works |
|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Magnetic field creates eddy currents in cookware, generating heat via resistance (Joule heating). |
| Cooktop Surface | Remains cool to the touch; only heats up from the pan. |
| Cookware Requirement | Must be magnetic (e.g., cast iron, magnetic stainless steel). |
| Primary Benefit | Extremely fast heating and high energy efficiency (~90%). |
Upgrade your lab's heating capabilities with KINTEK precision.
Just as induction technology revolutionizes cooking with direct, efficient heat, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment delivers unparalleled control and reliability for your most critical applications. Whether you need precise temperature management for synthesis, sample preparation, or materials testing, our ovens, furnaces, and heating elements are engineered for performance and safety.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your laboratory's unique needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



