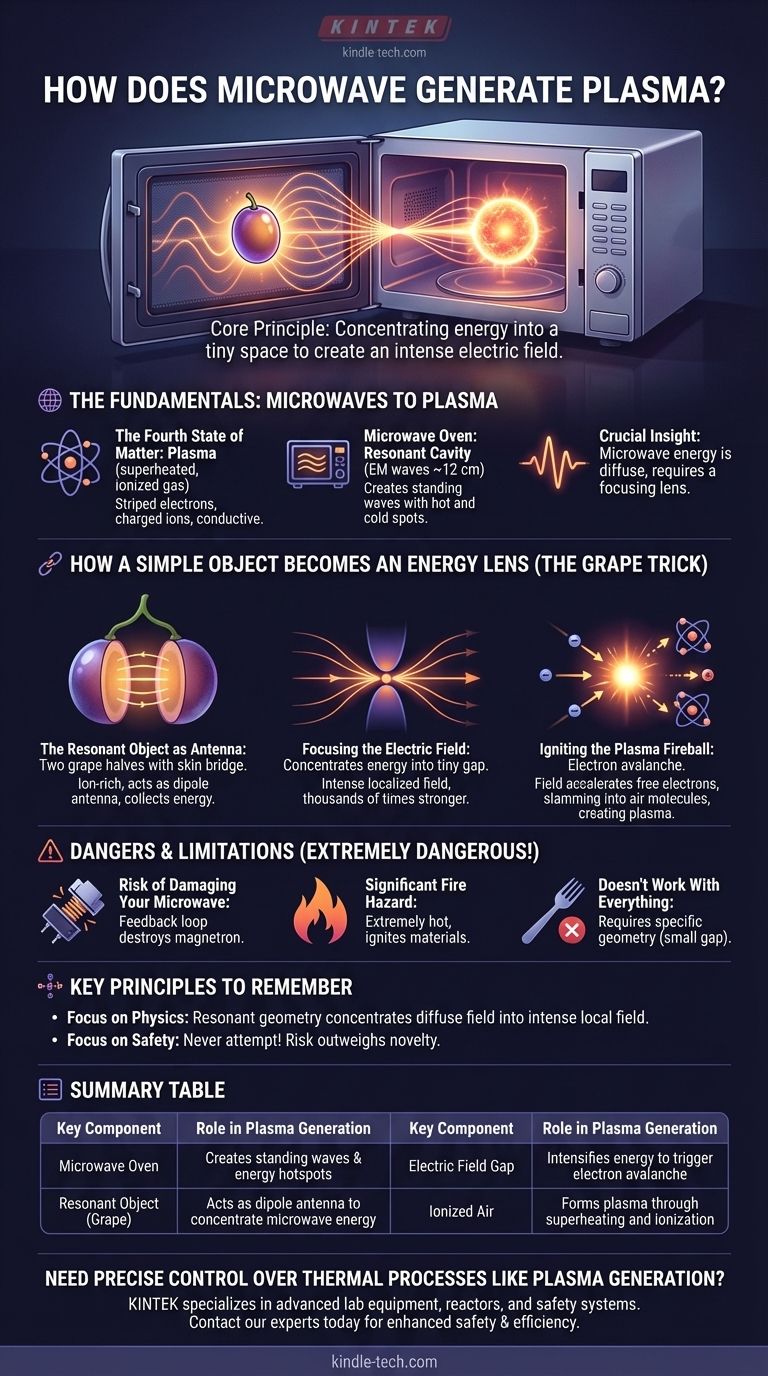
At its core, a microwave generates plasma by using an object to concentrate its energy into a tiny space. This creates an electric field so intense that it rips electrons from atoms, creating a superheated, glowing ball of ionized gas, which we call plasma. This process doesn't happen with just any object; it requires a specific size and geometry to act as a focusing lens for the microwave radiation.
The crucial insight is that the microwave oven itself doesn't create plasma directly. Instead, specific objects placed inside—like two halves of a grape—act as antennas, concentrating the diffuse microwave energy into a single point with enough power to ignite the air into a plasma state.

The Fundamentals: From Microwaves to Plasma
To understand how a household appliance can achieve this, we first need to break down the key components: the microwaves, the object, and the plasma itself.
The Fourth State of Matter
Plasma is often called the "fourth state of matter," distinct from solid, liquid, and gas. It's a superheated gas where atoms have been stripped of one or more of their electrons.
This process, called ionization, leaves behind a mixture of negatively charged free electrons and positively charged ions. This soup of charged particles is electrically conductive and reacts strongly to electric and magnetic fields.
The Microwave Oven as a Resonant Cavity
Your microwave oven's magnetron generates electromagnetic waves with a wavelength of about 12 centimeters (4.7 inches).
These waves flood the metal box of the oven, reflecting off the walls and creating a complex pattern of standing waves. This means there are "hot spots" and "cold spots" of energy throughout the oven's cavity.
How a Simple Object Becomes an Energy Lens
The real magic happens when you introduce an object with just the right properties. The classic example is a grape cut nearly in half, leaving a thin bridge of skin connecting the two hemispheres.
The Object as a Dipole Antenna
The two halves of the grape, which are filled with an ion-rich liquid (electrolytes), act as a dipole antenna. Because the grape's size is close to the wavelength of the microwaves, it resonates with the microwave energy very efficiently.
Each half of the grape collects energy, and the electrical charge builds up on opposite sides of the small skin bridge connecting them.
Focusing the Electric Field
This antenna effect funnels microwave energy from a large area and concentrates it into the tiny gap of the skin bridge. This creates an extremely intense localized electric field—many thousands of times stronger than the general field inside the oven.
This is the same principle used by a magnifying glass, which focuses diffuse sunlight into a single, hot point capable of starting a fire.
Igniting the Plasma Fireball
This incredibly strong electric field in the gap is powerful enough to accelerate the few free electrons that are always present in the air.
These electrons slam into neutral air molecules, knocking more electrons loose. This sets off a chain reaction, or electron avalanche, that rapidly ionizes the air in the gap. This newly formed, superheated, and glowing mixture of ions and electrons is the plasma fireball you see.
Understanding the Dangers and Limitations
While scientifically fascinating, attempting to create plasma in a home microwave is extremely dangerous and should never be done.
Risk of Damaging Your Microwave
The plasma fireball can reflect microwave energy back into the magnetron, the component that generates them. This feedback can permanently destroy the magnetron, rendering your oven useless.
Significant Fire Hazard
The plasma is incredibly hot—thousands of degrees—and can easily ignite nearby materials, including the object used to create it (like the grape) or even the microwave's internal components.
It Doesn't Work With Everything
This phenomenon is highly dependent on the geometry and composition of the object. A single, solid grape won't work. A metal fork will arc, but through a different mechanism of creating a short circuit. The "antenna" effect requires specific dimensions and a small gap to concentrate the field.
Key Principles to Remember
Understanding this process is about recognizing how fundamental physics can manifest in surprising ways.
- If your primary focus is the 'grape trick': The key is that the two grape halves act as a dipole antenna, focusing microwave energy into the thin skin bridge connecting them.
- If your primary focus is the underlying physics: The core principle is using an object's resonant geometry to concentrate a diffuse microwave field into an intense local electric field, which then triggers an electron avalanche in the air.
- If your primary focus is safety: Never attempt this experiment, as the high risk of destroying your appliance and starting a fire far outweighs the novelty.
Ultimately, generating plasma in a microwave is a powerful demonstration of how seemingly simple waves and objects can interact to produce extraordinary results.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in Plasma Generation |
|---|---|
| Microwave Oven | Creates standing waves with resonant energy hotspots |
| Resonant Object (e.g., grape halves) | Acts as a dipole antenna to concentrate microwave energy |
| Electric Field Gap | Intensifies energy to trigger electron avalanche |
| Ionized Air | Forms plasma through superheating and ionization |
Need precise control over thermal processes like plasma generation? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including reactors and safety systems tailored for plasma research. Contact our experts today to explore solutions that enhance your laboratory's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















