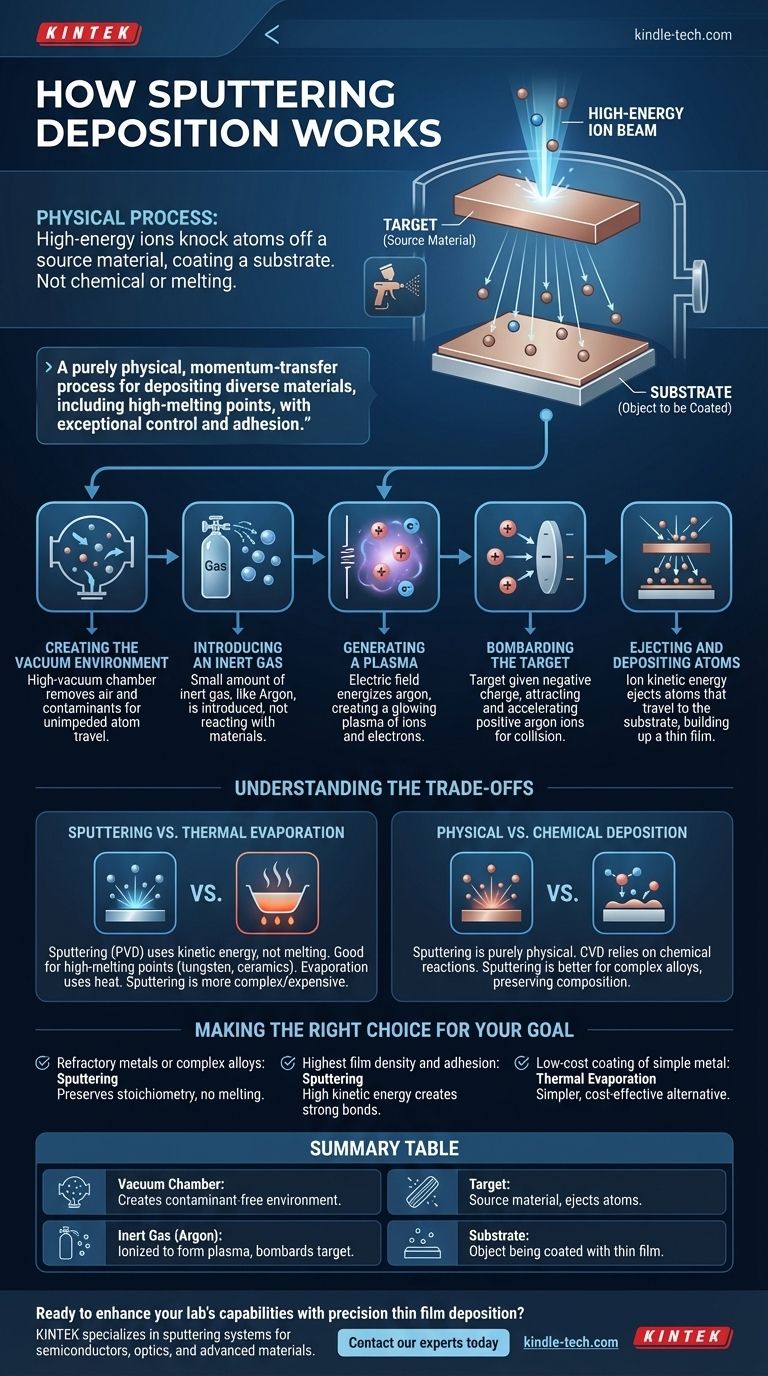
At its core, sputtering deposition is a physical process that uses high-energy ions to knock atoms off a source material, much like a sandblaster chips away paint. These dislodged atoms then travel through a vacuum and coat a separate object, called a substrate, with a highly uniform and adherent thin film. This method is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing for everything from microchips to optical coatings.
Sputtering is not a chemical reaction or a melting process. Instead, it is a purely physical, momentum-transfer process that allows for the deposition of a wide range of materials, especially those with high melting points, onto a substrate with exceptional control and adhesion.
The Core Mechanism: From Plasma to Thin Film
To understand how sputtering works, it's best to visualize it as a sequence of events occurring inside a vacuum chamber. Each step is precisely controlled to achieve the desired film characteristics.
Step 1: Creating the Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. Removing air and other contaminants is critical to ensure that the sputtered atoms can travel unimpeded from the source to the substrate and to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
Step 2: Introducing an Inert Gas
A small, controlled amount of an inert gas—most commonly argon—is introduced into the chamber. Being inert, argon will not chemically react with the target material or the substrate.
Step 3: Generating a Plasma
An electric field is applied within the chamber, energizing the argon gas and stripping electrons from the argon atoms. This creates a glowing, electrically charged gas known as a plasma, which consists of positive argon ions and free electrons.
Step 4: Bombarding the Target
The source material, known as the target, is given a negative electrical charge. This attracts the positively charged argon ions from the plasma, causing them to accelerate and collide with the target surface at high speed.
Step 5: Ejecting and Depositing Atoms
The bombardment from the argon ions transfers kinetic energy to the target material, knocking individual atoms free. These ejected atoms then travel in a straight line until they strike the substrate (the object being coated), gradually building up a thin film layer by layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sputtering is not the only deposition method, and it comes with specific considerations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to choosing the right process.
Sputtering vs. Thermal Evaporation
Sputtering is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), but it differs significantly from another PVD method: thermal evaporation. Evaporation involves heating a material until it boils, with the resulting vapor condensing on the substrate. Sputtering, by contrast, uses kinetic energy and works without melting the target.
This distinction means sputtering can deposit materials with extremely high melting points (like tungsten or ceramics) that are difficult or impossible to evaporate. However, the equipment for sputtering is generally more complex and expensive than for simple thermal evaporation.
Physical vs. Chemical Deposition
It is also crucial to distinguish sputtering from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In CVD, gases react chemically on the substrate's surface to form the film. Sputtering is a purely physical transfer—no chemical reactions are intended to form the film itself. This gives sputtering an advantage when depositing complex alloys, as it preserves the original material's composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your material, budget, and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or complex alloys: Sputtering is the superior choice because it doesn't rely on melting and preserves the material's stoichiometry.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film density and adhesion: The high kinetic energy of sputtered atoms often results in a stronger, more durable bond to the substrate compared to other methods.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost coating of a simple, low-melting-point metal: Thermal evaporation may be a more cost-effective and simpler alternative to consider.
By understanding sputtering as a controlled, physical transfer of atoms, you can leverage its unique strengths for creating high-performance thin films.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in the Process |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Creates a contaminant-free environment for unimpeded atom travel. |
| Inert Gas (Argon) | Ionized to form plasma, providing ions to bombard the target. |
| Target | The source material whose atoms are ejected by ion bombardment. |
| Substrate | The object being coated, where the ejected atoms form a thin film. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision thin film deposition? KINTEK specializes in high-performance sputtering systems and lab equipment designed for researchers and manufacturers in semiconductors, optics, and advanced materials. Our solutions ensure superior film adhesion, uniformity, and material versatility. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















