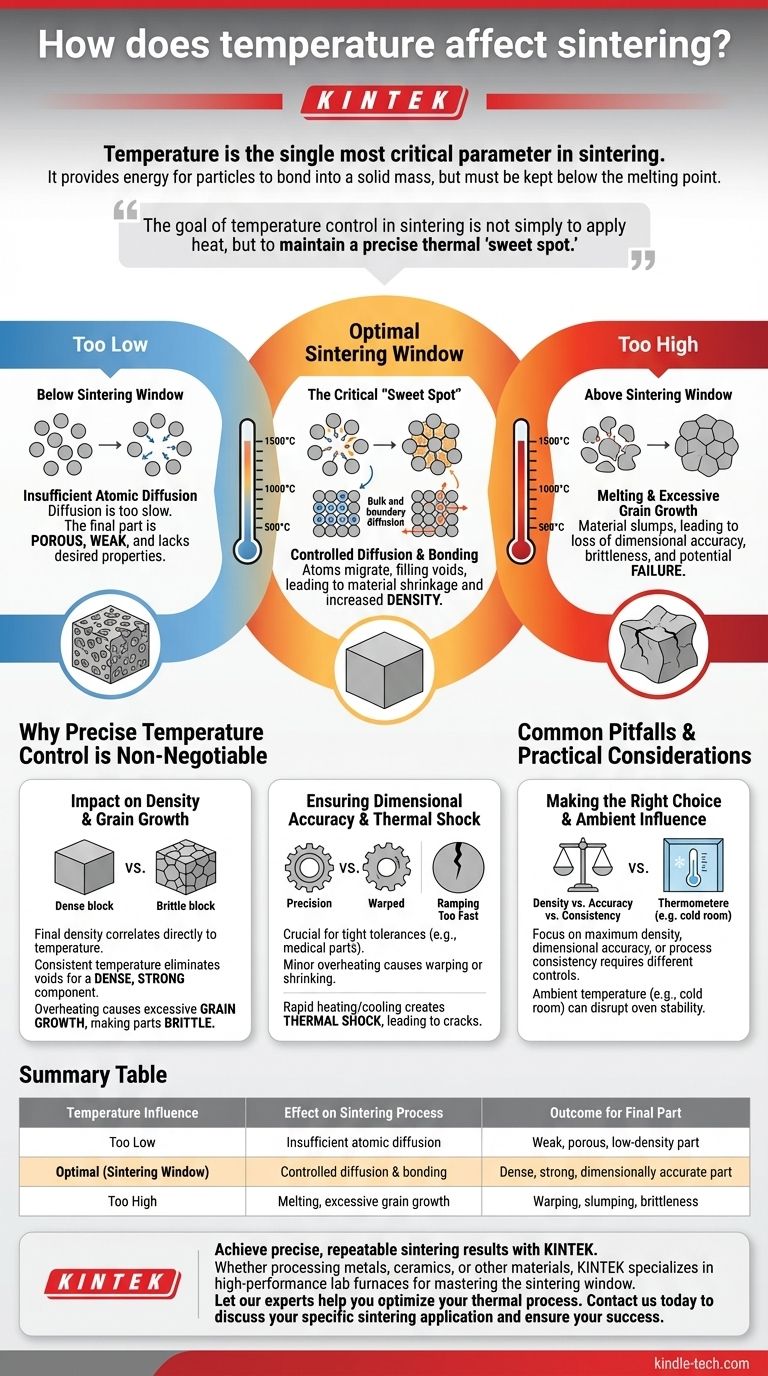
In short, temperature is the single most critical parameter in sintering. It provides the necessary energy for individual material particles to bond together into a solid mass, but must be kept below the material's melting point to prevent the part from deforming or liquefying.
The goal of temperature control in sintering is not simply to apply heat, but to maintain a precise thermal "sweet spot." This window must be hot enough to activate atomic diffusion but cool enough to preserve the part's structural shape and integrity.

The Fundamental Role of Temperature in Sintering
Temperature acts as the primary catalyst for the physical changes that define the sintering process. Without sufficient thermal energy, the bonding required to densify a material simply will not occur.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works because heat gives atoms the kinetic energy they need to move. At the right temperature, atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, filling the voids between them.
This process, known as atomic diffusion, is what fuses the particles together and causes the material to shrink and increase in density.
The Critical "Sintering Window"
Every material has an optimal temperature range for sintering. This is often referred to as the sintering window.
- Below this window: Diffusion is too slow. The final part will be porous, weak, and lack the desired mechanical properties.
- Above this window: The material begins to melt. This leads to slumping, loss of dimensional accuracy, and potentially complete failure of the part.
Key Diffusion Pathways
Temperature directly influences the primary mechanisms of material transport. The two most important are bulk diffusion (atoms moving through the particle's crystal lattice) and grain boundary diffusion (atoms moving along the interface between particles). Both are heavily dependent on reaching the correct temperature.
Why Precise Temperature Control is Non-Negotiable
Simply reaching the sintering temperature is not enough; it must be controlled with high precision throughout the cycle. Fluctuations can have significant consequences for the final product's quality.
Impact on Density and Porosity
The final density of a sintered part is directly correlated to the temperature achieved. Consistent and accurate temperature ensures that voids between particles are systematically eliminated, resulting in a dense, strong component.
Preventing Unwanted Grain Growth
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, the microscopic crystalline structures (grains) within the material can grow excessively large. This can paradoxically make the final product more brittle and prone to fracture.
Ensuring Dimensional Accuracy
For components with tight tolerances, such as dental crowns or precision engine parts, temperature control is paramount. Even minor overheating can cause the part to warp or shrink unpredictably, rendering it useless.
Common Pitfalls and Practical Considerations
Achieving the correct temperature inside the furnace involves more than just setting the controller. External and process-related factors can undermine the consistency of your results.
The Influence of Ambient Temperature
The environment where the equipment operates matters. As the references note, a sintering oven in a cold room (e.g., below 50°F / 10°C) may struggle to heat up properly and maintain a stable target temperature.
This can introduce inconsistency into the process, compromising the quality and repeatability of the results.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
The rate at which a part is heated and cooled is just as important as the peak temperature. Ramping the temperature up or down too quickly can create internal stresses, leading to cracks and structural failure—a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
Material-Specific Requirements
There is no universal sintering temperature. Metals, ceramics, and polymers each have vastly different sintering windows based on their composition, particle size, and binding agents. Always adhere to the material manufacturer's specifications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling temperature is about managing a series of trade-offs to achieve a specific outcome. Your primary objective will determine your focus.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: You must operate at the upper end of the material's specified sintering window, ensuring precise control to avoid overshooting into the melting range.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: You must prioritize stable, consistent temperature control and a carefully managed cooling cycle to prevent any warping or deformation.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and repeatability: You must standardize the entire thermal cycle, including controlling the ambient room temperature and using calibrated equipment.
Ultimately, mastering sintering requires treating temperature not as a setting, but as a dynamic process to be meticulously controlled.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Influence | Effect on Sintering Process | Outcome for Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Too Low | Insufficient atomic diffusion | Weak, porous, low-density part |
| Optimal (Sintering Window) | Controlled diffusion & bonding | Dense, strong, dimensionally accurate part |
| Too High | Melting, excessive grain growth | Warping, slumping, brittleness |
Achieve precise, repeatable sintering results with KINTEK.
Whether you are processing metals, ceramics, or other materials, the correct furnace temperature is non-negotiable for part density, strength, and dimensional accuracy. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces that deliver the stable, uniform heat essential for mastering the sintering window.
Let our experts help you optimize your thermal process. Contact us today to discuss your specific sintering application and ensure your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role do laboratory high-temperature furnaces play in T91/TP316H weld aging? Accelerate Service Life Testing
- How does a vacuum drying oven contribute to the formation of PEO/LLZTO composite electrolyte membranes?
- What is the application of heat treatment in aerospace industry? Achieve Mission-Critical Performance
- Can aluminum and steel be brazed? Master the Metallurgical Challenges for a Strong Joint
- How is heating done in sintering operation? Master the Core Methods for Dense, Strong Parts
- Why are resistance furnaces used for SHS preheating? Mastering Controlled Ignition & Thermal Explosion for Lab Success
- What is catalytic fast pyrolysis process? The Key to Upgrading Bio-Oil for Clean Fuel
- Is calcination done in a blast furnace? Clarifying the Purpose of Industrial Furnaces



















