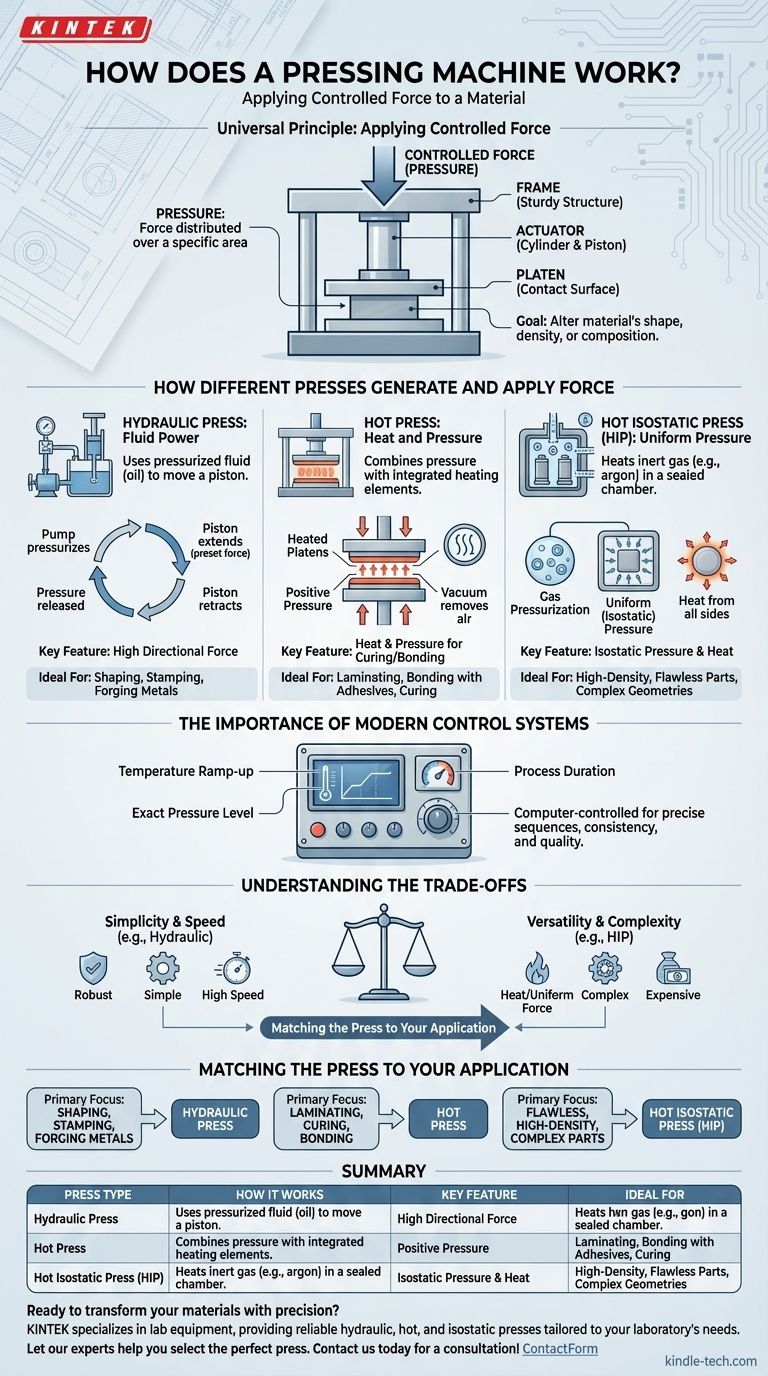
At its core, a pressing machine works by applying controlled force to a material. This force is most commonly generated by a hydraulic system, where a pump pressurizes a fluid (like oil) to move a cylinder and exert immense pressure. Depending on the application, this fundamental action can be combined with other elements like heat, vacuum, or uniform gas pressure to shape, bond, or compact materials with high precision.
A pressing machine is a device designed to exert a specific, controlled force on a workpiece. While the methods vary—from simple fluid dynamics to complex heat and gas systems—the universal goal is to physically alter a material's shape, density, or composition.
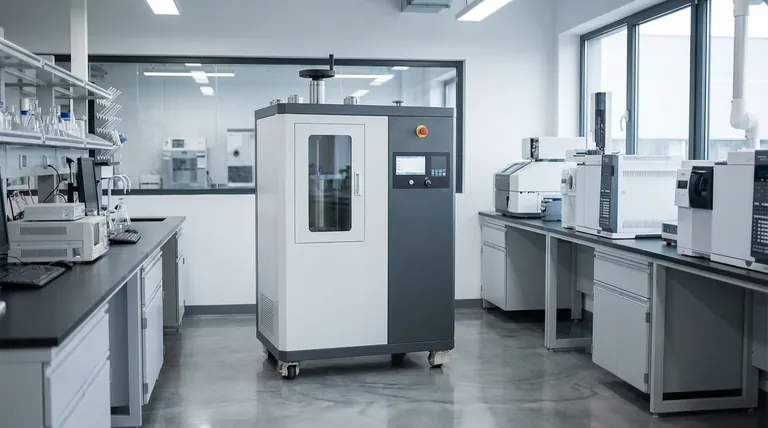

The Universal Principle: Applying Controlled Force
Every press, regardless of its complexity, is built around the fundamental concept of applying force. This is achieved through a few key components and principles working in concert.
The Role of Pressure
The machine doesn't just push; it applies a calculated pressure—force distributed over a specific area. This is the critical variable that allows the machine to forge metal, laminate wood, or densify ceramic powders.
Core Mechanical Components
Most presses share a common structure: a sturdy frame to withstand the operational forces, a platen or die that makes contact with the workpiece, and an actuator (typically a cylinder and piston) that generates the movement and force.
How Different Presses Generate and Apply Force
The primary distinction between types of presses lies in how they generate force and what other environmental conditions they create.
The Hydraulic Press: Using Fluid Power
A hydraulic press operates on a simple principle: a pump pressurizes a contained fluid, usually oil. This pressure acts on a large piston, multiplying the initial force significantly.
The process is cyclical. The pump engages, forcing the cylinder to extend and press against the material with a preset force. Once the operation is complete, the pressure is released, and the cylinder retracts.
The Hot Press: Combining Heat and Pressure
For materials that require curing or forming with adhesives, a hot press is used. It integrates heating elements into the platens.
This type of machine often applies positive pressure while using a vacuum to remove air and ensure a tight bond. It is designed to operate with controlled pressure and temperature to process materials without causing deformation.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Uniform Pressure from All Sides
For advanced applications, a hot isostatic press places components inside a sealed chamber. Instead of a piston, the machine heats an inert gas (like argon) to a high temperature and pressure.
This heated gas exerts uniform, or isostatic, pressure on the component from all directions. This method is ideal for creating highly dense parts with complex shapes and eliminating internal voids.
The Importance of Modern Control Systems
The effectiveness of a modern press is determined by its control system. Simple presses may have manual controls, but advanced manufacturing relies on automation.
Programming the Process
Computer-controlled systems allow operators to program a precise sequence of operations. This is critical for processes involving variable conditions.
Key Control Variables
Operators can set the temperature ramp-up speed, the exact pressure level, and the process duration. This programmability ensures that each part is produced with consistent quality and performance, meeting exact specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right press involves balancing capability, complexity, and cost. Each technology comes with inherent trade-offs.
Simplicity vs. Versatility
A standard hydraulic press is a robust and relatively simple workhorse for forming and shaping. However, it lacks the ability to apply heat or uniform pressure needed for advanced materials and composites.
Directional vs. Uniform Force
A hydraulic press applies force in one direction. A hot isostatic press applies it from all sides, which is superior for densifying powders or healing defects in castings but is a much more complex and expensive process.
Speed vs. Material Properties
Hot presses often use specific cycles, such as high pressure at lower temperatures with short cycle times. This is a deliberate trade-off designed to reduce workpiece deformation while ensuring a proper bond or cure.
Matching the Press to Your Application
To select the right equipment, you must first define your primary manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is shaping, stamping, or forging metals: A standard hydraulic press provides the necessary directional force and reliability.
- If your primary focus is laminating, curing, or bonding materials with adhesives: A hot press is essential for applying both heat and pressure in a controlled environment.
- If your primary focus is creating flawless, high-density parts or processing complex geometries: Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is the definitive solution for its ability to apply uniform heat and pressure.
Understanding these core operating principles empowers you to select the precise tool needed to transform raw materials into finished products.
Summary Table:
| Press Type | How It Works | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Press | Uses pressurized fluid to move a piston and apply force. | High directional force. | Shaping, stamping, or forging metals. |
| Hot Press | Combines pressure with heat from integrated platens. | Heat and pressure for curing/bonding. | Laminating or bonding materials with adhesives. |
| Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) | Heats gas in a sealed chamber for uniform pressure from all sides. | Isostatic (uniform) pressure and heat. | Creating high-density, flawless parts with complex geometries. |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
The right pressing machine is critical for achieving consistent quality in shaping, bonding, or densifying your materials. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable hydraulic, hot, and isostatic presses tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect press to enhance your R&D and production processes. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why are hydraulic presses and pressure dies used for composite electrodes? Optimize Solid-State Battery Conductivity
- Why are laboratory hydraulic presses critical for assessing geopolymer performance? Ensure Reliable Material Testing
- What is the process of forging press? Achieve Superior Strength for Critical Metal Components
- What equipment is needed for XRF analysis? A Guide to the Essential Tools for Accurate Results
- How do you explain XRF results? A Guide to Interpreting Elemental Analysis Data
- What is screw press forging? Achieve High-Precision, Near-Net-Shape Metal Parts
- Why are hydraulic presses required when studying FATT50? Precision Tools for Grain Refinement & Impact Toughness
- How do you make IR pellets? A Step-by-Step Guide to Flawless FTIR Sample Preparation



















