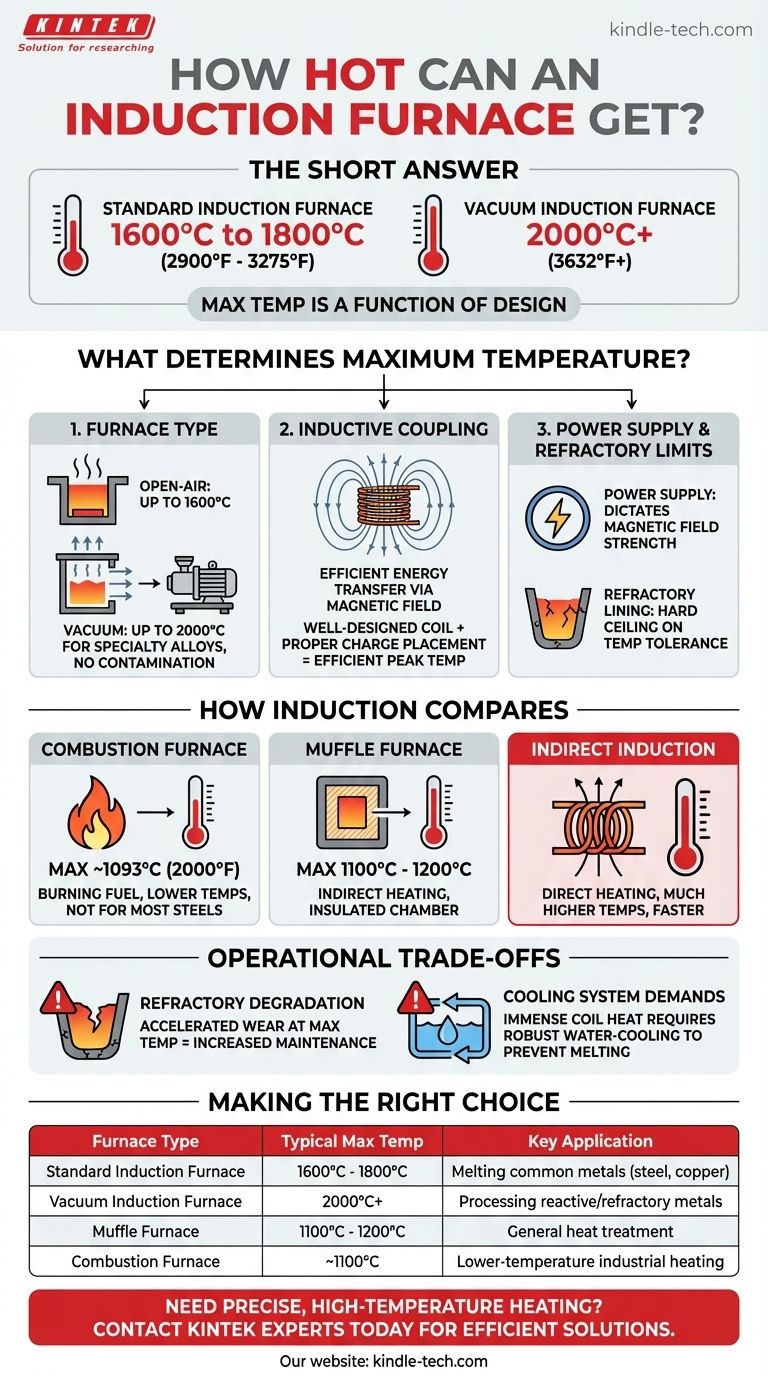
The short answer is that a standard induction furnace can reach temperatures of 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3275°F). However, specialized models, such as vacuum induction furnaces, can achieve significantly higher temperatures, often reaching or exceeding 2000°C (3632°F).
The maximum temperature of an induction furnace is not a single value but a function of its specific design. Key factors include the furnace type (e.g., open-air vs. vacuum), the power of its electrical systems, and the materials used in its construction.

What Determines an Induction Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
An induction furnace's impressive heating capability comes from its unique method of operation, but its ultimate temperature limit is governed by several critical design and physics principles.
The Role of Furnace Type
The environment in which the heating occurs is paramount. A small or standard induction furnace operating in open air is typically rated for up to 1600°C.
For higher temperature applications, a vacuum induction furnace is used. By removing the atmosphere, it prevents heat loss and material contamination, allowing it to reach temperatures of 2000°C for processing specialty alloys and reactive metals.
The Principle of Inductive Coupling
Heating efficiency is directly tied to inductive coupling, which is how effectively the magnetic field generated by the coil transfers energy to the metal charge inside.
A well-designed coil and proper placement of the charge material ensure maximum energy transfer, enabling the system to reach its peak temperature more efficiently.
Power Supply and Refractory Limits
Ultimately, the furnace is limited by its components. The power supply dictates the strength of the magnetic field, and the refractory lining (the crucible holding the molten metal) has a maximum temperature it can withstand before failing. These two factors create a hard ceiling on the furnace's operational range.
How Induction Compares to Other Furnace Technologies
Understanding the temperature capabilities of induction is clearer when compared to other common industrial heating methods.
Induction vs. Combustion Furnaces
Furnaces that rely on burning fuel, like a natural gas furnace, operate at fundamentally lower temperatures. They typically reach a maximum of around 1093°C (2000°F), making them suitable for some applications but insufficient for melting most steels and specialty alloys.
Induction vs. Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace works by heating an insulated chamber, which then radiates heat to the material inside. While some can reach high temperatures (typically 1100°C to 1200°C), their mechanism is indirect.
Induction heating is direct, heating the material itself from within via an electric current. This direct method is what allows induction furnaces to achieve much higher temperatures much more quickly.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Reaching extreme temperatures is not without its challenges. The primary limitation is the physical endurance of the furnace components.
Refractory Material Degradation
The crucible or refractory lining that contains the molten charge is a consumable item. Running the furnace consistently at its maximum rated temperature will accelerate the wear and degradation of this lining, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Cooling System Demands
The induction coils themselves generate immense heat and must be water-cooled to prevent them from melting. The capacity of the cooling system is a critical limiting factor; if it cannot dissipate heat fast enough, the furnace cannot safely sustain its peak temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is melting common ferrous and non-ferrous metals (up to 1800°C): A standard induction furnace provides unmatched speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is processing high-purity, reactive, or refractory metals (up to 2000°C): A vacuum induction furnace is the necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment in a controlled atmosphere below 1200°C: A muffle furnace may be a more suitable and cost-effective choice.
Matching the technology's capabilities to your specific temperature requirements is the key to achieving efficient and successful results.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Induction Furnace | 1600°C - 1800°C | Melting common metals (steel, copper) |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | 2000°C+ | Processing reactive/refractory metals |
| Muffle Furnace | 1100°C - 1200°C | General heat treatment |
| Combustion Furnace | ~1100°C | Lower-temperature industrial heating |
Need precise, high-temperature heating for your lab or production? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for efficiency and durability. Whether you're melting common alloys or processing specialty metals, our solutions ensure optimal performance and temperature control. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is vacuum induction melting used for? Creating Ultra-Pure Metals for Demanding Industries
- What are the advantages of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultimate Purity & Precision for High-Performance Alloys
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals



















