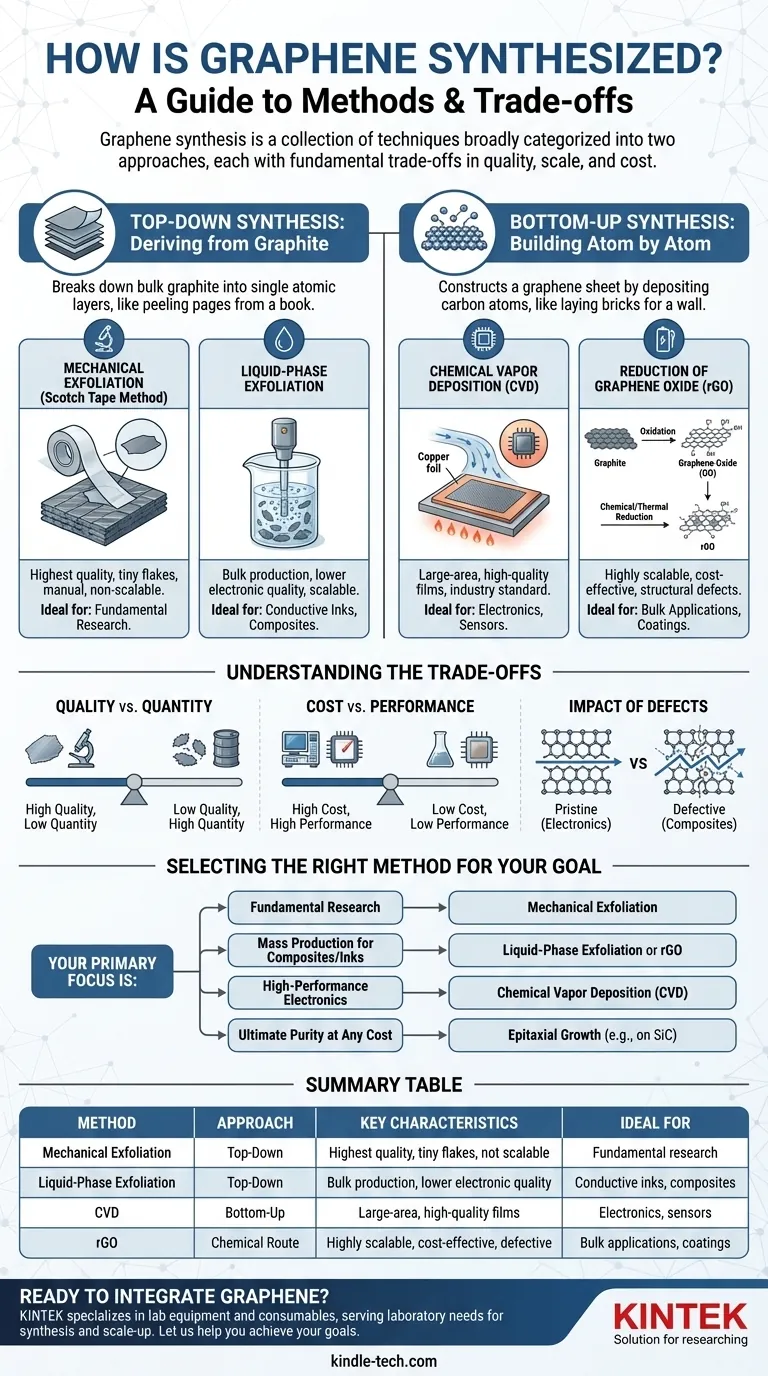
Graphene synthesis is not a single process, but a collection of techniques broadly categorized into two approaches. The first is "top-down," which involves breaking down bulk graphite into single atomic layers. The second is "bottom-up," where graphene is built atom-by-atom on a substrate, most notably through Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The choice of synthesis method is a critical engineering decision dictated by the end application. There is no single "best" way to make graphene; each technique presents a fundamental trade-off between quality, scale, and cost.

The Two Fundamental Approaches
At the highest level, all synthesis methods fall into one of two categories, defined by whether you are building up from atoms or breaking down from a larger material.
Top-Down Synthesis: Deriving Graphene from Graphite
This approach starts with graphite—essentially a stack of countless graphene layers—and separates those layers. It is conceptually similar to peeling individual pages from a thick book.
These methods are often suited for producing large quantities of graphene flakes, which can be dispersed in liquids to create inks, coatings, or composites.
Bottom-Up Synthesis: Building Graphene Atom by Atom
This approach constructs a graphene sheet by depositing individual carbon atoms onto a catalytic substrate. This is analogous to laying individual bricks to form a perfect, continuous wall.
Bottom-up methods are the gold standard for creating the large, high-quality, and uniform sheets of graphene required for advanced electronics and semiconductor applications.
Key Synthesis Methods and Their Applications
The specific method chosen depends entirely on whether the goal is a pristine sheet for a transistor or a bulk powder for a composite material.
Mechanical Exfoliation: The Original Research Method
This is the famous "Scotch tape" method, where adhesive tape is used to peel layers from a piece of graphite until a single-layer flake is isolated.
While it produces exceptionally high-quality, defect-free graphene, the process is manual, yields tiny flakes, and is not scalable beyond fundamental laboratory research.
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: For Bulk Production
In this method, graphite is submerged in a liquid and subjected to high energy (such as sonication) to break the layers apart. This creates a dispersion of graphene flakes.
This technique is scalable for mass production of materials like conductive inks and polymer composites, but the resulting graphene often has lower electrical quality and smaller flake sizes.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The Standard for Electronics
CVD involves flowing a carbon-containing gas (like methane) over a heated metal catalyst foil (typically copper or nickel). The carbon atoms assemble into a continuous graphene sheet on the metal's surface.
CVD is the most promising technique for producing the large-area, high-quality films essential for electronic and photonic devices. Advanced CVD techniques can even produce large, single-crystal sheets for ultimate performance.
Reduction of Graphene Oxide (rGO): A Scalable Chemical Route
This multi-step process begins with the harsh chemical oxidation of graphite to form graphene oxide (GO), which is easily exfoliated in water. The GO is then chemically or thermally "reduced" to remove the oxygen groups.
This method is highly scalable and cost-effective for bulk applications. However, the reduction process is imperfect, leaving behind defects that degrade the material's electrical and thermal properties compared to pristine graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a synthesis method is an exercise in managing competing priorities. The ideal method for one application is often completely unsuitable for another.
Quality vs. Quantity
Mechanical exfoliation produces near-perfect graphene but in microscopic amounts. In contrast, liquid-phase exfoliation and rGO production can generate tons of material, but with inherent structural defects and smaller flake sizes.
Cost vs. Performance
Methods capable of producing high-performance electronic-grade graphene, like CVD and epitaxial growth on silicon carbide, are complex and expensive. Chemical methods that produce rGO are far cheaper but yield a material unsuitable for high-performance electronics.
The Impact of Defects
For electronics, every defect matters. Grain boundaries in polycrystalline CVD graphene or residual oxygen in rGO can scatter electrons and degrade device performance. For a polymer composite, these defects may be less critical than the overall quantity and dispersion of the graphene filler.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Goal
The optimal synthesis method depends entirely on your specific objective and constraints.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Mechanical exfoliation provides the pristine, high-quality flakes necessary for academic study.
- If your primary focus is mass production for composites or inks: Liquid-phase exfoliation or the reduction of graphene oxide offer scalable, cost-effective solutions.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the industry standard for creating the large, uniform films required for transistors and sensors.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity at any cost: Epitaxial growth on substrates like silicon carbide produces some of the highest-quality graphene, albeit at a significant price point.
Ultimately, understanding the landscape of graphene synthesis is about matching the right tool to the right technical problem.
Summary Table:
| Method | Approach | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Top-Down | Highest quality, tiny flakes, not scalable | Fundamental research |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Top-Down | Bulk production, lower electronic quality | Conductive inks, composites |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Bottom-Up | Large-area, high-quality films | Electronics, sensors |
| Reduction of Graphene Oxide (rGO) | Chemical Route | Highly scalable, cost-effective, defective | Bulk applications, coatings |
Ready to Integrate Graphene into Your Research or Product Development?
Choosing the right synthesis method is just the first step. You need reliable equipment to execute your process, whether it's a CVD system for high-quality films or a furnace for thermal reduction of GO.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the tools and expertise to support your graphene synthesis journey, from research to scale-up.
Let us help you achieve your goals. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques



















