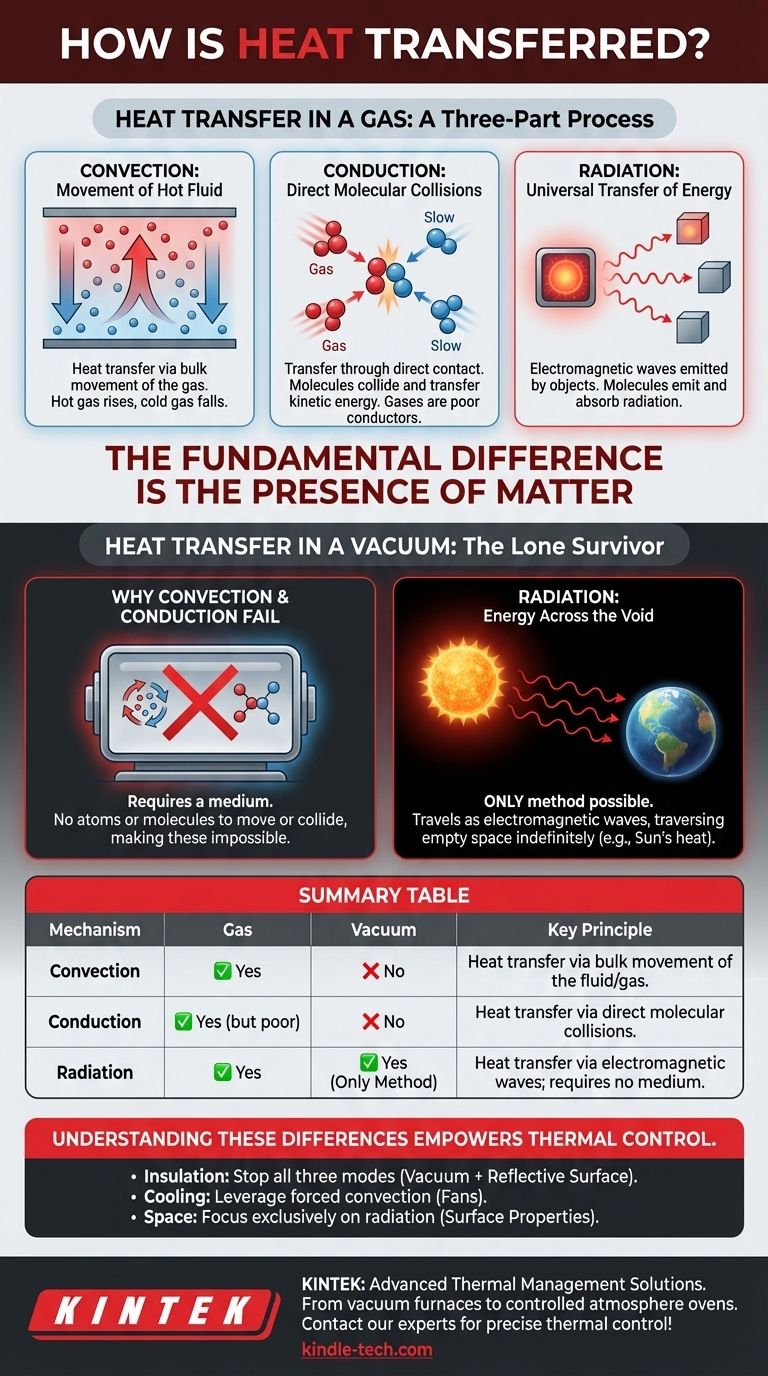
At its core, heat is transferred through a gas by a combination of three mechanisms: convection, conduction, and radiation. In a vacuum, however, only one of these is possible. Because a vacuum lacks a physical medium, heat can only be transferred through electromagnetic waves, a process known as thermal radiation.
The fundamental difference is the presence of matter. A gas uses the movement and collision of its molecules for convection and conduction, while the empty space of a vacuum forces heat to travel exclusively as radiation.

Heat Transfer in a Gas: A Three-Part Process
When heat moves through a gas, like the air in a room or the nitrogen mentioned in industrial processes, it's a dynamic interplay between the movement of the gas itself, collisions between its molecules, and the emission of energy waves.
Convection: The Movement of Hot Fluid
Convection is typically the most significant form of heat transfer in a gas. It occurs when a portion of the gas is heated, becomes less dense, and rises.
This movement of the hot gas itself transfers thermal energy from one place to another. A simple example is the air rising from a hot radiator, which then circulates to warm an entire room. This bulk movement of the medium is what defines convection.
Conduction: Direct Molecular Collisions
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact. In a gas, fast-moving (hot) molecules collide with slow-moving (cold) molecules, transferring kinetic energy in the process.
However, gases are poor conductors of heat. Their molecules are far apart, making these collisions much less frequent and efficient than in a solid, where molecules are tightly packed.
Radiation: The Universal Transfer of Energy
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. This is energy released in the form of electromagnetic waves (specifically, infrared radiation for most everyday objects).
In a gas, molecules both emit and absorb this radiation. While often less dominant than convection in Earth-bound applications, it is a constantly present factor in any heat transfer scenario.
Heat Transfer in a Vacuum: The Lone Survivor
A perfect vacuum is, by definition, empty space. It contains no atoms or molecules to move or collide. This fundamentally changes the rules of heat transfer.
Why Convection and Conduction Fail
Both convection and conduction require a medium. Convection needs a fluid (like a gas or liquid) that can physically move. Conduction needs molecules that can collide with each other.
Since a vacuum has neither, these two methods of heat transfer are completely impossible. There is nothing to move and nothing to collide.
Radiation: Energy Across the Void
Thermal radiation is the only way heat can travel through a vacuum. It does not require a medium. The energy travels as an electromagnetic wave, capable of traversing empty space indefinitely.
The most profound example of this is the Sun. Its heat travels 93 million miles through the vacuum of space to warm the Earth, a transfer made possible exclusively by radiation.
Understanding the Key Differences
The efficiency and dominance of each heat transfer method are entirely dependent on the environment. Understanding these differences is critical for engineering and scientific applications.
The Role of a Medium is Everything
The central takeaway is that matter is the vehicle for conduction and convection. Removing that matter, as in a vacuum, leaves radiation as the sole option. This is the principle behind a vacuum flask (thermos), which uses a vacuum to stop conduction and convection, and a silvered coating to reduce radiation.
Density and Pressure Impact
In a gas, the effectiveness of convection and conduction is directly related to its density and pressure. A denser gas will be a better conductor (more collisions) and can support stronger convective currents. At very low pressures approaching a vacuum, both effects diminish significantly.
Surface Properties Drive Radiation
The rate of radiative heat transfer is heavily influenced by an object's surface properties, specifically its emissivity. A matte black surface is a highly effective emitter and absorber of radiation, while a polished, shiny surface is a poor one. This is why emergency space blankets are reflective—to minimize radiative heat loss from the body.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to managing heat depends entirely on which transfer mechanism you want to encourage or prevent.
- If your primary focus is insulating a container: Your goal is to stop all three modes. Use a vacuum to eliminate conduction and convection, and a reflective surface to minimize radiation.
- If your primary focus is cooling a hot component with a fan: You are primarily leveraging forced convection by using the fan to move air across the component's surface, carrying heat away.
- If your primary focus is calculating heat exchange in space: You must ignore conduction and convection and focus exclusively on radiation, modeling how objects emit and absorb energy.
Understanding these three fundamental modes of heat transfer empowers you to control temperature in any environment, from your kitchen to the vacuum of space.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Gas | Vacuum | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convection | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | Heat transfer via bulk movement of the fluid/gas. |
| Conduction | ✅ Yes (but poor) | ❌ No | Heat transfer via direct molecular collisions. |
| Radiation | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes (Only Method) | Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves; requires no medium. |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment designed with advanced thermal management, from vacuum furnaces to controlled atmosphere ovens. Our expertise ensures your materials are heated or cooled efficiently and accurately, whether you're leveraging convection, conduction, or radiation. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your lab's thermal performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- What is the temperature of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Material Properties & Pristine Finishes
- How long does it take for a house to cool down after heat treatment? A Guide to Safe & Speedy Recovery
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials



















