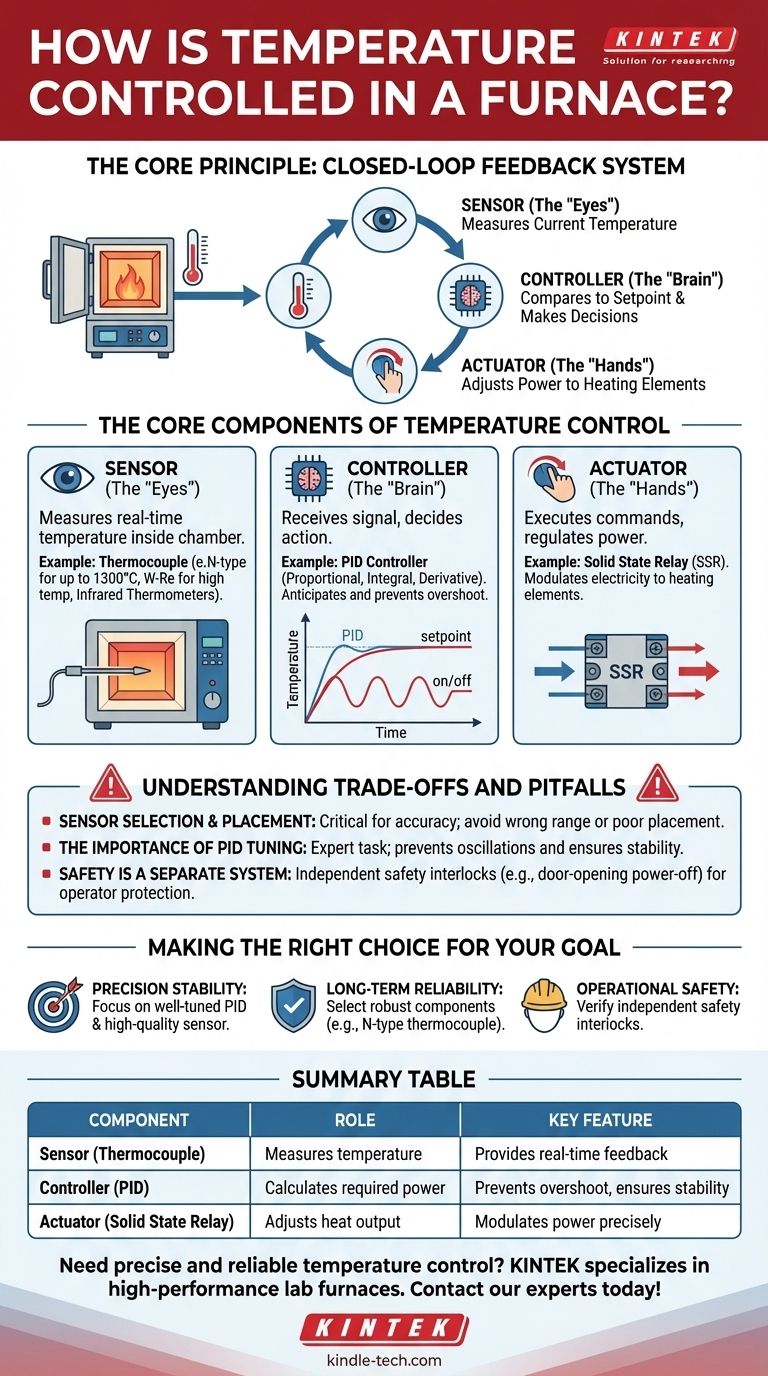
At its core, furnace temperature is controlled through a precise, closed-loop feedback system. This system constantly measures the current temperature, compares it to the desired setpoint, and intelligently adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to eliminate any difference.
The essential principle is not simply heating, but continuous correction. Modern furnaces achieve this using a combination of a sensor to measure temperature, a controller to make decisions, and an actuator to regulate power, ensuring the system remains stable and accurate.
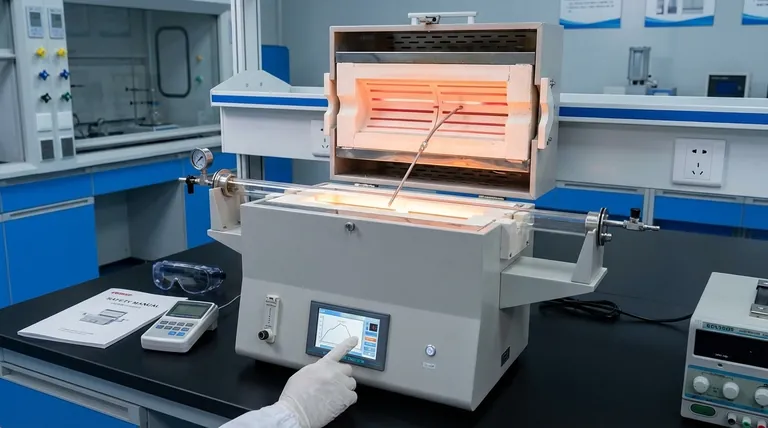

The Core Components of Temperature Control
A furnace's temperature control system can be understood as having three primary parts working in unison: the sensor, the controller, and the actuator.
The Sensor (The "Eyes")
The system's "eyes" are a temperature sensor that provides a real-time measurement from inside the furnace chamber.
The most common sensor is a thermocouple. This device consists of two different metals joined at one end. A temperature change creates a tiny, measurable voltage, which the controller can interpret as a specific temperature.
Different applications require different thermocouples. For example, a W-Re (Tungsten-Rhenium) thermocouple is often used in high-temperature vacuum furnaces, while an N-type thermocouple is a durable choice for general use up to about 1300°C. Some systems also use non-contact infrared thermometers.
The Controller (The "Brain")
The controller is the brain of the operation. It receives the temperature signal from the sensor and decides what to do next.
The most prevalent and effective type is the PID controller. PID stands for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative—three mathematical functions that allow the controller to react not just to the current error, but also to past errors and the rate of temperature change.
This "smart" control allows the system to anticipate and prevent overshooting the target temperature, leading to a much more stable and precise result than a simple on/off thermostat.
The Actuator (The "Hands")
The actuator executes the controller's commands. It's the component that physically adjusts the heat output.
In modern electric furnaces, this is typically a Solid State Relay (SSR). An SSR is an electronic switch with no moving parts that can turn power on and off thousands of times per second.
The PID controller sends a precise signal to the SSR, which then modulates the flow of electricity to the furnace's heating elements, delivering just the right amount of energy to maintain the setpoint.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Achieving perfect temperature control involves balancing performance, cost, and reliability. Understanding the potential failure points is critical.
Sensor Selection and Placement
The entire system is only as good as its sensor. Using a thermocouple outside of its intended temperature range will lead to inaccurate readings and rapid degradation.
Furthermore, sensor placement is crucial. A thermocouple that is too close to a heating element or the door may not reflect the true temperature of the work area, leading to processing errors. Some vacuum furnaces even use mechanisms to automatically insert and retract the thermocouple to protect it during extreme temperature ramps.
The Importance of PID Tuning
A PID controller is not "plug-and-play." It must be "tuned" for the specific thermal properties of the furnace.
Poor tuning can lead to wild temperature oscillations (swinging above and below the setpoint) or an extremely slow response time. Proper tuning is an expert task that ensures the system is both fast and stable.
Safety is a Separate System
Temperature control ensures process accuracy, but safety interlocks ensure operator protection. These are not the same thing.
A feature like a door-opening power-off switch is a critical safety mechanism. It operates independently of the PID controller to immediately cut power to the heating elements if the door is opened, preventing exposure to extreme heat and electrical hazards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates which aspect of the temperature control system you should prioritize.
- If your primary focus is high-precision stability: Ensure the furnace uses a well-tuned PID controller and a high-quality sensor appropriate for your exact temperature range.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Select a system with robust components known for long service life, such as an N-type thermocouple for mid-range applications.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Verify the furnace includes independent safety interlocks, such as door power-off switches, that are separate from the primary control loop.
Ultimately, effective temperature control comes from a thoughtful integration of high-quality components designed to work together as a single, intelligent system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor (Thermocouple) | Measures temperature | Provides real-time feedback |
| Controller (PID) | Calculates required power | Prevents overshoot, ensures stability |
| Actuator (Solid State Relay) | Adjusts heat output | Modulates power precisely |
Need precise and reliable temperature control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces with advanced PID controllers, durable thermocouples, and robust safety features. Our equipment ensures the accuracy and repeatability your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















