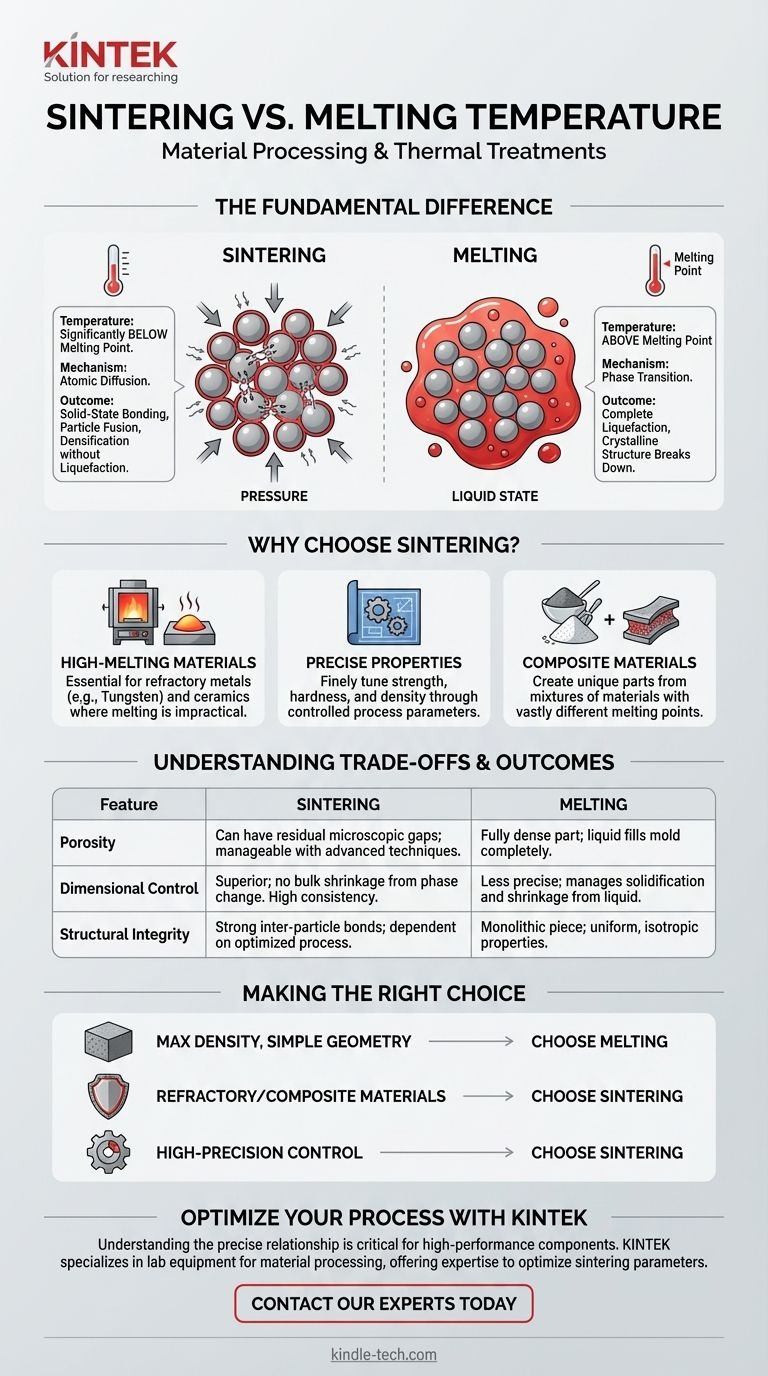
In material processing, the sintering temperature is intentionally set to a point significantly below the material's melting temperature. Sintering is a thermal treatment that uses heat and often pressure to bond particles together, causing them to fuse and densify without ever reaching a liquid state. This is fundamentally different from melting, which requires heating a material above its melting point to induce a complete phase change from solid to liquid.
The core distinction is one of mechanism: Sintering relies on atomic diffusion across particle boundaries to create a solid-state bond, while melting relies on thermal energy alone to break the crystalline structure and create a liquid. The sintering temperature is therefore a carefully controlled variable that activates diffusion without causing liquefaction.

The Principle: Atomic Diffusion vs. State Change
To understand the relationship between these temperatures, you must first understand the different physical processes at work. They are not variations of the same process; they are entirely distinct methods for consolidating material.
How Melting Works
Melting is a phase transition. When you heat a material to its melting point, you are supplying enough thermal energy to overcome the forces holding its atoms in a fixed crystalline lattice. The structure breaks down, and the material flows as a liquid. This process is driven solely by heat.
How Sintering Works
Sintering operates below the melting point. The applied heat energizes the atoms, but not enough to break the entire structure. Instead, it allows atoms to move and diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This atomic movement reduces the surface area and pores between particles, causing them to fuse into a solid, coherent mass.
The Critical Role of Temperature in Sintering
The sintering temperature is a precisely controlled parameter. It must be high enough to allow for significant atomic mobility and diffusion but remain safely below the melting point to prevent liquefaction.
Applying pressure during the process forces the particles into intimate contact, which dramatically aids the diffusion process and can allow for sintering to occur at even lower temperatures.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
The decision to sinter rather than melt is a strategic one, driven by material limitations and desired final properties.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is essential for manufacturing parts from refractory metals (like tungsten) and ceramics. Their melting points are so high that melting and casting them is often impractical, uneconomical, or technologically prohibitive. Sintering provides a viable path to create solid components at lower temperatures.
Achieving Precise Material Properties
Because sintering does not involve a full liquid phase, it offers greater control over the final product. Engineers can finely tune the process to control properties like strength, hardness, and density. This level of control is difficult to achieve in a casting process, which involves managing solidification and shrinkage from a liquid state.
Creating Composite Materials
Sintering уникально подходит for creating parts from a mixture of different materials, especially when they have vastly different melting points or do not readily form alloys. The powders can be mixed and then sintered, bonding them together in the solid state to create a composite with unique, blended properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between sintering and melting involves clear-eyed consideration of their inherent advantages and limitations.
Porosity and Density
Melting and casting produce a fully dense part, as the liquid material fills the mold cavity completely. Sintering, by contrast, can leave residual microscopic gaps or porosity between the original particles. While advanced sintering techniques can achieve near-full density, managing porosity is a key aspect of the process.
Dimensional Control and Consistency
Sintering often provides superior dimensional accuracy. The material does not undergo the bulk shrinkage associated with a liquid-to-solid phase change. This results in greater consistency and control over the final dimensions of the component, reducing the need for extensive post-processing.
Structural Integrity
A properly cast part is a monolithic piece with uniform, isotropic properties. A sintered part's strength is dependent on the quality of the bonds formed between the initial particles. While very strong, these inter-particle bonds can be points of failure if the sintering process is not optimized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of process depends entirely on your material constraints and the desired characteristics of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and a simple geometry: Melting and casting is often the most direct path to a fully dense, non-porous object from a single material.
- If your primary focus is processing refractory materials or composites: Sintering is the superior and often the only viable manufacturing method.
- If your primary focus is high-precision control over final dimensions and microstructure: Sintering provides more granular control over density, porosity, and dimensional tolerances than casting.
Ultimately, you select a process based on whether your goal is to fuse particles together with precision or to completely remold the material from a liquid state.
Summary Table:
| Process | Temperature Relative to Melting Point | Primary Mechanism | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering | Significantly below | Atomic diffusion | Solid-state bonding, controlled porosity |
| Melting | Above | Phase transition (solid to liquid) | Fully dense, monolithic part |
Need to choose the right thermal process for your materials?
Understanding the precise relationship between sintering and melting temperatures is critical for developing high-performance components, especially when working with refractory metals or ceramic composites.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for material processing, offering the tools and expertise to help you optimize your sintering parameters for superior strength, density, and dimensional accuracy.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material synthesis and achieve your specific property goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature accuracy of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating
- How to use a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Operation
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and induction furnace? Choosing the Right Heat Source for Your Lab
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab
- What are the components of a muffle furnace? Unlock the Core Systems for Precise, Safe Heating



















