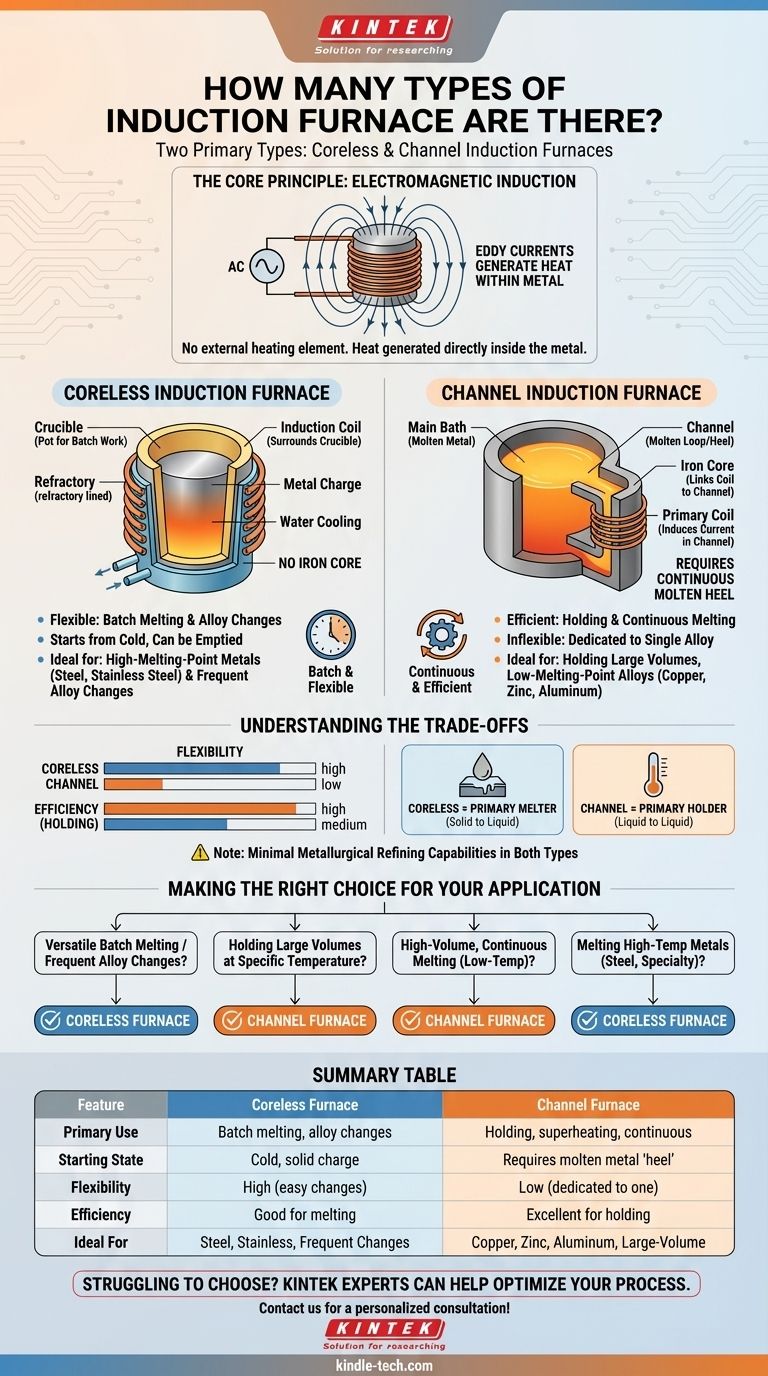
Fundamentally, there are two primary types of induction furnaces. These are the coreless induction furnace and the channel induction furnace. While both use the principle of electromagnetic induction to heat and melt metal, their internal construction and operating characteristics make them suitable for distinctly different industrial applications.
The choice between an induction furnace is not a matter of which is superior, but which is correct for the task. The coreless furnace offers flexibility for melting diverse metals in batches, while the channel furnace excels at efficiently holding or continuously melting large volumes of a single alloy.

The Core Principle: How Induction Heats Metal
Before comparing the furnace types, it's essential to understand the shared technology that powers them. Induction furnaces operate without any external heating element or flame touching the metal.
The Role of Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a coil of copper wire through which a powerful alternating current (AC) is passed. This current generates a strong, rapidly reversing magnetic field in the center of the coil where the metal is located.
Generating Heat from Within
This magnetic field induces powerful secondary electric currents, known as eddy currents, directly within the metal charge. The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to dissipate as immense heat, melting the charge from the inside out. This process also creates a natural stirring action, ensuring a uniform temperature and homogenous alloy.
Deconstructing the Two Primary Furnace Types
The key difference between a coreless and a channel furnace lies in how they apply this inductive principle. One is essentially a crucible for batch work, while the other functions like a continuous-flow heater.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
In a coreless furnace, the metal charge is placed directly into a refractory-lined crucible. This crucible is surrounded by the water-cooled, current-carrying induction coil. There is no iron core connecting the coil and the metal.
This design functions like a simple pot. You can fill it with a cold, solid charge of metal, melt it completely, pour it out, and start over with a different alloy if needed.
Coreless Furnace Applications
Because of its ability to start from cold and be completely emptied, the coreless furnace is exceptionally versatile. It is the preferred choice for foundries that require batch melting, need to frequently change alloys, or work with high-melting-point metals like steel and stainless steel.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace uses an iron core to link the primary induction coil to a loop, or "channel," of molten metal. This loop of liquid metal પાણીacts as a single-turn secondary winding of a transformer.
Crucially, a channel furnace cannot start from a cold, solid charge. It requires a continuous loop of molten metal—a "heel"—to be present in the channel at all times to complete the circuit. Heat generated in this small channel circulates through the main bath of metal in the furnace.
Channel Furnace Applications
The channel furnace is not typically used for melting from a solid state. Instead, it is an extremely energy-efficient unit for holding large volumes of molten metal at a precise temperature. It is also used for superheating or for the continuous, high-volume melting of lower-melting-point alloys like copper, zinc, and aluminum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong furnace type leads to inefficiency and operational challenges. The decision hinges on understanding their fundamental trade-offs.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The coreless furnace is highly flexible. It can melt any compatible metal from a cold start and can be shut down and restarted easily. This versatility comes at a slightly lower electrical efficiency compared to a channel furnace operating under ideal conditions.
The channel furnace is highly efficient for holding and superheating, but it is inflexible. It must run continuously and is dedicated to a single alloy довго, as changing the metal would require a difficult and costly draining and pre-heating process.
Melting vs. Holding
Think of a coreless furnace as a primary melter. Its main job is to turn solid metal into liquid.
Think of a channel furnace as a primary holder. Its main job is to keep a large bath of already-liquid metal at the perfect temperature enerji-efficiently.
A Note on Refining
It is critical to note that neither furnace type offers significant metallurgical refining capabilities. While they are excellent for melting and alloying with minimal metal loss, they do not remove impurities from the base charge in the way that other processes, like an electric arc furnace, can.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The correct furnace is the one that aligns with your specific operational goals. Your choice should be based on your process requirements for volume, alloy type, and continuity.
- If your primary focus is versatile batch melting or frequent alloy changes: The coreless furnace is the correct choice for its ability to start from cold and be completely emptied.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of molten metal at a specific temperature: The channel furnace offers superior energy efficiency for this continuous task.
- If your primary focus is the high-volume, continuous melting of a single low-temp alloy: A channel furnace is often the most economical solution.
- If your primary focus is melting high-temperature metals like steel or specialty alloys: The coreless design is the industry standard due to its operational flexibility and material compatibility.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's inherent design with your production workflow is the key to achieving an efficient and cost-effective melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting, alloy changes | Holding, superheating, continuous melting |
| Starting State | Cold, solid charge | Requires molten metal 'heel' |
| Flexibility | High (easy alloy changes) | Low (dedicated to one alloy) |
| Efficiency | Good for melting | Excellent for holding |
| Ideal For | Steel, stainless steel, frequent alloy changes | Copper, zinc, aluminum, large-volume holding |
Struggling to choose the right induction furnace for your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect coreless or channel furnace to optimize your melting process, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















