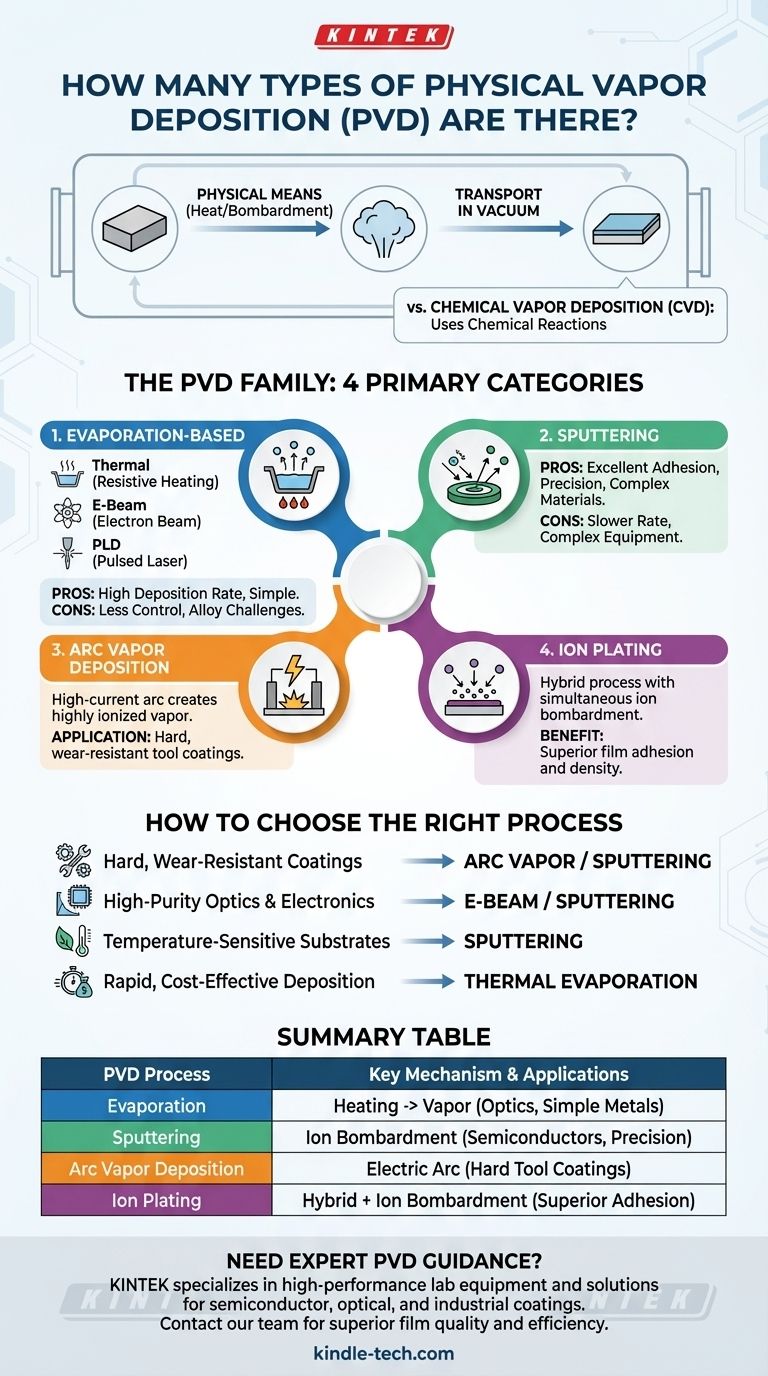
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) isn't a single technique but a family of processes. While there are many specific variations, they are generally classified into four primary categories: evaporation, sputtering, arc vapor deposition, and ion plating. The two most dominant and widely used of these are evaporation and sputtering.
The key to understanding Physical Vapor Deposition is to focus not on a specific number of types, but on the fundamental physical mechanism used to do the same thing: turn a solid material into a vapor, transport it through a vacuum, and condense it onto a substrate as a thin film.

The PVD Landscape: A High-Level View
Before diving into the types of PVD, it's crucial to distinguish it from its counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
PVD vs. CVD: A Quick Distinction
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) uses purely physical means—like heating or bombardment—to turn a solid source material into a vapor. There is no chemical reaction involved in creating the film.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), in contrast, introduces precursor gases into a chamber. These gases react or decompose on the substrate's surface to form the desired film. It is a chemical process.
The Core PVD Processes
Each category of PVD represents a different strategy for vaporizing the source material.
Evaporation-Based Deposition
This is conceptually the simplest PVD method. The process involves heating a source material in a vacuum chamber until its atoms boil off, travel through the vacuum, and condense onto the cooler substrate.
Thermal Evaporation
This is the most basic form, where the source material is heated by passing a high current through a resistive element, like a tungsten boat, that holds it.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
Instead of a simple heater, a high-energy beam of electrons is focused on the source material. This allows for the evaporation of materials with very high melting points and provides greater control over the process.
Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)
In this advanced technique, a high-power laser is aimed at the source material (the "target"). The intense energy of the laser instantly vaporizes the surface, creating a plume of material that deposits on the substrate.
Sputter Deposition (Sputtering)
Sputtering does not use heat to vaporize the material. Instead, it works like atomic-scale sandblasting.
The Sputtering Mechanism
A target made of the desired coating material is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically from an inert gas like Argon). This bombardment physically knocks atoms off the target's surface, which then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Key Characteristics
Sputtering is known for producing films with excellent adhesion and density. It also allows for the deposition of complex alloys and compounds with high precision.
Other Major PVD Methods
Arc Vapor Deposition
This method uses a high-current, low-voltage electric arc to vaporize the source material. The intense energy of the arc creates a highly ionized vapor, resulting in extremely hard and dense coatings. It is a common choice for protecting cutting tools.
Ion Plating
Ion plating is a hybrid process that enhances standard deposition. It combines either evaporation or sputtering with a simultaneous bombardment of the substrate by energetic ions. This bombardment improves film adhesion and density significantly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD process involves balancing speed, cost, and the desired properties of the final film. The most common decision is between evaporation and sputtering.
Evaporation: Speed and Simplicity
The primary advantage of evaporation is its high deposition rate. It can produce thick films relatively quickly and often involves simpler, less expensive equipment.
However, it offers less control over the film's structure and can struggle with depositing complex alloys, as materials with different boiling points will evaporate at different rates.
Sputtering: Precision and Adhesion
Sputtering's main strengths are its exceptional process control and film quality. It creates dense, uniform films with superior adhesion, making it ideal for applications requiring high performance and reliability, such as in semiconductors.
The trade-off is a slower deposition rate compared to evaporation, and the equipment is typically more complex and costly.
How to Choose the Right PVD Process
Your application's goal is the single most important factor in selecting a PVD method.
- If your primary focus is hard, wear-resistant coatings for tools: Arc vapor deposition or sputtering are the industry standards for their ability to create dense, durable films.
- If your primary focus is high-purity optical or electronic films: E-beam evaporation and sputtering are preferred for their precision and control over material properties.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates: Sputtering is often the better choice as it imparts less direct heat to the substrate compared to thermal evaporation.
- If your primary focus is rapid, cost-effective deposition of simpler metals: Basic thermal evaporation provides the highest speed for the lowest equipment complexity.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental mechanism—how the vapor is created—is the key to selecting the right PVD process for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| PVD Process | Key Mechanism | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation | Heating source material to vaporize | Optics, simple metal coatings |
| Sputtering | Bombarding target with ions to eject atoms | Semiconductors, high-precision electronics |
| Arc Vapor Deposition | Using electric arc to vaporize material | Hard, wear-resistant tool coatings |
| Ion Plating | Combining deposition with ion bombardment | Dense coatings requiring superior adhesion |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right PVD process for your lab's specific application? KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including PVD systems tailored for semiconductor, optical, and industrial coating needs. Our experts can help you choose the ideal solution for superior film quality, adhesion, and process efficiency. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures



















