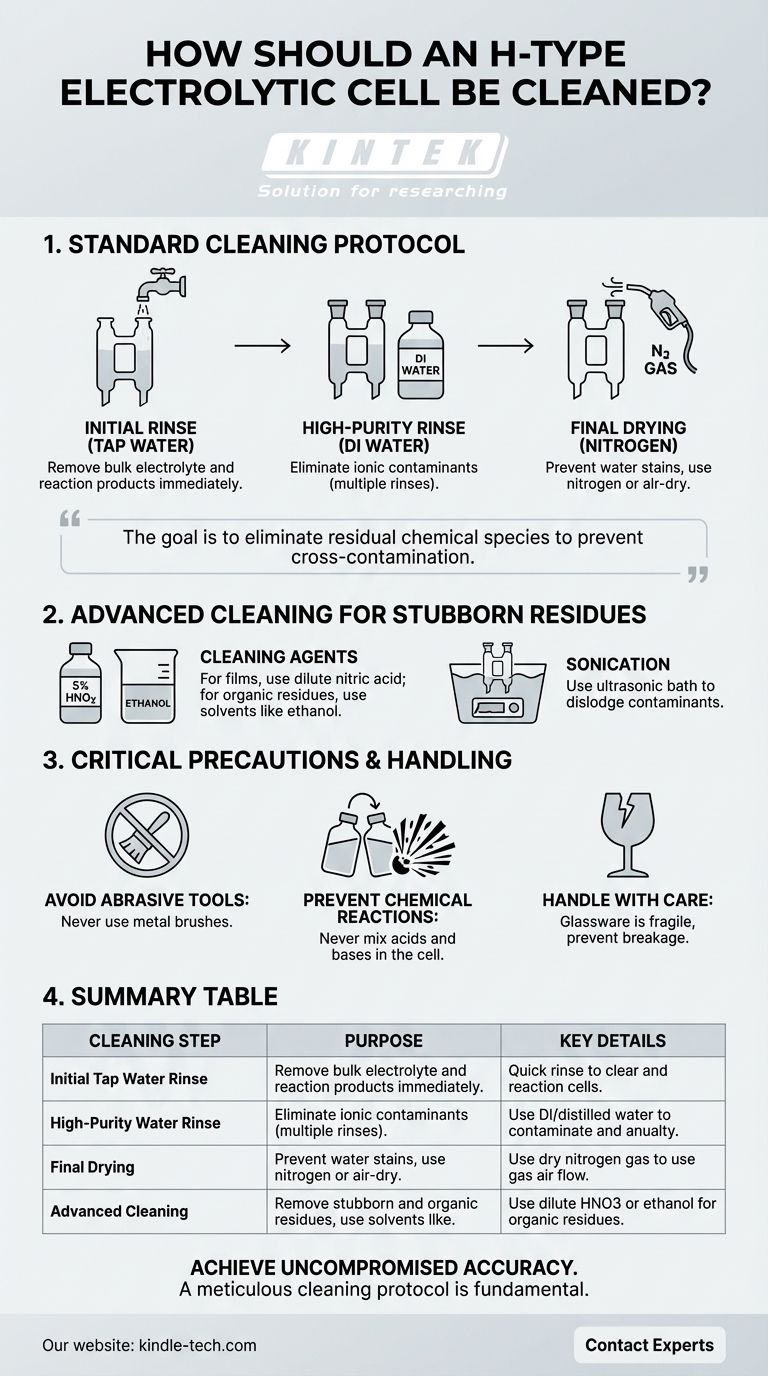
To properly clean an H-type electrolytic cell after use, you must follow a multi-step rinsing and drying process. Begin by rinsing all parts with tap water to remove the bulk of the electrolyte and reaction products, then perform multiple rinses with deionized or distilled water to eliminate any remaining ionic contaminants. For stubborn residue, a carefully selected cleaning agent may be used, followed by a final drying step, preferably with nitrogen gas, to prevent water stains and ensure the cell is ready for the next experiment.
The goal of cleaning an electrolytic cell is not just to make it look clean, but to eliminate any residual chemical species that could cross-contaminate and compromise the results of your subsequent experiments. A meticulous cleaning protocol is fundamental to achieving reproducible and accurate electrochemical data.

The Standard Post-Experiment Cleaning Protocol
This procedure should be performed immediately after each experiment to prevent residues from drying and adhering to the cell surfaces.
Step 1: Waste Removal and Initial Rinse
First, carefully remove the electrodes and the ion-exchange membrane. Properly dispose of the waste electrolyte and any solid products according to your lab's safety and environmental regulations.
Immediately rinse all components of the glass cell with tap water. This initial step is designed to wash away the majority of the residual salts and reaction byproducts quickly.
Step 2: High-Purity Rinse
After the tap water rinse, follow up with several thorough rinses using deionized (DI) or distilled water. This is a critical step.
Tap water contains various ions (like Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Cl⁻) that can adsorb onto the glass surface and interfere with future experiments. The high-purity water removes these ions, ensuring the cell is chemically inert.
Step 3: Final Drying
The final step is to dry the cell completely. The preferred method is to use a gentle stream of dry nitrogen gas.
This method is fast and prevents the formation of water spots, which are mineral or silica residues left behind as water evaporates. If nitrogen is unavailable, allowing the cell to air-dry in a dust-free environment is an alternative, though slower. An oven can be used, but ensure the temperature is moderate (e.g., 80°C) to avoid thermal stress on the glass.
Advanced Cleaning for Stubborn Residues
Sometimes, a simple water rinse is not enough to remove persistent films or adsorbed species.
Choosing the Right Cleaning Agent
If you notice stubborn dirt, you may need a more aggressive cleaning agent. The choice depends entirely on the nature of the residue from your experiment.
A common deep-cleaning procedure involves soaking the cell in dilute nitric acid (e.g., 5% HNO₃), followed by ultrasonic cleaning and copious rinsing with DI water. For organic residues, rinsing with a solvent like ethanol may be effective before the water rinses.
The Role of Sonication
For difficult-to-remove residues, immersing the cell in a cleaning solution within an ultrasonic bath can be highly effective. The cavitation bubbles gently scrub the glass surfaces, dislodging contaminants without causing mechanical damage. A typical cycle might be 15 minutes, repeated as necessary.
Critical Precautions and Handling
Mistakes during cleaning can be more damaging than the experiment itself. Adhering to these precautions is essential for safety and the longevity of your equipment.
Avoid Abrasive Tools
Never use metal brushes or other hard-bristled tools to clean the cell. The glass is easily scratched, and these micro-scratches can become sites for contamination and weaken the cell's structural integrity.
Prevent Dangerous Chemical Reactions
Be extremely cautious when using chemical cleaning agents. Never mix acids and bases (such as nitric acid and sodium hydroxide) directly within the cell, as this can trigger a dangerous and highly exothermic reaction.
Handle Glassware with Care
Remember that the H-type cell is made of glass and is fragile. Always handle it gently to prevent chipping or breakage, especially when inserting or removing electrodes and other components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Protocol
Your cleaning regimen should match the sensitivity of your work. A one-size-fits-all approach is not always optimal.
- If your primary focus is routine analysis: The standard protocol of tap water, followed by multiple DI water rinses and nitrogen drying, is sufficient for most applications.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity trace analysis: Incorporate a periodic deep clean with dilute acid and sonication to ensure no interfering species remain.
- If your experiments involve organic compounds: An initial rinse with a suitable solvent like ethanol or acetone may be necessary before proceeding with the standard water-based cleaning.
Ultimately, a consistent and thorough cleaning protocol is a cornerstone of reliable electrochemical research.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Step | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Tap Water Rinse | Remove bulk electrolyte and reaction products. | Quick rinse immediately after experiment. |
| High-Purity Water Rinse | Eliminate ionic contaminants (e.g., from tap water). | Use deionized (DI) or distilled water; multiple rinses. |
| Final Drying | Prevent water stains and contamination. | Use dry nitrogen gas or air-dry in a dust-free environment. |
| Advanced Cleaning (if needed) | Remove stubborn residues (e.g., films, adsorbed species). | Use dilute nitric acid (5% HNO₃) or ethanol, often with sonication. |
Achieve Uncompromised Accuracy in Your Lab
A meticulous cleaning protocol is fundamental to the integrity of your electrochemical research. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable electrolytic cells and precision cleaning tools, to support your laboratory's needs.
Ensure your experiments are never compromised by contamination. Contact our experts today to find the right equipment and consumables for your specific application and to learn more about best practices for maintaining your lab instruments.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- What are the standard opening specifications for an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Asymmetrical Ports for Precise Electrochemistry
- How should failures or malfunctions of an H-type electrolytic cell be handled? A Guide to Safe and Effective Troubleshooting
- What preparation steps are needed before starting an experiment with an H-type electrolytic cell? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Results
- How should the H-type electrolytic cell be stored when not in use? Expert Storage & Maintenance Guide
- What should be observed during an experiment with the H-type electrolytic cell? Key Monitoring for Precise Results