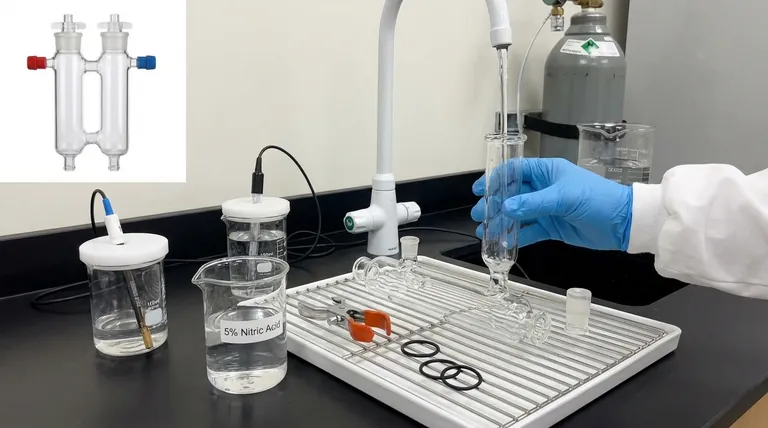
To properly clean an H-type electrolytic cell, you must follow a multi-stage process designed to remove all organic and inorganic contaminants. For a new cell, this typically involves an initial rinse, a prolonged soak in a dilute acid like 5% nitric acid, multiple ultrasonic cleanings with deionized water, and thorough drying with an oven or inert gas. This rigorous procedure is not just about cleanliness; it's the foundation for achieving accurate and reproducible electrochemical results.
The core principle is that an electrolytic cell is a precision instrument. Meticulous cleaning is not a preliminary chore but a critical step in the experiment itself, directly impacting the validity and reliability of your data by eliminating unwanted variables.

Why Meticulous Cleaning is Non-Negotiable
The entire purpose of using an H-type cell is to isolate the anode and cathode chambers. Any contamination can compromise this isolation, introduce side reactions, or foul electrode surfaces, rendering your results meaningless.
The Problem with New Cells
A brand-new glass cell may appear clean, but it often carries residues from the manufacturing and packaging process. These can include machine oils, releasing agents, and fine particulate dust that will interfere with your experiment. An acid soak is essential to strip away these initial contaminants.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
For a cell that has been used before, the primary risk is cross-contamination from previous experiments. Even trace amounts of a prior electrolyte, analyte, or reaction product can dramatically alter the outcome of your current work. Simple rinsing is rarely sufficient to remove adsorbed species from the glass walls or electrode surfaces.
The Standard Protocol for a New Cell
This procedure ensures your cell is in an ideal state for sensitive electrochemical measurements. Always handle glass components with care to prevent breakage.
Step 1: Initial Inspection
Before any cleaning, thoroughly inspect every component. Check the main glass body for any cracks or fractures. Ensure the electrodes are clean and undamaged, and verify that the ion-exchange membrane is intact, with no visible tears or signs of aging.
Step 2: The Acid Soak
Disassemble the cell. Place the glass components in a container and submerge them completely in a 5% nitric acid (HNO₃) solution for at least two hours. This step is crucial for digesting organic residues and leaching out metallic impurities from the glass surface.
Step 3: Ultrasonic Cleaning and Rinsing
After the acid soak, rinse the components with tap water, followed by a thorough rinse with deionized (DI) water. Then, place the components in a beaker of fresh DI water and sonicate for 15 minutes. Discard the water, refill with fresh DI water, and repeat the sonication process two more times for a total of three cycles.
Step 4: Final Drying
To prevent water spots and ensure no residual moisture, the cell must be dried completely. You can either place the components in an oven at 80°C for at least one hour or blow-dry them with a stream of clean, dry nitrogen gas.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
Proper preparation goes beyond the cleaning agent. How you handle the components is just as important.
Handling the Ion-Exchange Membrane
The ion-exchange membrane (e.g., Nafion) is a delicate and critical component. It should not be subjected to the same aggressive cleaning as the glass body. Its cleaning and conditioning protocol is specific to its material and should be performed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Cleaning Between Experiments
The intensive acid soak protocol is typically only necessary for a new cell or one that is heavily contaminated. For routine cleaning between experiments, a simpler process is often sufficient. Thoroughly rinse all parts with DI water and use a suitable solvent if you need to remove a specific, known residue from the previous experiment.
Electrode-Specific Cleaning
Remember that your electrodes (e.g., platinum, glassy carbon) have their own specific cleaning and polishing procedures. These must be performed separately from the cell body cleaning and are essential for maintaining a well-defined, active electrode surface area.
Applying This to Your Experiment
Your cleaning strategy should match the demands of your work.
- If you are using a brand-new cell: You must perform the full acid soak and ultrasonic cleaning protocol to establish a clean baseline.
- If you are running routine daily experiments with similar chemistry: A thorough triple rinse with DI water and proper drying may be sufficient between runs.
- If you suspect contamination or are starting a new type of experiment: Revert to the full, intensive cleaning protocol to eliminate any risk of cross-contamination.
Ultimately, your preparation of the electrolytic cell is the first and most critical step in ensuring the integrity of your electrochemical data.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Inspection | Check for cracks, damage | Ensure cell integrity |
| 2. Acid Soak | Submerge in 5% nitric acid for 2+ hours | Remove organic/inorganic residues |
| 3. Ultrasonic Cleaning | Three 15-min cycles in deionized water | Eliminate trace contaminants |
| 4. Final Drying | Oven (80°C) or nitrogen gas stream | Prevent moisture and water spots |
Ready to achieve precise and reproducible electrochemical results? The foundation of any successful experiment is a meticulously clean cell. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for demanding laboratory environments. Our expertise ensures your H-type electrolytic cells and other precision instruments are maintained to the highest standards. Don't let contamination compromise your data—contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- How should the H-type electrolytic cell be stored when not in use? Expert Storage & Maintenance Guide
- What are the standard opening specifications for an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Asymmetrical Ports for Precise Electrochemistry
- What is the function of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Master Precise Reaction Control
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What are the key safety operation guidelines for using the H-type electrolytic cell? Best Practices for Your Lab