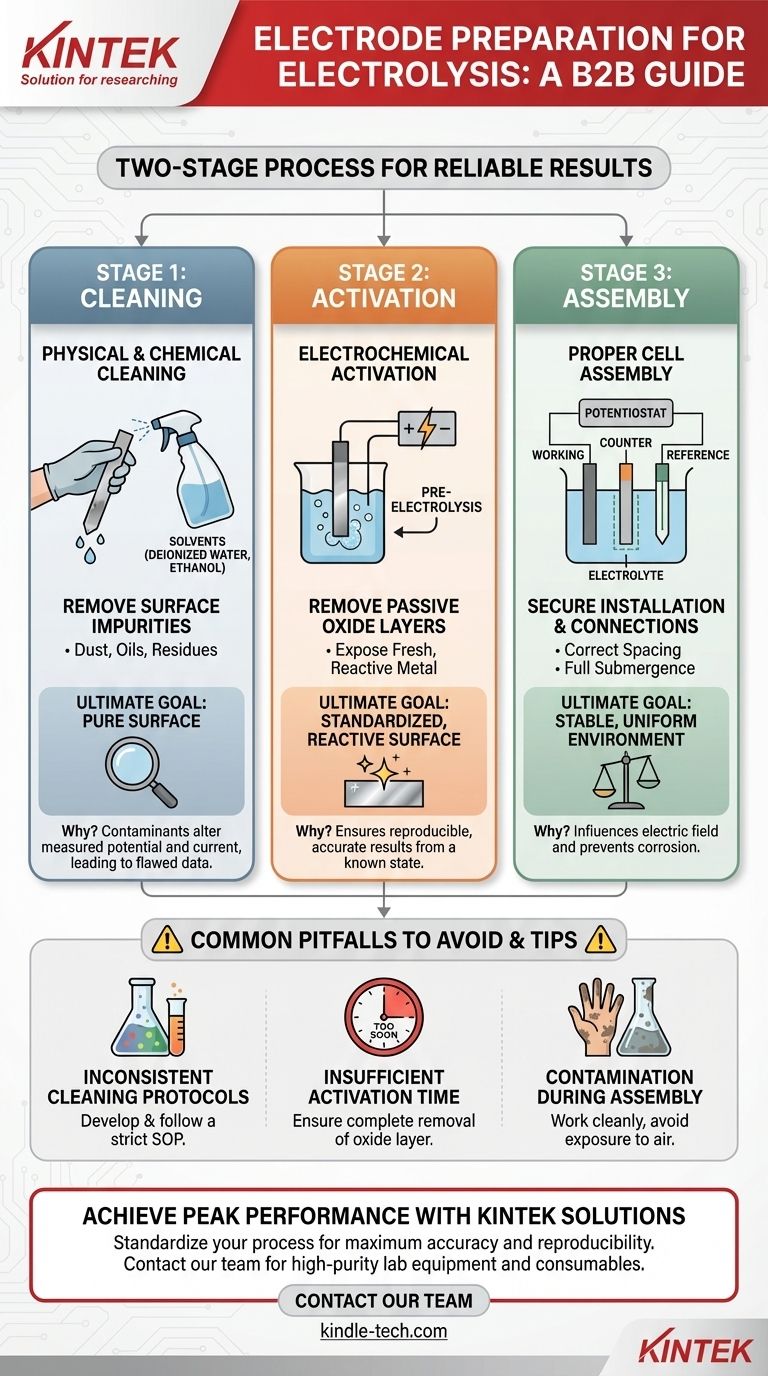
To properly prepare electrodes, you must perform a two-stage process. First, physically and chemically clean the electrode surfaces to remove any impurities using solvents like deionized water or ethanol. Second, electrochemically activate the electrodes by running a brief pre-electrolysis in the electrolyte solution to remove any passive oxide layers and create a reactive surface.
The ultimate goal of electrode preparation is not just cleanliness, but achieving a standardized and electrochemically active surface. This ensures your experimental results are accurate, repeatable, and reflect the true behavior of your system, not surface contamination.
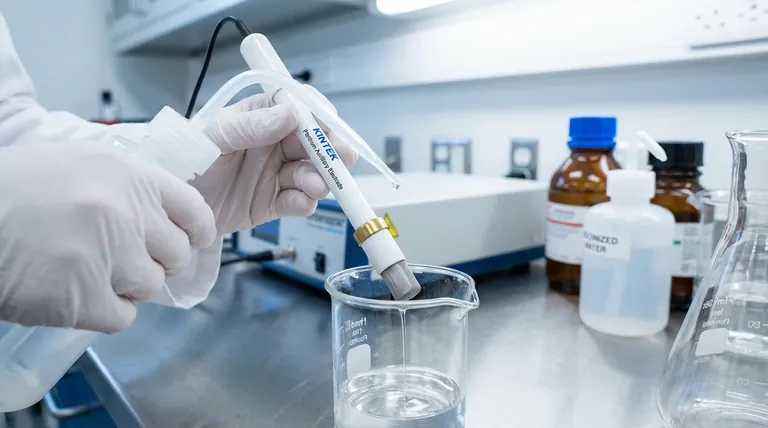

The Foundation: Physical and Chemical Cleaning
Proper preparation begins long before the electrode enters the cell. This initial phase is about removing any external contaminants that could interfere with your measurements.
Removing Surface Impurities
Your electrodes can accumulate dust, oils, or residues from previous experiments. These impurities can block active sites or introduce unwanted side reactions.
A simple rinse with a high-purity solvent is the first line of defense. Deionized water is excellent for removing salts and polar contaminants, while ethanol is effective for organic residues and oils.
Why a Pure Surface is Non-Negotiable
Contaminants can act as catalysts, poisons, or simply inert barriers. Their presence can drastically alter the measured potential and current, leading to flawed data and incorrect conclusions about your reaction's kinetics.
The Critical Step: Electrochemical Activation
Once the electrode is physically clean, it must be made electrochemically ready. Many metals naturally form a thin, non-conductive oxide layer when exposed to air. Activation removes this passive layer.
Understanding Pre-Electrolysis
Pre-electrolysis is the process of running your experiment for a short period before you begin collecting data. This is typically done in the same electrolyte you will use for the main experiment.
This initial run effectively "wakes up" the electrode. By applying a potential, you can reduce or oxidize the passive surface layer, exposing the fresh, highly reactive metal underneath.
The Goal of an Active Surface
An inactive or partially active electrode will yield sluggish results and a higher-than-expected overpotential. By standardizing the activation step, you ensure that every experiment begins from the same known, reactive state, which is the cornerstone of reproducible electrochemistry.
Proper Cell Assembly
The final preparation steps involve correctly assembling the electrolysis cell to ensure a stable and uniform electrochemical environment.
Electrode Installation and Spacing
Install the electrodes securely in the reaction vessel. Pay close attention to the spacing between the working electrode, counter electrode, and reference electrode, as this influences the electric field and potential distribution in the cell.
Connecting to the Workstation
Connect the electrode wires to the correct terminals on your potentiostat or electrochemical workstation. Mismatched connections are a common source of error.
Submerging in Electrolyte
Add the electrolyte solution, ensuring the active surfaces of all electrodes are fully submerged. Crucially, the connecting rods or clips above the electrode surface should remain out of the electrolyte to prevent corrosion and unwanted side reactions.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with a defined procedure, small mistakes can compromise your results. Being aware of these common pitfalls is essential for achieving high-quality data.
Inconsistent Cleaning Protocols
Using different solvents, cleaning times, or methods between experiments will introduce variability. The key to reproducibility is having a standardized operating procedure (SOP) for preparation that you follow meticulously every time.
Insufficient Activation Time
Ending the pre-electrolysis step too early can leave patches of the passive oxide layer intact. This results in a non-uniform surface and data that is not representative of the material's true activity.
Contamination During Assembly
Using dirty glassware, impure electrolyte, or exposing the cleaned electrodes to the open air for too long can re-contaminate the surface you just prepared. Work cleanly and efficiently once the cleaning process has begun.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your preparation strategy should align with your experimental objectives.
- If your primary focus is reproducibility: Develop a strict, step-by-step protocol for both cleaning and activation and adhere to it without deviation for every single trial.
- If your primary focus is accuracy and kinetic studies: Place extra emphasis on the pre-electrolysis step to guarantee a fully active, pristine surface that provides a true measure of your reaction's performance.
Ultimately, rigorous and consistent electrode preparation is the foundation upon which all reliable electrochemical data is built.
Summary Table:
| Preparation Step | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Physical & Chemical Cleaning | Rinse with solvents (e.g., deionized water, ethanol) | Remove surface impurities like dust, oils, and residues. |
| Electrochemical Activation | Perform pre-electrolysis in the electrolyte | Remove passive oxide layers and create a standardized, reactive surface. |
| Cell Assembly | Correctly install, space, and connect electrodes | Ensure a stable and uniform electrochemical environment for testing. |
Achieve Peak Performance in Your Electrochemical Experiments
Proper electrode preparation is the foundation of reliable data. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables you need for every step—from cleaning solvents to electrochemical workstations.
Let our experts help you standardize your process for maximum accuracy and reproducibility. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
- Li-Air Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a Platinum (Pt) electrode for zirconium testing? Ensure High-Precision Data Integrity
- Why is platinum typically selected as the auxiliary electrode for electrochemical testing of oxazoline inhibitors?
- Why is a platinum wire (PtW) counter electrode preferred for cathode LSV tests? Ensure High-Precision Research
- Why is platinum wire selected as the auxiliary electrode? Achieve High-Precision Corrosion Data with Inert Electrodes
- What is the benefit of using a platinized platinum wire as a counter electrode? Optimize Operando Study Precision



















