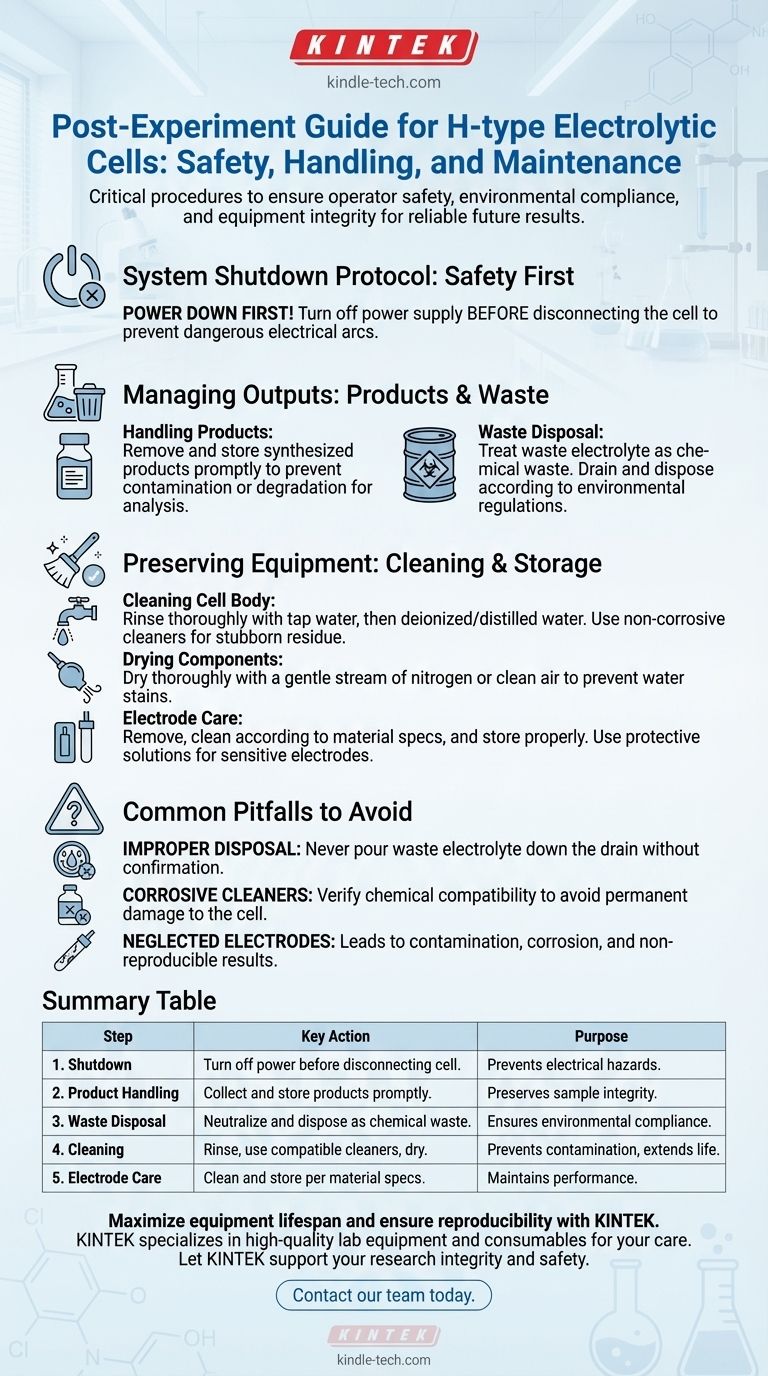
Proper post-experiment handling is a critical final step for any work involving an H-type electrolytic cell. Once the experiment concludes, you must first turn off the power supply before disconnecting the cell. The products should be carefully removed and stored for analysis, while the waste liquid must be collected and disposed of in strict accordance with environmental safety regulations.
The post-experiment phase is not merely about cleanup; it is a crucial procedure that ensures operator safety, maintains environmental compliance, and preserves the integrity of your equipment for future, reliable results.

The Systematic Shutdown Protocol: Safety First
Before handling any materials, the first priority is to safely power down the system. This non-negotiable step prevents serious electrical hazards.
Disconnecting Power Correctly
The power supply must be turned off before disconnecting the electrolytic cell. Attempting to disconnect the cell while the power is still active can generate dangerous electrical arcs, posing a significant safety risk.
Managing Experimental Outputs: Products and Waste
Once the system is safely powered down, you can proceed to handle the materials generated during the experiment. This involves a clear distinction between valuable products and hazardous waste.
Handling and Storing Products
If the goal of your experiment was to synthesize a product, it must be removed from the cell promptly. Proper collection and storage are essential to prevent contamination or degradation before subsequent processing or analysis.
Neutralizing and Disposing of Waste Electrolyte
The remaining waste liquid, or electrolyte, must be treated as chemical waste. It should be drained from the cell and handled according to your institution's specific environmental protection and waste disposal regulations to prevent pollution.
Preserving Your Equipment: Cleaning and Storage
Thorough cleaning after each use is vital for the longevity of the H-type cell and the validity of future experiments. Contamination from previous runs is a common source of error.
Cleaning the Cell Body
Begin by rinsing all parts of the cell with tap water to remove the bulk of the residual chemicals. Follow this with multiple rinses using deionized or distilled water. For stubborn residue, use a cleaning agent that is effective but confirmed to be non-corrosive to the cell's materials.
Drying the Components
After rinsing, dry the cell's interior thoroughly. A gentle stream of nitrogen or clean, dry air is ideal for this purpose, as it prevents water stains or residue that could interfere with future experiments.
Caring for the Electrodes
Electrodes are often the most sensitive and expensive components. Remove them carefully, clean them according to their specific material requirements, and store them properly. Electrodes susceptible to oxidation or corrosion may require special protective measures, such as immersion in a designated protective solution.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in the post-experiment phase can be costly, compromising safety, results, and equipment.
Improper Waste Disposal
Never pour waste electrolyte down the drain unless you have confirmed it is permissible by your organization's safety protocols. Improper disposal can cause significant environmental harm and violate regulations.
Using Corrosive Cleaning Agents
Using the wrong cleaner can permanently damage the cell, especially if it's made of glass or specialized polymers. Always verify chemical compatibility before cleaning.
Neglecting Electrode Care
Improperly cleaned or stored electrodes can become contaminated or corroded, leading to inaccurate and non-reproducible results in subsequent experiments. This is a primary cause of experimental failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your post-experiment workflow should align with your overarching priorities.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: Always disconnect power before handling the cell and treat all waste liquid according to established environmental protocols.
- If your primary focus is data integrity: Carefully collect and store all products immediately to prevent degradation or contamination before analysis.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Implement a rigorous cleaning and drying protocol for both the cell and the electrodes after every single use.
A disciplined approach to post-experiment handling protects your safety, your results, and your investment.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Shutdown | Turn off power before disconnecting cell. | Prevents electrical hazards. |
| 2. Product Handling | Collect and store products promptly. | Preserves sample integrity for analysis. |
| 3. Waste Disposal | Neutralize and dispose of electrolyte as chemical waste. | Ensures environmental compliance. |
| 4. Cleaning | Rinse with water, use compatible cleaners, dry thoroughly. | Prevents contamination, extends equipment life. |
| 5. Electrode Care | Clean and store electrodes according to material specs. | Maintains performance and reproducibility. |
Maximize the lifespan of your lab equipment and ensure experimental reproducibility with KINTEK.
Proper handling and maintenance are crucial for accurate results and laboratory safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrolytic cells and the necessary tools for their care. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and establish best practices for your specific applications.
Let KINTEK support your research integrity and operational safety. Contact our team today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What should be observed during an experiment with the H-type electrolytic cell? Key Monitoring for Precise Results
- What preparation steps are needed before starting an experiment with an H-type electrolytic cell? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Results
- What is the function of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Master Precise Reaction Control
- What are the key safety operation guidelines for using the H-type electrolytic cell? Best Practices for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control