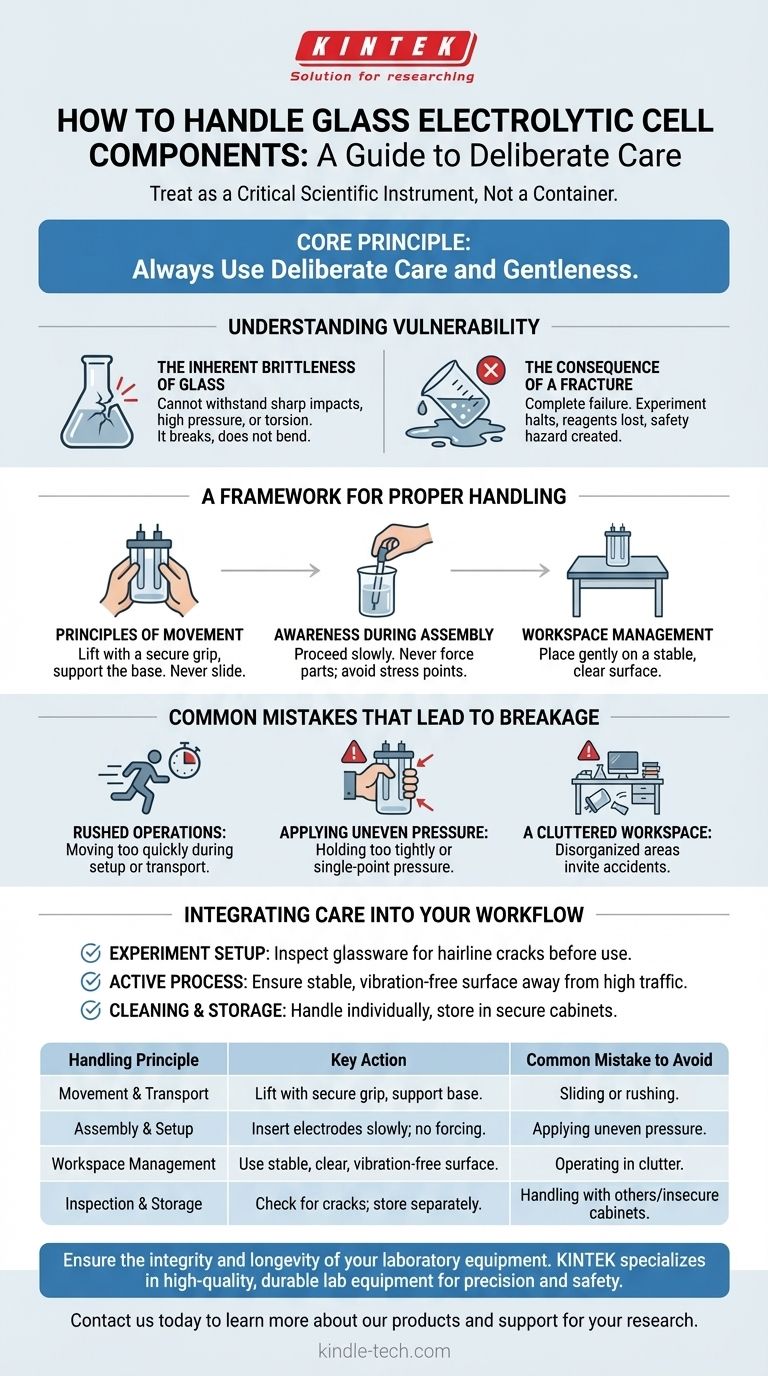
To handle the glass components of an electrolytic cell correctly, you must use deliberate care and gentleness at all times. The cell body is made of glass, an inherently fragile material. Any breakage will compromise your experiment, result in the loss of reagents, and create a safety hazard.
The core principle is to treat the glass cell not as a simple container, but as a critical scientific instrument. Proper handling is essential for preserving its structural integrity, which is fundamental to experimental success and laboratory safety.

Understanding the Core Vulnerability: Material Fragility
An electrolytic cell is a precise system composed of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. The glass body contains these components, creating the controlled environment necessary for the electrochemical reaction to occur. Its physical integrity is non-negotiable.
The Inherent Brittleness of Glass
The primary reason for cautious handling is the material itself. Glass is brittle, meaning it cannot withstand sharp impacts, high pressure, or sudden torsion without fracturing.
Unlike more durable materials, glass does not bend or deform under stress; it simply breaks. This is why a consistent, gentle approach is required.
The Consequence of a Fracture
A crack or break is more than just physical damage. It represents a complete failure of the apparatus.
A fracture will cause the electrolyte to leak, immediately halting the experiment. This compromises the closed system required for electrolysis, invalidates your results, and can lead to chemical spills.
A Framework for Proper Handling
Adopting a methodical approach to handling the glass cell will dramatically reduce the risk of breakage. The core instruction from all procedural guides is to be gentle and cautious.
Principles of Movement
Always lift and carry the cell with a secure grip, supporting it from the base whenever possible. Never slide it across a benchtop, as this can catch on an uneven surface and cause it to tip or fracture.
When setting the cell down, do so slowly and deliberately. Place it gently onto a stable, clear surface.
Awareness During Assembly
When inserting electrodes or other components into the cell, proceed slowly. Never force parts that do not fit easily. Applying undue pressure creates stress points in the glass that can easily lead to a fracture.
Common Mistakes That Lead to Breakage
Accidents are almost always preventable. Understanding the common failure points helps reinforce the need for a deliberate workflow.
Rushed Operations
Moving too quickly is the most common cause of laboratory accidents. Rushing during setup, transport, or cleaning increases the likelihood of bumping the cell against a hard surface or dropping it.
Applying Uneven Pressure
Holding the cell too tightly or applying pressure to a single point can concentrate force and cause the glass to break. Always use a firm but gentle, distributed grip.
A Cluttered Workspace
Placing the cell in a disorganized or cluttered area invites accidents. Ensure the workspace is clear of other equipment or materials that could be knocked into the cell.
Integrating Care into Your Workflow
Building habits around careful handling ensures the longevity of your equipment and the reliability of your data. Your approach should change based on the task at hand.
- If you are setting up an experiment: Always inspect the glassware for hairline cracks or chips before adding any reagents.
- If you are actively running a process: Ensure the cell is on a stable, vibration-free surface away from high-traffic areas of the lab.
- If you are cleaning or storing the cell: Handle it individually, not with other glassware, and store it in a secure cabinet where it cannot be jostled.
Ultimately, treating the electrolytic cell with deliberate caution is the most effective strategy for protecting your investment and ensuring successful outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Handling Principle | Key Action | Common Mistake to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Movement & Transport | Lift with a secure grip, supporting the base. | Sliding or rushing, which can cause tipping. |
| Assembly & Setup | Insert electrodes slowly; never force components. | Applying uneven pressure, creating stress points. |
| Workspace Management | Use a stable, clear, and vibration-free surface. | Operating in a cluttered or high-traffic area. |
| Inspection & Storage | Check for cracks before use; store separately. | Handling with other glassware or in insecure cabinets. |
Ensure the integrity and longevity of your laboratory equipment. Proper handling is crucial for successful experiments. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality, durable lab equipment and consumables, including electrolytic cells, designed for precision and safety.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can support your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- How can leaks be prevented when using a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure a Reliable and Safe Electrochemical Setup
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the proper way to handle a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Accurate and Safe Electrochemical Experiments
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be operated during an experiment? Master Precise Control for Reliable Results