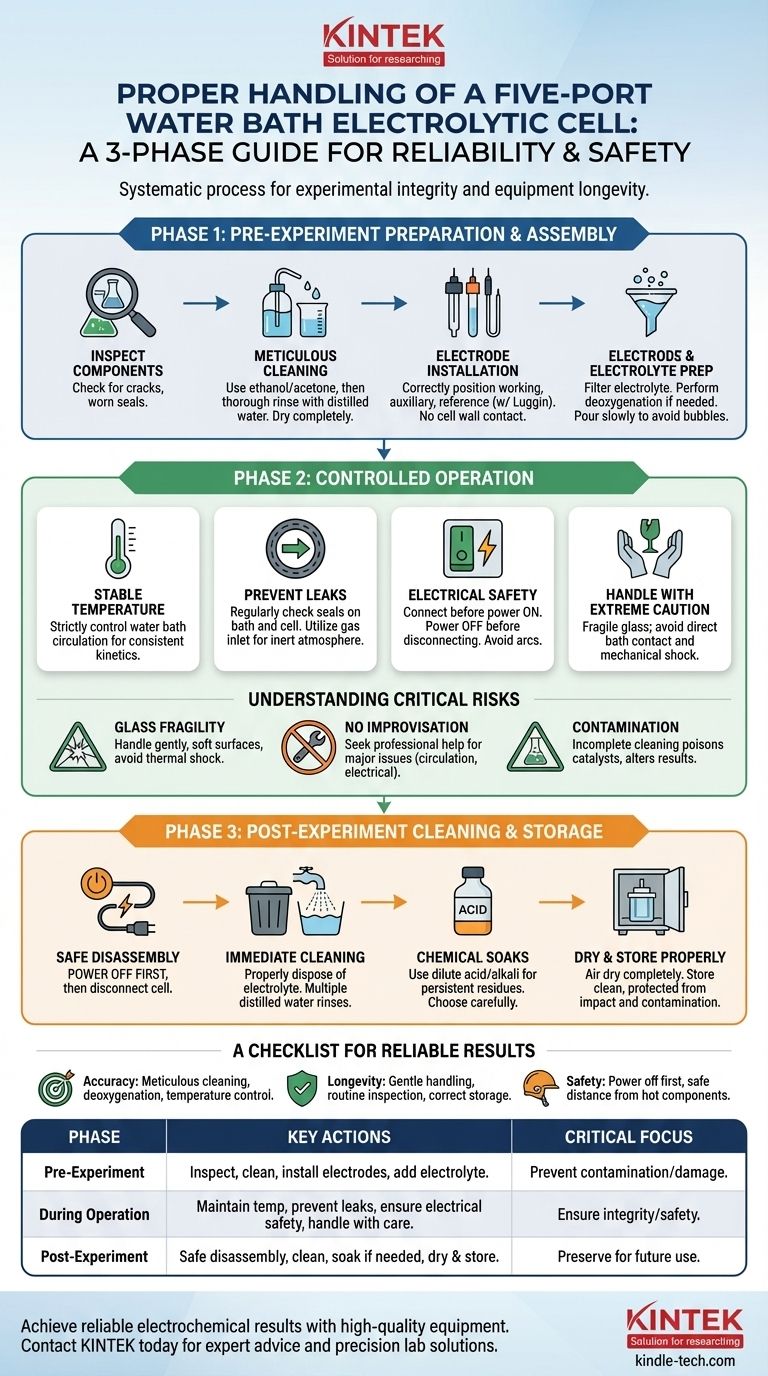
Properly handling a five-port water bath electrolytic cell is a systematic process focused on maintaining experimental integrity and ensuring safety. The procedure is divided into three critical phases: meticulous pre-experiment preparation, controlled operation, and thorough post-experiment cleaning and storage. Each step is designed to protect the fragile glass components, prevent contamination, and ensure accurate, repeatable results.
An electrolytic cell is not merely glassware; it is a precision instrument. Treating it as such, by following a strict protocol for preparation, operation, and maintenance, is the single most important factor in achieving reliable electrochemical data and ensuring the equipment's longevity.
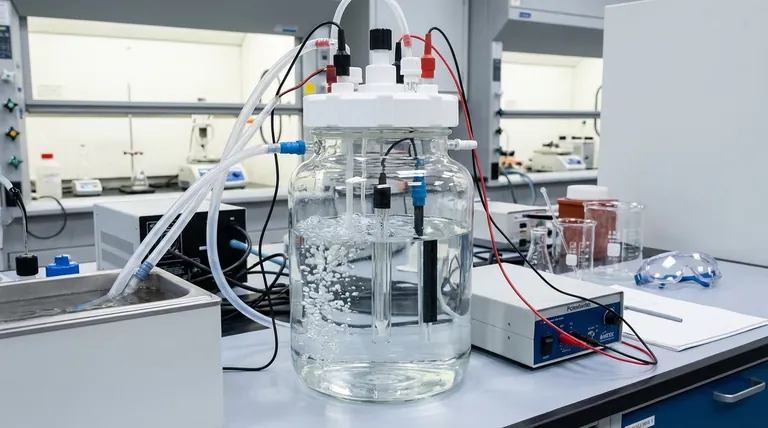

Phase 1: Pre-Experiment Preparation and Assembly
Before any experiment can begin, the cell must be inspected and assembled with meticulous care. This foundational stage prevents a majority of common experimental failures.
Inspect All Components for Damage
Before assembly, carefully examine every part of the cell. Look for hairline cracks in the glass body and check that all seals are pliable and free from signs of aging or degradation.
Perform Meticulous Cleaning
Start by cleaning the cell body with a suitable solvent, such as ethanol or acetone, to remove organic residues. Follow this with a thorough rinse using distilled or deionized water to remove any remaining solvent, then allow it to dry completely.
Ensure Correct Electrode Installation
Install the working, auxiliary, and reference electrodes according to your experimental design. Ensure they are positioned correctly and securely connected, taking care that no electrode touches the cell wall. The reference electrode can be used with a Luggin capillary to minimize iR drop.
Prepare and Add the Electrolyte
The electrolyte should be filtered to remove any particulate matter. If your experiment is sensitive to oxygen, perform deoxygenation before introducing the solution into the cell. Pour the prepared electrolyte slowly down the side of the cell to prevent splashing and bubble formation.
Phase 2: Controlled Operation
During the experiment, your focus shifts to maintaining stable conditions and monitoring the system's integrity.
Maintain Stable Temperature
Strictly control the water bath circulation system to maintain the desired temperature. Fluctuations can significantly impact reaction kinetics and alter your results.
Prevent Leaks
Regularly check the seals on both the water bath and the electrolytic cell itself. Water or gas leaks can compromise your experiment, damage equipment, and create safety hazards. The cell is designed to be equipped with a gas inlet for purging or maintaining an inert atmosphere.
Ensure Electrical Safety
Always connect the cell to the power source or potentiostat before turning the power on. Conversely, always turn the power off before disconnecting anything. This prevents electrical arcs that can damage equipment or cause injury.
Handle with Extreme Caution
Remember that the entire apparatus is made of glass and is fragile. Avoid direct contact with the high-temperature water bath to prevent burns and always handle the cell gently.
Understanding the Critical Risks
Proper handling is fundamentally about risk mitigation. Ignoring these points can invalidate results, destroy equipment, and compromise lab safety.
The Inherent Fragility of Glass
This cannot be overstated. All glass components must be handled gently and set down on soft surfaces. Avoid any mechanical shock or rapid, extreme temperature changes that could cause the glass to fracture.
The Danger of Improvisation
If you encounter a significant problem, do not attempt to fix it yourself. Issues like a malfunctioning circulation system, damaged electrical connection points, or severely compromised seals require professional attention.
The Consequences of Contamination
Improper or incomplete cleaning introduces contaminants that can poison catalysts, create unwanted side reactions, or alter the electrochemical behavior of your system, rendering your data useless.
Phase 3: Post-Experiment Cleaning and Storage
The experiment is not over until the equipment is properly cleaned and stored. This final phase ensures the cell is ready for future use and preserves its lifespan.
Initiate Safe Disassembly
As with setup, ensure the power source is turned off before disconnecting the electrolytic cell. This is the first and most critical step in disassembly.
Perform Immediate and Thorough Cleaning
Promptly and safely discard the used electrolyte according to your lab's disposal protocols. Immediately rinse the cell multiple times with distilled water to remove residual salts and reaction products.
Use Chemical Soaks When Necessary
If residues persist, a soak in a suitable dilute acid or alkali solution may be required for thorough cleaning. Choose the cleaning reagent carefully to avoid corroding any part of the cell or the electrodes.
Dry and Store Properly
After a final rinse with distilled water, allow the cell to dry completely. Store the clean cell and all electrodes in a dry, clean, and protected location where they will not be subject to impact or contamination.
A Checklist for Reliable Results
Your approach to handling the cell should align with your primary objective for the experiment.
- If your primary focus is experimental accuracy: Prioritize meticulous cleaning protocols, proper electrolyte deoxygenation, and precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Emphasize gentle handling, routine inspection for micro-cracks or seal wear, and correct storage procedures.
- If your primary focus is personal safety: Always follow the "power off first" rule for any connection changes and maintain a safe distance from high-temperature components.
Adhering to this disciplined methodology transforms a fragile piece of glassware into a reliable instrument for scientific discovery.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Key Actions | Critical Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Experiment | Inspect components, clean meticulously, install electrodes, add prepared electrolyte. | Prevent contamination and damage. |
| During Operation | Maintain stable temperature, prevent leaks, ensure electrical safety, handle with care. | Ensure experimental integrity and user safety. |
| Post-Experiment | Safe disassembly, immediate cleaning, chemical soaks if needed, proper drying and storage. | Preserve equipment for future use. |
Achieve reliable and repeatable electrochemical results with the right equipment and support. Proper handling is crucial, but it starts with a high-quality electrolytic cell. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving the exacting needs of electrochemical laboratories. Our range of durable electrolytic cells and expert support ensures your research is built on a foundation of quality and reliability.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect electrolytic cell for your application and get expert advice on maintenance and best practices.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
People Also Ask
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis
- How can leaks be prevented when using a five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Ensure a Reliable and Safe Electrochemical Setup
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be operated during an experiment? Master Precise Control for Reliable Results
- How can contamination be avoided during experiments with the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the 3-Pillar Protocol
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results