Under the right conditions, a brazed stainless steel joint is exceptionally strong. In many cases, a properly designed and executed braze joint will be stronger than the stainless steel base metal itself, meaning the parent material will fail before the joint does.
The strength of a brazed stainless steel joint is not a fixed value, but a direct result of process control. Success depends entirely on overcoming the material's natural oxide layer to create a perfect metallurgical bond, and failure to do so will result in a dramatically weaker joint.
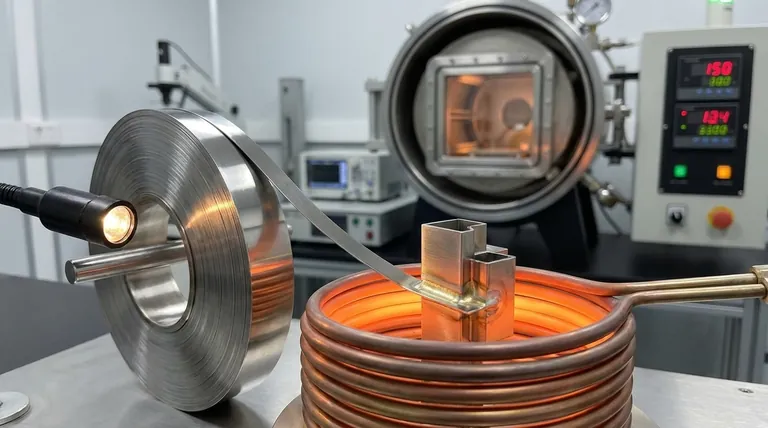
The Source of Strength in a Brazed Joint
The high strength of a brazed connection comes from fundamental metallurgical principles, not from simple adhesion.
Beyond a Simple "Glue"
Brazing creates a metallurgical bond. The molten filler metal alloys with the surface of the stainless steel, forming a new, composite material at the interface that is incredibly strong and continuous.
The Power of Capillary Action
A correctly designed joint has a very small, uniform gap between the parts. When the filler metal melts, it is drawn into this gap by capillary action. This ensures the entire joint area is filled, leaving no voids or gaps that could become stress points and initiate a failure.
Why the Joint Can Exceed Base Metal Strength
When the filler metal solidifies within this thin joint clearance, its mechanical properties are enhanced. The surrounding, stronger base metal constrains the filler, preventing it from deforming easily and significantly increasing the overall tensile strength of the assembly at the joint area.
The Critical Challenge: The Stainless Steel Oxide Layer
The primary obstacle to achieving a strong braze on stainless steel is its own protective nature.
What is the Passive Layer?
Stainless steel is "stainless" because of a thin, invisible, and chemically inert layer of chromium oxide on its surface. This "passive layer" instantly re-forms in the presence of oxygen and is what prevents rust and corrosion.
How Oxides Inhibit Bonding
This same protective oxide layer prevents the molten filler metal from "wetting" or making direct contact with the parent steel underneath. A brazing filler cannot bond to an oxide; it can only bond to clean, pure metal.
Methods for Overcoming the Oxide Layer
To create a strong joint, this oxide layer must be removed and prevented from re-forming during the high-heat process. The most common and effective method for high-strength applications is vacuum brazing. By performing the process in a high vacuum, oxygen is removed, which allows the oxide layer to be eliminated and prevents it from re-forming.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While strong, brazing stainless steel is a sensitive process with specific risks that must be managed.
Risk of Stress Cracking
Certain grades of stainless steel, particularly austenitic types (like 304 or 316), are susceptible to stress corrosion cracking during the brazing cycle. This risk is especially high when using filler metals containing zinc, such as copper-zinc alloys. Careful selection of the filler metal is critical.
High Process Sensitivity
The final strength is not guaranteed; it is earned. It depends on many variables: correct joint design, surface flatness, heating and cooling rates, and brazing temperature. A lack of precise control over any of these factors will compromise the integrity of the joint.
Not a Replacement for Welding
Brazing operates at a lower temperature than welding, which is a major advantage for reducing part distortion and thermal stress. However, it is a different process. Welding fuses the base metals directly, while brazing joins them with a separate filler metal. The choice depends on the specific application, geometry, and materials being joined.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these principles to guide your decision-making process for joining stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and reliability: Use a meticulously controlled process like vacuum brazing with a nickel-based filler alloy and ensure your joint design has tight, uniform clearances.
- If your primary focus is minimizing heat distortion on a complex assembly: Brazing is an excellent choice due to its lower process temperatures, but proper component fixturing and filler metal selection are paramount.
- If your primary focus is joining stainless steel to a different metal (e.g., copper): Brazing is often the superior method, but you must select a filler metal that is compatible with both materials to prevent cracking and galvanic corrosion.
Ultimately, achieving a strong brazed joint is a matter of understanding and controlling the fundamental science of the materials involved.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Joint Strength | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Oxide Layer Removal | Critical | Must be removed via vacuum or flux to allow metallurgical bonding. |
| Joint Design & Gap | High | Tight, uniform clearance (0.001-0.005 in) is essential for capillary action. |
| Filler Metal Selection | High | Must be compatible with base metal; nickel-based alloys for high strength. |
| Process Control | High | Precise temperature and heating/cooling rates prevent stress cracking. |
Need a reliable, high-strength joint for your stainless steel components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables for demanding applications. Our expertise in thermal processing, including brazing solutions, ensures your stainless steel assemblies achieve maximum strength and reliability. We provide the equipment and consumables necessary for controlled environments like vacuum brazing, helping you overcome the challenge of the oxide layer for a perfect metallurgical bond.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific stainless steel joining requirements and discover the right solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Battery Lab Equipment 304 Stainless Steel Strip Foil 20um Thick for Battery Test
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three-Section Clamp
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- What procedures should be followed after using nickel or copper foam? A Guide to Reliable Reuse and Performance
- Can carbon nanotubes be used in batteries? Boost Battery Performance with Conductive Nanotubes
- Is there a battery tester for lithium batteries? Unlock Accurate Health Diagnostics Beyond Voltage
- What are the two methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of a metal? Barrier vs. Sacrificial Protection Explained
- How do you test the capacity of a lithium-ion battery? A Guide to Accurate Measurement



















