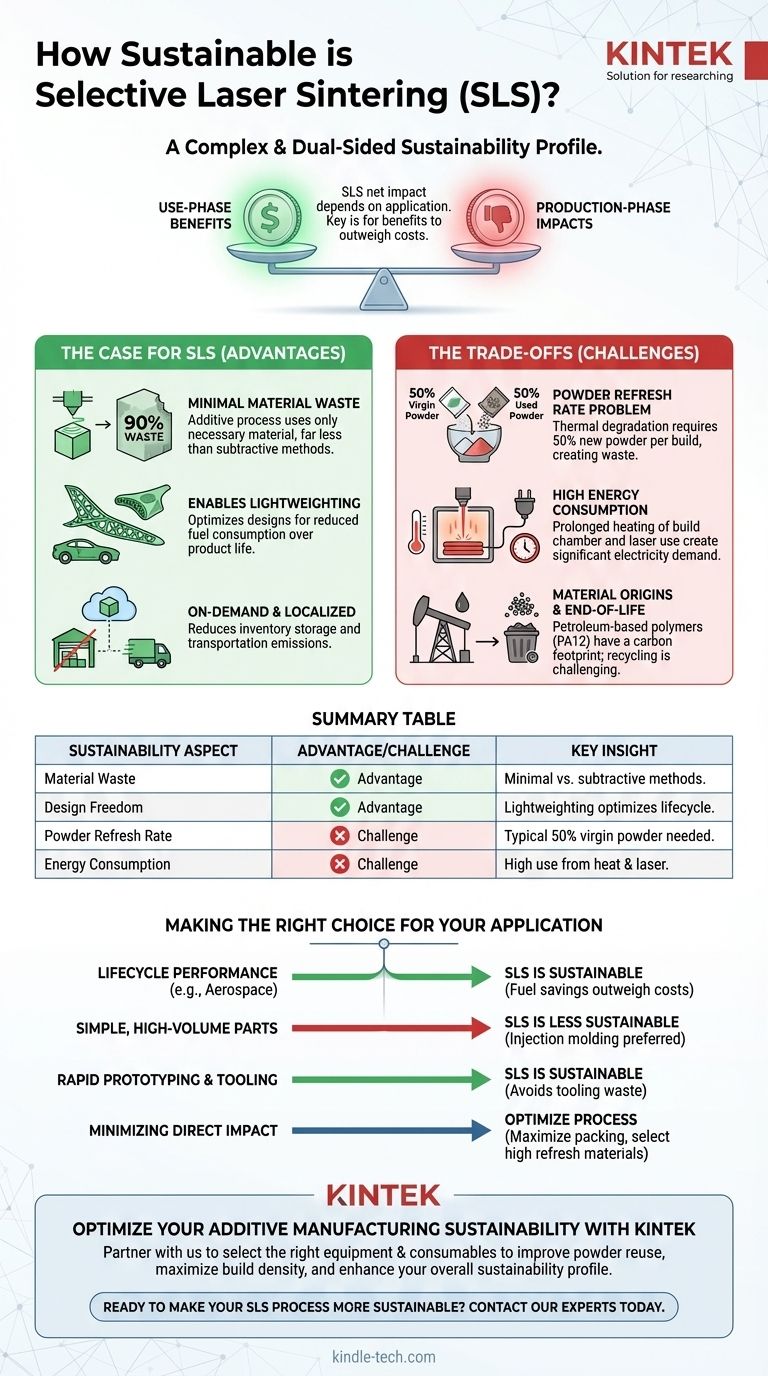
At its core, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) presents a complex and dual-sided sustainability profile. While the technology offers significant advantages by minimizing material waste per part and enabling highly optimized, lightweight designs, it faces considerable challenges related to high energy consumption and the lifecycle of its powdered materials. Its net environmental impact is not inherent to the technology itself, but rather how it is applied.
While SLS enables the creation of lightweight parts that dramatically improve sustainability during a product's use-phase, the manufacturing process itself carries a notable environmental cost. The key to sustainability with SLS is to ensure the use-phase benefits decisively outweigh the production-phase impacts.

The Case for SLS as a Sustainable Technology
The primary sustainability benefits of SLS are centered on how it changes the design and logistics of manufacturing, moving away from the inefficiencies of traditional methods.
Minimal Material Waste in Part Creation
Unlike subtractive manufacturing (like CNC machining), which carves a part from a solid block and can waste up to 90% of the raw material, SLS is an additive process.
It builds parts layer-by-layer, using only the material necessary for the part's geometry and its supports. This results in significantly less direct production waste.
Enabling Lightweight and Optimized Designs
SLS gives engineers the freedom to create complex internal geometries, such as lattices and organically-shaped structures, that are impossible to produce with other methods.
This capability, known as lightweighting, is critical in industries like aerospace and automotive. A lighter part on an airplane or vehicle reduces fuel consumption over its entire operational life, creating a massive downstream environmental benefit.
On-Demand and Localized Production
SLS technology is tool-less, meaning it requires no molds or custom fixtures. This allows for on-demand production of parts, reducing the need for large, energy-intensive warehouses to store inventory.
Furthermore, it supports a distributed manufacturing model, where parts can be printed locally, slashing transportation distances and associated carbon emissions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Environmental Costs
Despite its advantages, the operational reality of SLS involves significant environmental drawbacks that must be carefully managed.
The Powder Refresh Rate Problem
This is the most significant sustainability challenge for SLS. The unsintered powder in the build chamber is exposed to high temperatures for extended periods, which degrades its properties.
Because of this thermal degradation, you cannot simply reuse 100% of the leftover powder. It must be mixed with a high percentage of new, virgin powder to maintain part quality. This ratio is called the refresh rate.
A typical refresh rate is 50%, meaning for every new build, 50% of the powder must be virgin material. The remaining "used" powder that can no longer be refreshed often becomes waste, though efforts to downcycle it are growing.
High Energy Consumption
SLS machines are energy-intensive. The entire build chamber must be heated to just below the material's melting point and held at that temperature for the entire duration of the print, which can last for many hours or even days.
This prolonged, high-energy state, combined with the power required for the laser, results in a substantial electricity demand per part, especially for small builds with low packing density.
Material Origins and End-of-Life
The most common materials for SLS, such as Nylon 12 (PA12), are polymers derived from petroleum. Their production is fossil-fuel dependent and carries its own carbon footprint.
While bio-based polymers are becoming available, they are not yet mainstream. Furthermore, recycling finished SLS parts is not a widely established or simple process, meaning many parts are destined for landfills at their end of life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The sustainability of SLS is not absolute; it depends entirely on how you leverage its strengths to overcome its weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is lifecycle performance (e.g., aerospace, high-performance automotive): The massive fuel savings from a lightweighted component will almost certainly outweigh the energy and material costs of its production.
- If your primary focus is producing simple, high-volume plastic parts: The powder waste and high energy use of SLS make it far less sustainable than a well-optimized process like injection molding.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping and custom tooling: The benefit of avoiding hard tooling and reducing development waste often makes SLS a more sustainable choice than traditional prototyping methods.
- If your primary focus is minimizing direct manufacturing impact: Maximize the packing density of every build to produce as many parts as possible for the energy consumed, and select materials with a higher refresh rate.
By understanding this balance, you can strategically apply SLS where it delivers a true net-positive environmental impact.
Summary Table:
| Sustainability Aspect | Advantage/Challenge | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Material Waste | Advantage | Minimal waste vs. subtractive methods (e.g., CNC machining). |
| Design Freedom | Advantage | Lightweighting optimizes product lifecycle efficiency (e.g., in aerospace). |
| Powder Refresh Rate | Challenge | Typical 50% virgin powder requirement leads to material waste. |
| Energy Consumption | Challenge | High energy use from heated build chamber and laser over long print times. |
Optimize Your Additive Manufacturing Sustainability with KINTEK
Understanding the trade-offs of SLS is the first step. The next is partnering with a supplier who can help you maximize its benefits. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables that support efficient, high-quality SLS processes.
Whether you are focused on R&D, rapid prototyping, or production, we can help you select the right materials and equipment to improve powder reuse, maximize build density, and enhance your overall sustainability profile.
Ready to make your SLS process more sustainable? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can support your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of the extrusion process? High Costs and Geometric Limits Explained
- What is the process of calendering in plastic processing? A Guide to High-Volume Film & Sheet Production
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- What is the blown film extrusion technique? Mastering Biaxial Orientation for Superior Film Strength
- What is the difference between calendaring and calendering? Master the Key Spelling and Context



















