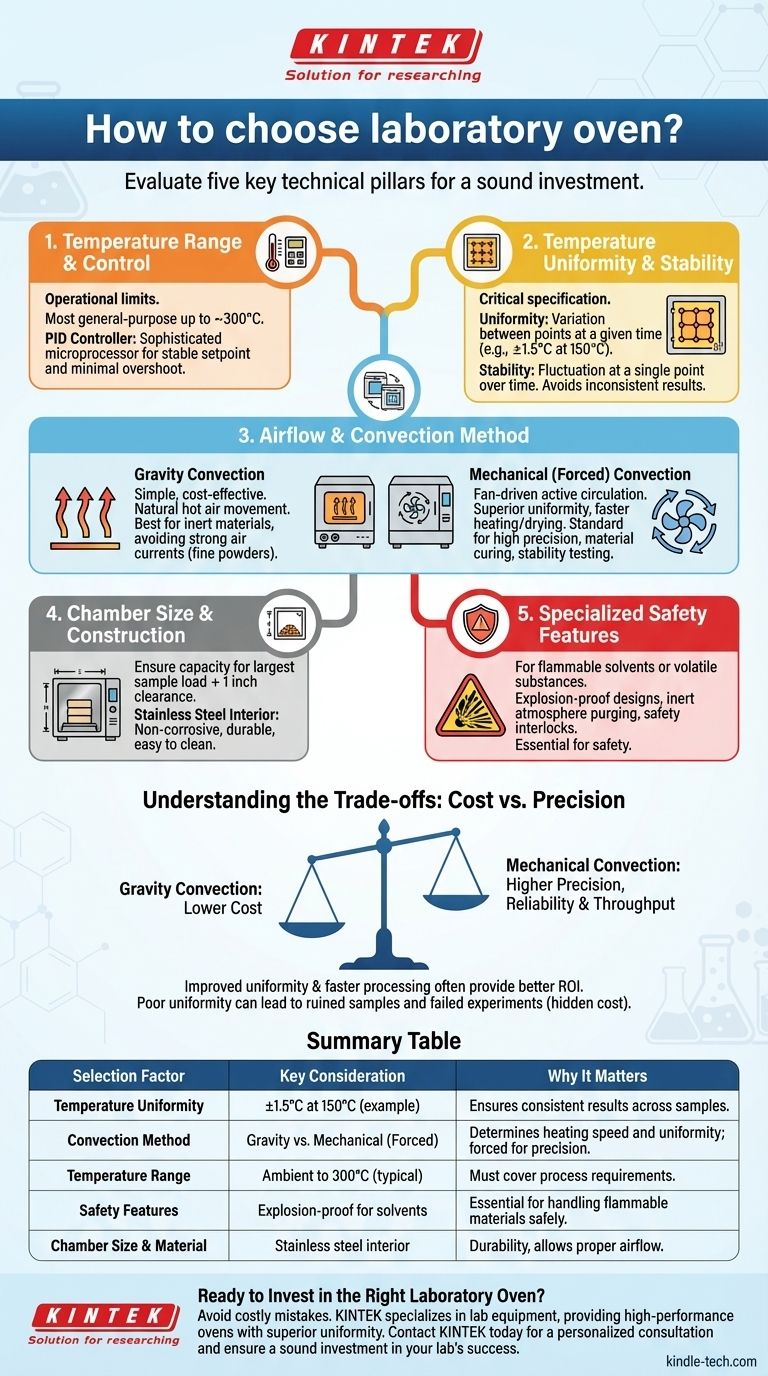
Choosing the right laboratory oven is a critical decision that goes far beyond simply matching a temperature range. To make a sound investment, you must evaluate five key technical pillars: temperature range and control, temperature uniformity, airflow method (convection), chamber size, and any specialized safety features required for your specific application.
The most common and costly mistake is selecting an oven based only on its maximum temperature and internal dimensions. The true determinant of a successful outcome is how the oven distributes heat—its convection method and resulting temperature uniformity—which must be precisely matched to the sensitivity of your process.

The Core Technical Pillars of Oven Selection
A laboratory oven is a precision instrument. Understanding its core components allows you to move past marketing materials and focus on the specifications that directly impact your results.
Temperature Range & Control
This is the most fundamental specification, defining the operational limits of the oven. Most general-purpose lab ovens operate from slightly above ambient temperature up to around 300°C.
Modern ovens use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which is a sophisticated microprocessor that minimizes temperature overshoot and maintains a stable setpoint. This is a non-negotiable feature for any serious scientific application.
Temperature Uniformity & Stability
This is arguably the most critical and misunderstood specification. It defines how consistent the temperature is throughout the entire chamber.
- Uniformity refers to the temperature variation between different points within the chamber at a given time. A specification might read "±1.5°C at 150°C."
- Stability refers to the temperature fluctuation at a single point over time.
Poor uniformity means a sample placed in the center of the oven experiences a different temperature than one near a wall, leading to inconsistent and unreliable results.
Airflow & Convection Method
The method used to circulate air is the primary driver of temperature uniformity and drying/heating speed. There are two main types.
Gravity Convection
This is the simplest and most cost-effective design. It relies on the natural movement of hot air: as air is heated, it rises, then cools and falls, creating a gentle circulation.
These ovens are best for simple drying of inert materials or processes that cannot tolerate strong air currents, such as working with fine powders that could be disturbed.
Mechanical (Forced) Convection
These ovens use a fan to actively circulate air, ensuring a much more even temperature distribution throughout the chamber. This results in superior uniformity and faster drying or heating times.
Forced convection is the standard for applications requiring high precision, such as material curing, stability testing, or any protocol where all samples must be processed under identical thermal conditions.
Chamber Size & Construction
While seemingly simple, this involves practical considerations. Ensure the internal dimensions can accommodate your largest sample load, with at least one inch of clearance on all sides to allow for proper airflow.
The interior should be constructed from a non-corrosive material, typically stainless steel, for durability and ease of cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Precision
Choosing an oven involves balancing your budget against the performance required for your application. A mistake here can either waste money on an over-specified unit or, more damagingly, invalidate your work with an inadequate one.
Gravity vs. Mechanical Convection
The primary trade-off is performance versus cost. A gravity convection oven will always be less expensive than a mechanical convection unit of the same size.
However, the improved temperature uniformity and faster processing times of a mechanical oven often provide a significant return on investment through more reliable data and higher throughput.
The Hidden Cost of Poor Uniformity
Saving money on a low-specification oven can be a false economy. If your process requires a precise temperature, poor uniformity can ruin expensive samples, invalidate test results, and force costly protocol repeats.
The cost of one failed experiment can easily exceed the price difference between a basic and a high-performance oven.
Specialized Safety Features
If you are working with flammable solvents or volatile substances, a standard laboratory oven is a significant explosion hazard. You must use an oven specifically designed for this purpose.
These safety ovens feature explosion-proof designs, inert atmosphere purging capabilities, and safety interlocks that prevent ignition. They are significantly more expensive but absolutely essential for safe operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct oven, start by defining your process, not by browsing product catalogs. Use these guidelines to align your needs with the right technology.
- If your primary focus is general glassware drying or simple heating of non-critical samples: A gravity convection oven offers an excellent balance of performance and value.
- If your primary focus is sensitive material curing, analytical testing, or any process requiring high reproducibility: You must invest in a mechanical (forced) convection oven to ensure superior temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is drying materials containing flammable solvents or outgassing volatile compounds: A specialized safety or explosion-proof oven is the only acceptable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput sample processing: A mechanical convection oven will significantly reduce drying times and improve your workflow efficiency.
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of your process requirements is the foundation for a sound investment in your laboratory's capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Key Consideration | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Uniformity | ±1.5°C at 150°C (example) | Ensures consistent results across all samples in the chamber. |
| Convection Method | Gravity vs. Mechanical (Forced) | Determines heating speed and uniformity; forced is standard for precision. |
| Temperature Range | Ambient to 300°C (typical) | Must cover your specific process requirements. |
| Safety Features | Explosion-proof for solvents | Essential for handling flammable materials safely. |
| Chamber Size & Material | Stainless steel interior | Provides durability and allows for proper airflow around samples. |
Ready to Invest in the Right Laboratory Oven?
Avoid the costly mistake of choosing an oven based on temperature and size alone. The precision of your results depends on the oven's technical capabilities.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide high-performance laboratory ovens with superior temperature uniformity and the right safety features for your application. Our experts will help you select the perfect model to enhance your workflow efficiency and data reliability.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your next oven is a sound investment in your lab's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results



















