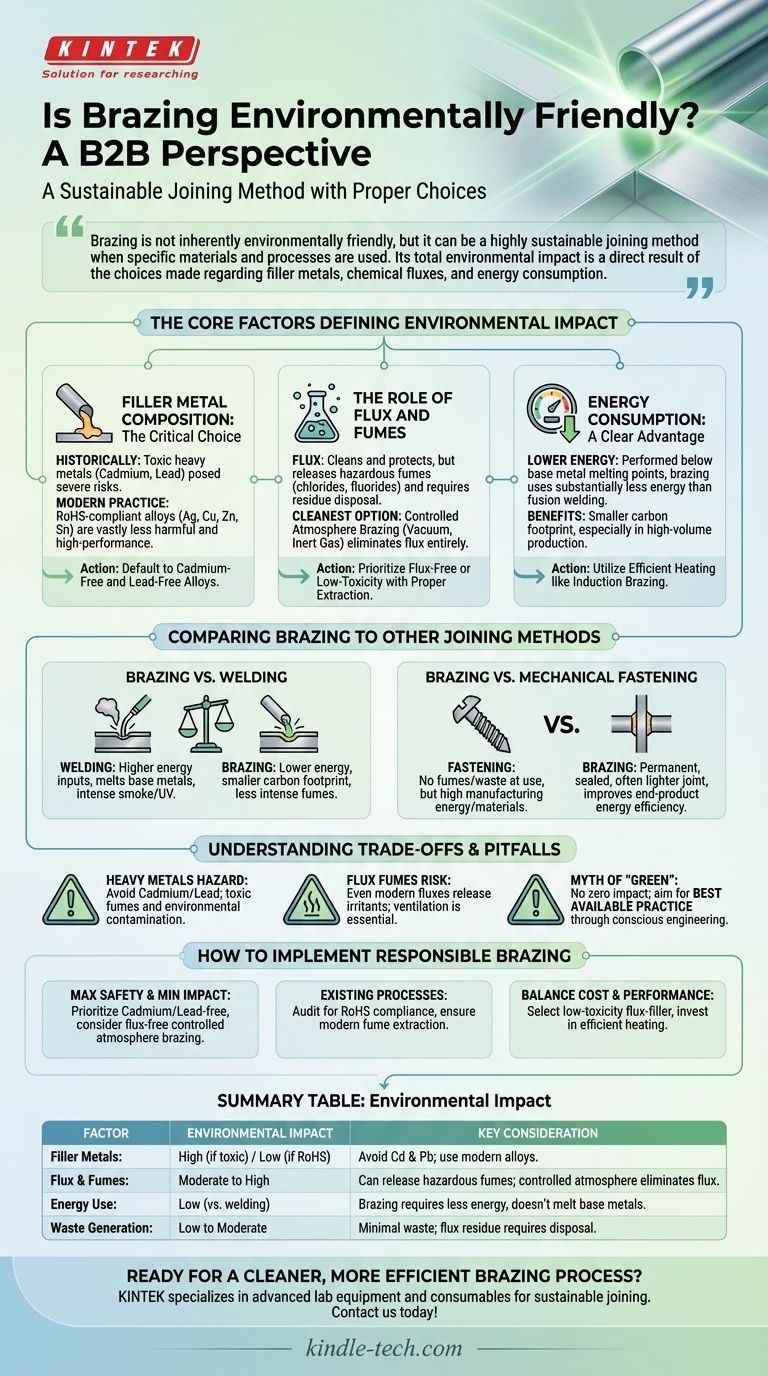
Brazing is not inherently environmentally friendly, but it can be a highly sustainable joining method when specific materials and processes are used. Its total environmental impact is a direct result of the choices made regarding filler metals, chemical fluxes, and energy consumption. While older methods utilizing toxic materials pose significant risks, modern brazing practices offer a low-energy, minimal-waste alternative to other fabrication techniques.
The environmental friendliness of brazing hinges on avoiding toxic materials like cadmium and lead. By using modern, RoHS-compliant filler metals and proper fume extraction, brazing becomes a low-energy, minimal-waste alternative to many other joining processes.
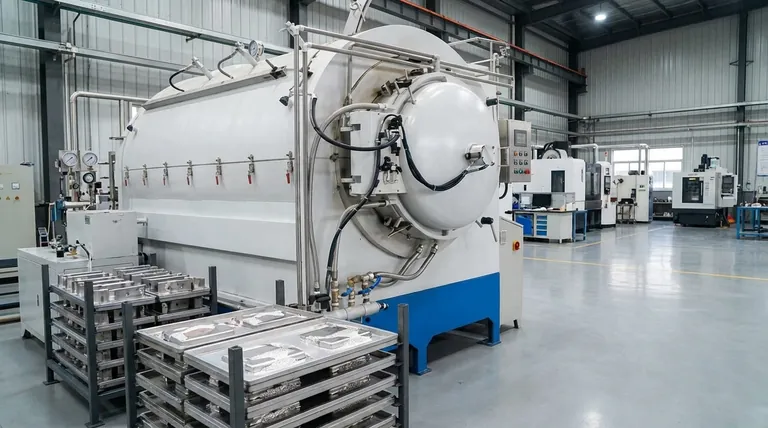

The Core Factors Defining Brazing's Environmental Impact
The "greenness" of any brazing operation is not a simple yes-or-no question. It is the sum of several distinct factors, each of which can be managed to reduce the overall footprint.
Filler Metal Composition: The Critical Choice
Historically, some of the most effective brazing filler metals contained cadmium and lead. These heavy metals are now known to be extremely toxic, posing severe risks to both human health and the environment.
Modern regulations, such as the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, have driven the industry toward safer alternatives. Today, high-performance filler metals are typically alloys of silver, copper, zinc, and tin, which are vastly less harmful.
The Role of Flux and Fumes
Brazing flux is a chemical agent required to clean the base metals and protect the joint from oxidation during heating. However, these fluxes often contain chlorides and fluorides.
When heated, flux releases fumes that can be hazardous to operators and act as air pollutants. The residue left after brazing must also be cleaned and disposed of as chemical waste. Advanced techniques like controlled atmosphere brazing (e.g., in a vacuum or inert gas) can eliminate the need for flux altogether, representing the cleanest option.
Energy Consumption: A Clear Advantage
This is where brazing holds a significant environmental advantage over processes like welding. Brazing is performed at temperatures below the melting point of the base materials.
This fundamental difference means that brazing requires substantially less energy to create a joint compared to fusion welding. Lower energy use translates directly to a smaller carbon footprint, especially in high-volume production environments.
Comparing Brazing to Other Joining Methods
To properly assess its impact, brazing must be viewed in context.
Brazing vs. Welding
Welding melts the base metals, demanding much higher energy inputs. It also tends to generate more intense smoke, ozone, and ultraviolet radiation.
However, some welding processes (like TIG) use inert shielding gas instead of flux, which can simplify fume management. The choice between them often depends on whether the energy savings from brazing outweigh the challenges of managing flux.
Brazing vs. Mechanical Fastening
Mechanical fasteners like screws and rivets produce no chemical fumes or waste during assembly. This makes them appear very clean at the point of use.
However, the manufacturing of the fasteners themselves consumes significant energy and raw materials. Brazing creates a permanent, sealed, and often lighter joint, which can improve the end product's energy efficiency over its lifecycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
True objectivity requires acknowledging the risks and common mistakes associated with brazing.
The Hazard of Heavy Metals
The single greatest environmental mistake is using a filler metal containing cadmium or lead when it is not explicitly required for a niche application. The fumes are toxic, and any waste contaminates the environment. Always default to cadmium-free and lead-free alloys.
The Risk from Flux Fumes
Even modern, "safe" fluxes can release irritating chemical fumes when heated. Proper ventilation and fume extraction are not optional; they are essential for operator safety and environmental responsibility.
The Myth of "Green" Brazing
No industrial process has zero impact. The goal is not to find a perfectly "green" solution but to implement the best available practice to minimize harm. Labeling brazing as simply "good" or "bad" is inaccurate; its impact is the direct result of conscious engineering and process choices.
How to Implement an Environmentally Responsible Brazing Process
Choosing the right approach depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental and safety goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety and minimal environmental impact: Prioritize cadmium-free and lead-free filler metals and investigate controlled atmosphere brazing to eliminate flux entirely.
- If you are working with existing processes: Audit your current filler metals for RoHS compliance and ensure your fume extraction systems are performing to modern standards.
- If you are balancing cost and performance: Select the lowest-toxicity flux-filler combination that meets your joint's strength requirements and invest in efficient heating methods like induction brazing to minimize energy waste.
Ultimately, responsible brazing is a system of deliberate choices that minimizes chemical hazards and conserves energy.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Environmental Impact | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Metals | High (if toxic) / Low (if RoHS) | Avoid cadmium and lead; use modern alloys (Ag, Cu, Zn, Sn). |
| Flux & Fumes | Moderate to High | Can release hazardous fumes; controlled atmosphere brazing eliminates flux. |
| Energy Use | Low (vs. welding) | Brazing requires less energy as it doesn't melt base metals. |
| Waste Generation | Low to Moderate | Minimal waste compared to mechanical fastening; flux residue requires proper disposal. |
Ready to implement a cleaner, more efficient brazing process in your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that support sustainable joining methods. Whether you need RoHS-compliant filler metals, fume extraction systems, or advice on controlled atmosphere brazing, our expertise helps you minimize environmental impact while achieving superior results. Contact us today to optimize your brazing operations for performance and sustainability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease



















