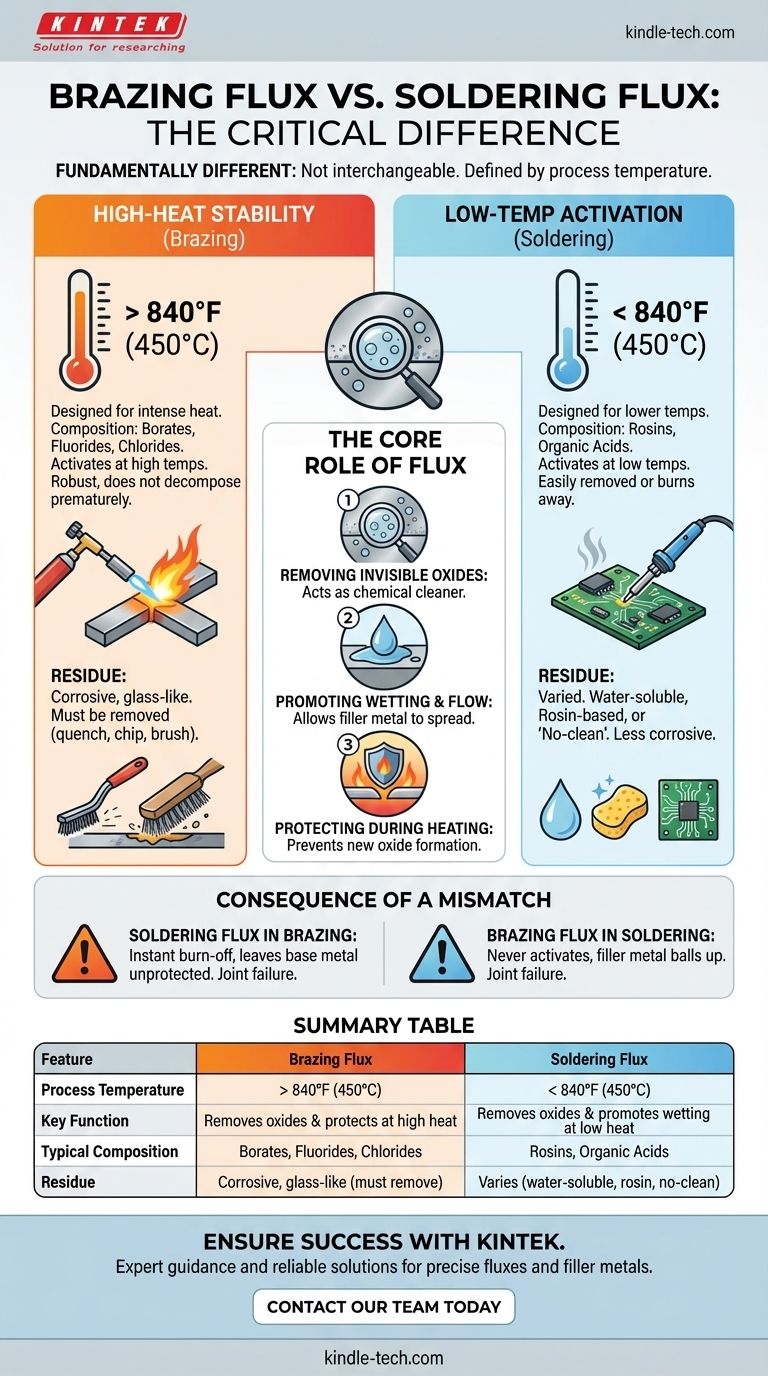
Yes, brazing flux and soldering flux are fundamentally different and cannot be used interchangeably. The primary difference is their chemical formulation, which is designed to match the distinct temperature ranges of each process. Brazing flux is engineered to remain stable and active at temperatures above 840°F (450°C), while soldering flux is designed to work at the much lower temperatures typical of soldering.
The core principle to understand is that flux must be active at the working temperature of your filler metal. Using the wrong flux will cause it to either fail to activate or burn away before the joint is made, resulting in immediate joint failure.
The Core Role of Flux: The Unseen Partner
To understand why the fluxes are different, you must first understand what flux does. It is not an optional additive; it is a chemical prerequisite for a successful joint.
Removing Invisible Oxides
All metals, even when they appear clean, are covered in a thin, invisible layer of oxide. This oxide layer prevents the molten filler metal from bonding with the base metal. Flux acts as a chemical cleaner, removing this oxide layer as the part is heated.
Promoting Wetting and Flow
Once the oxides are removed, the flux creates a clean, protected surface. This allows the molten filler metal to "wet" the base metals, which is the ability to spread evenly across the surface and be drawn into the joint by capillary action.
Protecting the Joint During Heating
As you heat the metal parts, the rate of oxidation increases dramatically. The flux creates a protective blanket over the joint area, preventing new oxides from forming while you work.
Why Temperature Dictates Flux Formulation
The vast difference in process temperatures between soldering and brazing is the single most important factor dictating flux chemistry.
The Brazing Flux Challenge: High-Heat Stability
Brazing occurs at high temperatures, typically from 1100°F to 2200°F (600°C to 1200°C). A brazing flux must be robust enough to withstand this intense heat without decomposing or burning away prematurely.
These fluxes are typically made from complex chemical compounds like borates, fluorides, and chlorides. They are inactive at room temperature and only become aggressive chemical cleaners at high heat.
The Soldering Flux Challenge: Low-Temperature Activation
Soldering occurs at much lower temperatures, usually below 840°F (450°C). A brazing flux would be useless here, as it would remain a dry, inert powder and never activate.
Soldering fluxes are formulated with rosins or organic acids that activate at these lower temperatures. They are designed to clean the surface эффекtively and then either burn away or be easily removed.
The Consequence of a Mismatch
If you use soldering flux for a brazing operation, it will instantly burn off and vaporize long before the brazing filler metal melts, leaving the base metal unprotected and ensuring the joint fails.
If you use brazing flux for a soldering operation, the temperature will never get high enough to activate the flux. The filler metal will ball up and refuse to flow, as if you were trying to solder on a dirty surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Residue
The chemical diferenças also impact what is left behind after the job is done.
Brazing Flux Residue: Corrosive and Glass-Like
Because they contain powerful chemical salts, brazing flux residues are highly corrosive. They must be thoroughly removed after the joint cools. This residue is often hard and glass-like, requiring quenching, chipping, or wire brushing to remove.
Soldering Flux Residue: A Spectrum of Options
Soldering fluxes offer more variety. Water-soluble fluxes are aggressive but clean easily with water. Rosin-based fluxes are much milder and less corrosive. Modern electronics often use "no-clean" fluxes, where the minimal residue is non-corrosive and can be left on the board.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To ensure a successful and durable joint, your choice must be deliberate and match the process तापमान.
- If your primary focus is high-strength joining with silver or bronze alloys (Brazing): You must use a brazing flux chemically designed to withstand and activate at temperatures above 840°F (450°C).
- If your primary focus is joining with lower-melting-point tin-based alloys (Soldering): You must use a soldering flux formulated to activate at temperatures below 840°F (450°C).
- If your primary focus is post-process cleaning and safety: Always remove corrosive brazing flux residue, and for soldering, choose the mildest flux (like a rosin or no-clean) that can accomplish the job.
Always treat the flux and the filler metal as a single, inseparable system to guarantee a reliable joint.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing Flux | Soldering Flux |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | > 840°F (450°C) | < 840°F (450°C) |
| Key Function | Removes oxides & protects at high heat | Removes oxides & promotes wetting at low heat |
| Typical Composition | Borates, Fluorides, Chlorides | Rosins, Organic Acids |
| Residue | Corrosive, glass-like (must be removed) | Varies (can be water-soluble, rosin, or no-clean) |
Ensure your brazing and soldering projects are a success with the right materials from KINTEK.
Choosing the correct flux is critical for creating strong, reliable joints. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the precise fluxes and filler metals your laboratory or workshop needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect products for your specific application and temperature requirements.
Don't risk joint failure—contact our team today for expert guidance and reliable solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Measuring Cylinder 10/50/100ml
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a laboratory high-temperature hydraulic press? Optimize MEA Fabrication for HCl Electrolysis
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- How does a heated laboratory hydraulic press facilitate densification in CSP? Optimize Mg-doped NASICON Sintering



















