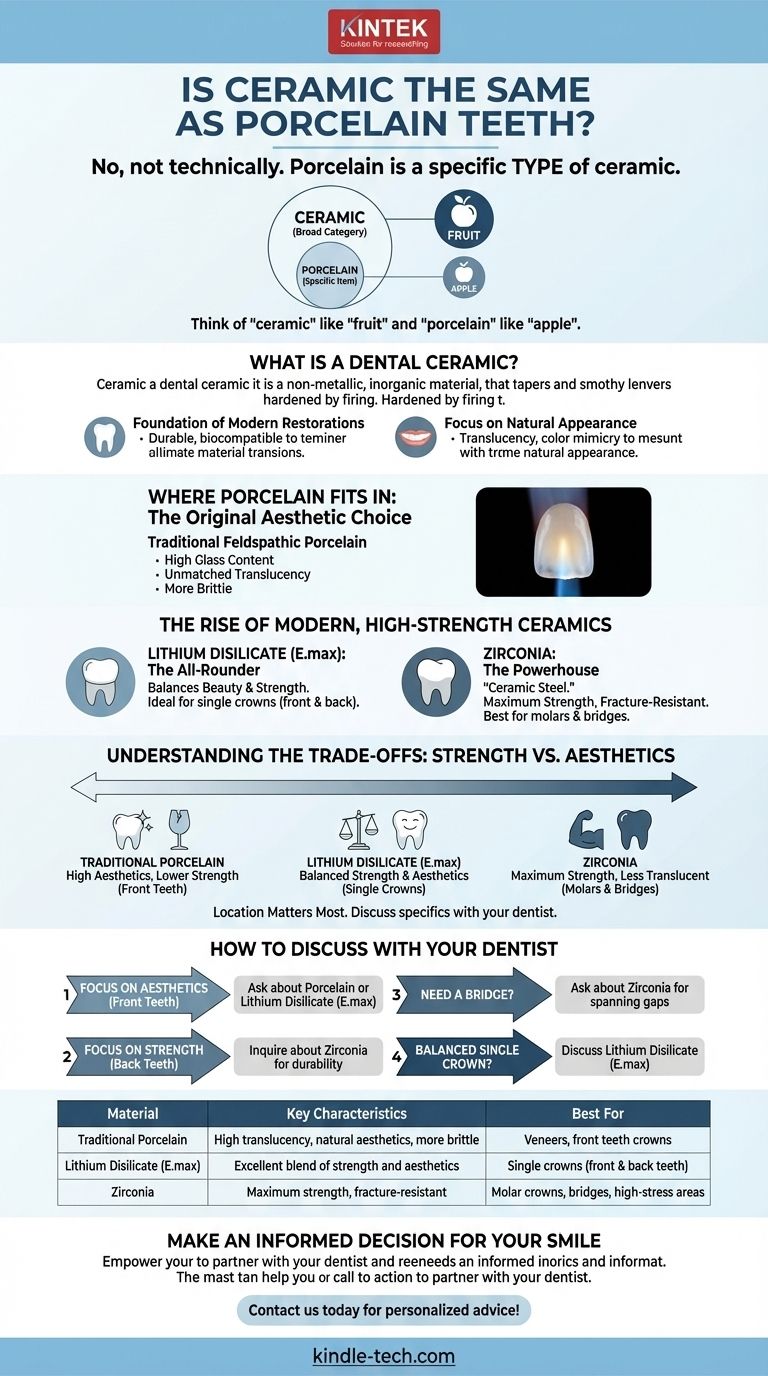
No, they are not technically the same, though the terms are often used interchangeably in conversation. The simplest way to understand it is that porcelain is a specific type of ceramic. Think of "ceramic" as the broad category, like "fruit," and "porcelain" as a specific item within that category, like "apple."
The critical distinction isn't between "ceramic" and "porcelain," but between traditional porcelain and the advanced, high-strength ceramics like Zirconia and Lithium Disilicate used in modern dentistry. Knowing which specific material is being used is far more important than the general terminology.

What is a Dental Ceramic?
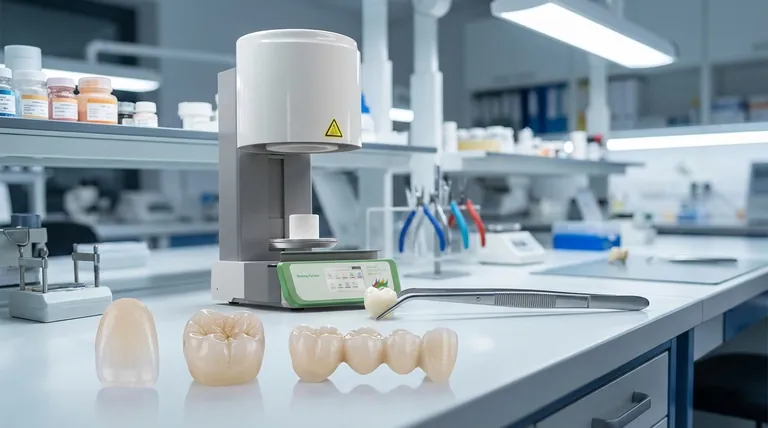
A dental ceramic is a non-metallic, inorganic material that is hardened by firing at a high temperature. This broad category of materials is prized in dentistry for several key reasons.
The Foundation of Modern Restorations
Ceramics are the go-to materials for creating durable, tooth-colored restorations like crowns, veneers, bridges, and even dental implants. They are exceptionally biocompatible, meaning they are non-toxic and well-tolerated by the human body.
A Focus on Natural Appearance
The primary advantage of all ceramics is their ability to mimic the translucency and color of a natural tooth. This allows for restorations that blend seamlessly with your smile, a stark contrast to older metal-based crowns.
Where Porcelain Fits In
Porcelain is the original aesthetic dental ceramic. It's a specific subtype with a high concentration of glass, which gives it unique properties.
The Classic Choice for Aesthetics
Traditional feldspathic porcelain is renowned for its unmatched translucency and lifelike appearance. Its composition allows light to pass through it in a way that is remarkably similar to natural tooth enamel.
Its Primary Limitation
This high glass content also makes traditional porcelain more brittle than its modern counterparts. While its beauty is undeniable, it is best suited for low-stress applications like veneers on front teeth.
The Rise of Modern, High-Strength Ceramics
To overcome the fragility of traditional porcelain, material science has produced incredibly robust and reliable new ceramics. These are the materials that now dominate modern restorative dentistry.
Lithium Disilicate (E.max): The All-Rounder
Lithium disilicate, often known by the brand name E.max, is a type of glass-ceramic that offers a superb blend of beauty and strength. It is significantly stronger than traditional porcelain, making it an excellent and highly aesthetic choice for single crowns on both front and back teeth.
Zirconia: The Powerhouse
Zirconia is the strongest dental ceramic available, sometimes called "ceramic steel." It is incredibly durable and resistant to fracture, making it the ideal material for crowns on back molars that endure heavy chewing forces. It is also the standard for multi-tooth bridges where maximum strength is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Aesthetics
Choosing the right ceramic involves a balance between mechanical strength and optical beauty. The location of the tooth in your mouth is the most critical factor in this decision.
The Spectrum of Materials
Think of dental ceramics on a spectrum. On one end is traditional porcelain, offering the highest aesthetics but lower strength. On the other end is Zirconia, providing maximum strength but historically being more opaque. Lithium Disilicate (E.max) sits comfortably in the middle.
Why Location Matters Most
For a veneer on a front tooth that is visible when you smile, aesthetics are paramount, making a material like porcelain or E.max ideal. For a molar crown that must withstand immense biting pressure, the uncompromising strength of Zirconia is the most logical choice.
Why the Terminology Gets Confused
A dentist may use the general term "ceramic crown" or even "porcelain crown" as a simplified way to describe a tooth-colored restoration. This is usually done for clarity, but it is always appropriate for you to ask for specifics about the exact material being recommended and why.
How to Discuss This With Your Dentist
Your goal is to understand the recommendation for your specific clinical needs. Use this framework to guide your conversation and ensure you are an active participant in your own care.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics (front teeth): Ask about options like feldspathic porcelain or Lithium Disilicate (E.max) for the most natural and translucent result.
- If your primary focus is strength (back teeth/molars): Inquire if Zirconia is the recommended material to ensure long-term durability under heavy biting forces.
- If you need a bridge to replace a missing tooth: Ask about Zirconia, as its superior strength is almost always required to successfully span a gap.
- If you want a balanced solution for a single crown: Discuss if Lithium Disilicate (E.max) is a suitable option, as it provides an excellent combination of strength and beauty.
Understanding these material differences empowers you to have a more informed conversation with your dentist and partner in achieving the best possible outcome for your smile.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Porcelain | High translucency, natural aesthetics, more brittle | Veneers, front teeth crowns |
| Lithium Disilicate (E.max) | Excellent blend of strength and aesthetics | Single crowns (front & back teeth) |
| Zirconia | Maximum strength, fracture-resistant | Molar crowns, bridges, high-stress areas |
Make an Informed Decision for Your Smile
Understanding the differences between porcelain, zirconia, and lithium disilicate is the first step toward a successful restoration. Your dentist can recommend the best material based on your specific needs—whether it's maximum aesthetics for a front tooth or superior strength for a molar.
Have more questions about dental ceramics or ready to discuss your treatment plan? Contact us today to speak with a dental professional and get personalized advice for your smile.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















