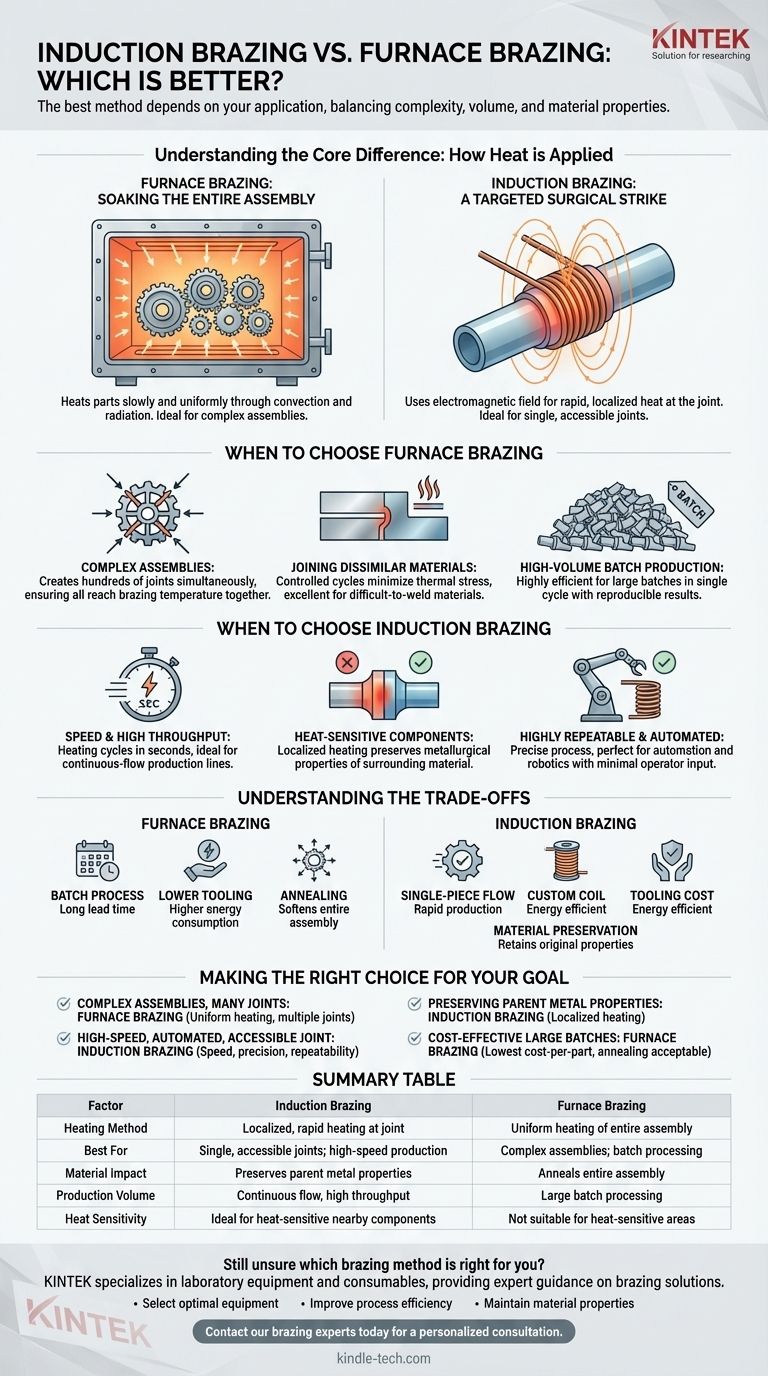
The short answer is that neither is inherently better. The "best" method depends entirely on your specific application, balancing factors like part complexity, production volume, material properties, and cost. Induction brazing excels at rapidly heating single, accessible joints, while furnace brazing is ideal for complex assemblies with multiple or inaccessible joints.
The core difference comes down to how heat is applied. Furnace brazing soaks the entire assembly in uniform heat, while induction brazing uses an electromagnetic field to generate intense, localized heat precisely at the joint area. Your choice hinges on whether you need to heat the whole part or just a small section of it.

Understanding the Core Difference: How Heat is Applied
To make an informed decision, you must first grasp the fundamental mechanics of each process. The method of heating dictates the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Furnace Brazing: Soaking the Entire Assembly
Furnace brazing places entire components or assemblies inside a chamber with a controlled atmosphere. The whole chamber is brought to brazing temperature, heating the parts slowly and uniformly through convection and radiation.
This process is analogous to a convection oven. It ensures every part of the assembly, including deep, internal joints, reaches a consistent temperature, which is critical for the braze alloy to flow evenly via capillary action.
Induction Brazing: A Targeted Surgical Strike
Induction brazing uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a custom-designed copper coil. This creates a powerful magnetic field that induces electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the metal part placed near the coil.
These currents generate rapid, localized heat precisely where it's needed, leaving the rest of the assembly relatively cool. It is a non-contact method that heats the part from within, offering exceptional speed and control.
When to Choose Furnace Brazing
Based on its uniform heating method, furnace brazing is the superior choice for specific scenarios.
For Complex Assemblies with Multiple Joints
Furnace brazing's greatest strength is its ability to create hundreds of joints simultaneously on a complex assembly. Because the entire part is heated uniformly, all joints reach the proper temperature at the same time.
This makes it possible to manufacture intricate components that would be impossible to join by other methods.
When Joining Dissimilar or Unweldable Materials
The controlled heating and cooling cycles minimize thermal stress, making furnace brazing an excellent choice for joining dissimilar metals or materials that are difficult to weld. The process can also be combined with heat treatments like hardening or annealing, saving time and cost.
For High-Volume Batch Production
In mass production environments, furnace brazing is highly efficient and economical. Large batches of parts can be processed in a single cycle with highly reproducible results and minimal need for skilled operators.
When to Choose Induction Brazing
Induction brazing's localized and rapid heating makes it the clear winner for a different set of applications.
For Speed and High Throughput
The heating cycle for an induction-brazed joint can be mere seconds, compared to the much longer cycle time of a furnace. This makes it ideal for integrating into a continuous-flow production line where speed is paramount.
When Heat-Sensitive Components are Nearby
If a part has areas that have been previously heat-treated or contains sensitive components that cannot withstand high temperatures, induction is the only viable option. By heating only the joint, it preserves the metallurgical properties of the surrounding material.
For Highly Repeatable, Automated Processes
The process is extremely precise and controllable. Once the power, frequency, and coil position are set, the results are identical every time, making it perfect for automation and robotics with minimal operator input.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods requires acknowledging their inherent limitations.
The Question of Scale: Batch vs. Continuous Flow
Furnace brazing is a batch process. It is perfect for processing many parts at once but introduces a long lead time for each batch. Induction brazing is a single-piece flow process, ideal for rapid, continuous production lines.
The Cost Factor: Tooling vs. Operation
Induction brazing requires a custom-designed coil for each unique joint geometry, which represents an upfront tooling cost. However, its energy efficiency can lead to lower operational costs. Furnace brazing requires less part-specific tooling but consumes more energy by heating a large chamber.
The Material Impact: Annealing vs. Preservation
A significant consequence of furnace brazing is that the entire assembly is annealed (softened) during the cycle. This may be undesirable if the parent metal needs to retain its hardness. Induction brazing avoids this, preserving the material's original properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select the process that aligns directly with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is brazing complex assemblies with many internal joints: Furnace brazing is the superior choice for its ability to heat uniformly and create hundreds of joints in a single cycle.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, automated production of a single, accessible joint: Induction brazing offers unparalleled speed, precision, and repeatability for integration into a production line.
- If your primary focus is preserving the temper or material properties of the parent metal: Induction brazing's localized heating is essential to avoid altering the entire component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for large batches of small parts: Furnace brazing often provides the lowest cost-per-part in mass production environments where annealing is acceptable.
By aligning the heating method with your specific design and production goals, you can ensure a reliable, efficient, and high-quality joining process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Induction Brazing | Furnace Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Localized, rapid heating at joint | Uniform heating of entire assembly |
| Best For | Single, accessible joints; high-speed production | Complex assemblies with multiple joints; batch processing |
| Material Impact | Preserves parent metal properties | Anneals entire assembly |
| Production Volume | Continuous flow, high throughput | Large batch processing |
| Heat Sensitivity | Ideal for heat-sensitive nearby components | Not suitable for heat-sensitive areas |
Still unsure which brazing method is right for your laboratory or production needs?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance on brazing solutions for research, quality control, and manufacturing applications. Our team can help you:
- Select the optimal brazing equipment for your specific materials and joint requirements
- Improve process efficiency and repeatability in your lab or production line
- Maintain material properties while achieving strong, reliable bonds
Contact our brazing experts today for a personalized consultation on how we can enhance your joining processes with the right equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- What is the basic of brazing? A Guide to Strong, Low-Heat Metal Joining
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















