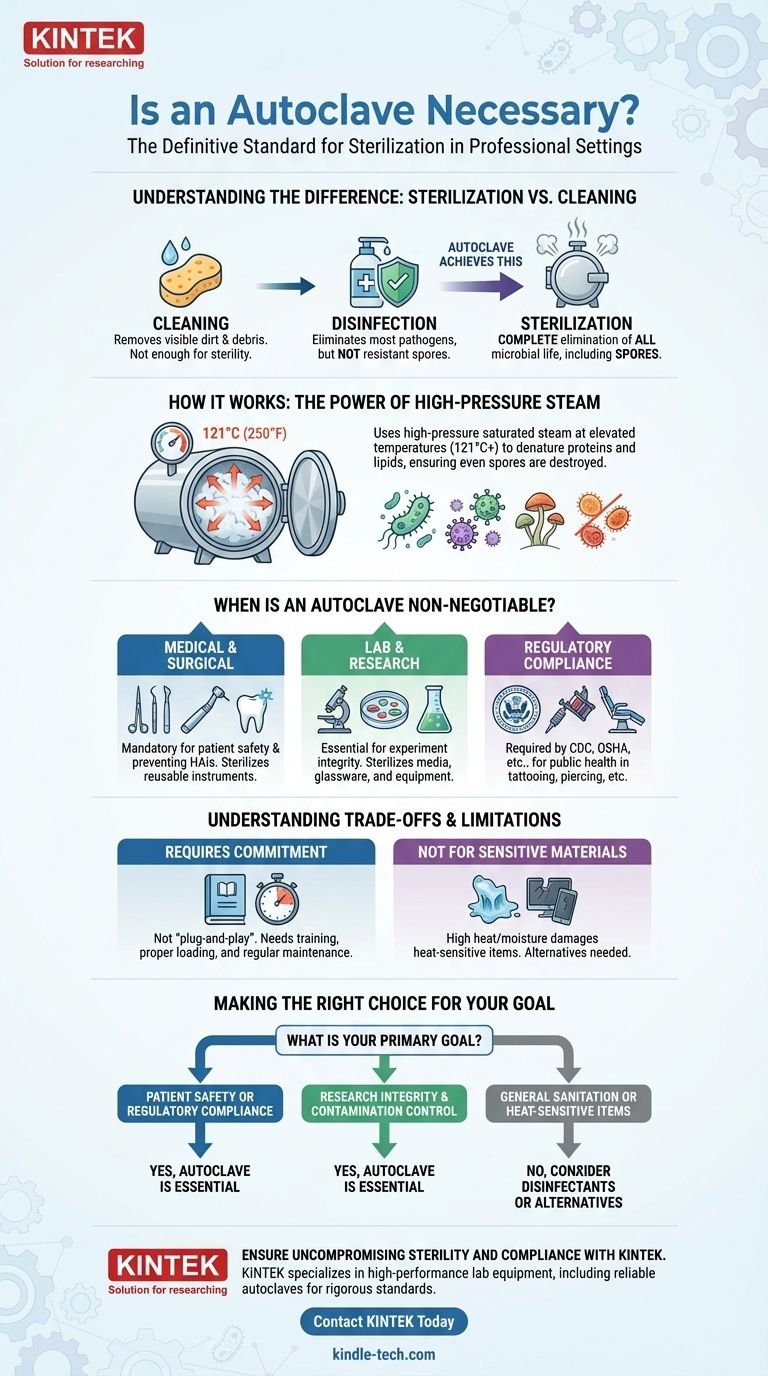
In many professional settings, yes, an autoclave is absolutely necessary. It is the definitive industry standard for sterilization, not just cleaning or disinfecting. By using high-pressure saturated steam, an autoclave eliminates all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and resilient spores—on equipment and other materials, which is a level of decontamination other methods cannot reliably achieve.
The question is not simply about whether an item is clean, but whether it is sterile. An autoclave is necessary whenever the absolute elimination of all microorganisms is required to ensure safety, prevent contamination, or comply with regulatory standards.

What an Autoclave Achieves: The Principle of Sterilization
To understand why an autoclave is so critical, you must first distinguish between cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing. These terms are not interchangeable.
Beyond Simple Cleaning
Cleaning removes visible dirt and debris. Disinfection eliminates most pathogenic microorganisms but not necessarily all microbial life, especially resistant bacterial spores.
Sterilization is the complete elimination or destruction of all forms of microbial life. This is the standard an autoclave is designed to meet.
The Power of High-Pressure Steam
An autoclave is essentially a highly controlled pressure chamber. By increasing the pressure, it allows water to reach temperatures far above its normal boiling point, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
This combination of intense heat and moisture is lethal to microorganisms. The steam rapidly denatures the essential proteins and lipids that constitute a cell, ensuring even the most robust spores are inactivated.
Why It's the Gold Standard
The process, known as steam sterilization, is highly reliable, effective, and relatively fast. In hospitals, laboratories, and other critical environments, its ability to ensure a complete kill makes it the preferred method for sterilizing heat-stable equipment.
When Is an Autoclave Non-Negotiable?
Certain applications have zero tolerance for microbial contamination, making an autoclave an essential piece of equipment.
Medical and Surgical Applications
Any reusable instrument that will come into contact with sterile body tissue—such as surgical tools, dental instruments, or implantable devices—must be sterilized.
Using an improperly sterilized instrument poses a severe risk of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). For this reason, autoclaves are mandatory in hospitals, operating rooms, and dental clinics.
Laboratory and Research Settings
In scientific research, especially in microbiology and biotechnology, preventing unwanted contamination is paramount to the integrity of an experiment.
Autoclaves are used to sterilize laboratory glassware, plasticware, and, most importantly, growth media. Failure to do so would introduce competing organisms that would render experimental results invalid.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Many industries are regulated by health and safety organizations, such as the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) or OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration).
These bodies often mandate and enforce sterilization protocols for public-facing services like tattooing, piercing, and podiatry to protect public health. Proper autoclave use and detailed logging are key parts of this compliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution, and its use requires a dedicated process.
The Commitment to Proper Operation
An autoclave is not a simple "plug-and-play" device. It requires user training on proper loading procedures, cycle selection, and safety protocols.
Furthermore, regular maintenance and performance monitoring—often documented in a detailed log—are crucial to ensure the machine is operating correctly and achieving complete sterilization in every cycle.
When an Autoclave Is Not the Right Tool
An autoclave is designed for items that can withstand high temperatures and moisture. It will destroy or damage heat-sensitive materials like certain plastics, electronics, or delicate instruments.
For general surface cleaning, like countertops or floors, chemical disinfectants are the appropriate and more practical choice. An autoclave is overkill for tasks that only require disinfection, not sterilization.
Alternatives for Sensitive Materials
When items cannot be autoclaved, other sterilization methods exist, such as ethylene oxide (EtO) gas, hydrogen peroxide gas plasma, or radiation.
However, these methods have their own complexities, costs, and safety considerations. They are specialized solutions for specific needs and are not a direct replacement for steam sterilization's broad utility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific requirement for microbial control dictates whether an autoclave is necessary.
- If your primary focus is patient safety in a clinical setting: An autoclave is a non-negotiable tool for sterilizing any critical or semi-critical reusable instruments.
- If your primary focus is research integrity in a laboratory: An autoclave is essential for preparing sterile media and equipment to prevent contamination that invalidates results.
- If your primary focus is general sanitation for low-risk items: An autoclave is unnecessary; chemical disinfectants are more appropriate, efficient, and cost-effective.
Ultimately, the necessity of an autoclave is determined by your professional commitment to eliminating risk and achieving true sterility.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Is an Autoclave Necessary? | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Medical/Surgical Instrument Reprocessing | Yes | Mandatory for patient safety; prevents healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). |
| Laboratory Research (e.g., microbiology) | Yes | Essential for experiment integrity; sterilizes media and equipment to prevent contamination. |
| Tattooing, Piercing, or Podiatry | Yes | Often required by regulatory bodies (e.g., CDC, OSHA) for public health compliance. |
| General Surface Cleaning (e.g., floors, countertops) | No | Chemical disinfectants are more practical and cost-effective for disinfection (not sterilization). |
| Heat-Sensitive Items (e.g., plastics, electronics) | No | Autoclaving will damage materials; alternative methods (e.g., gas plasma) are needed. |
Ensure Uncompromising Sterility and Compliance with KINTEK
If your work in a laboratory, medical, or dental setting demands the absolute elimination of microbial life—from bacteria and viruses to resilient spores—an autoclave is not just beneficial; it's essential. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reliable autoclaves designed to meet rigorous sterilization standards.
By choosing KINTEK, you gain:
- Guaranteed Sterility: Achieve complete microbial destruction with precise temperature and pressure control.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet CDC, OSHA, and other health authority requirements with validated processes.
- Enhanced Safety: Protect patients, staff, and research integrity by eliminating contamination risks.
- Durability and Support: Benefit from robust equipment built for daily use, backed by expert maintenance guidance.
Don't compromise on safety or quality. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect autoclave solution tailored to your laboratory's needs. Let us help you maintain the highest standards of sterility and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK



















