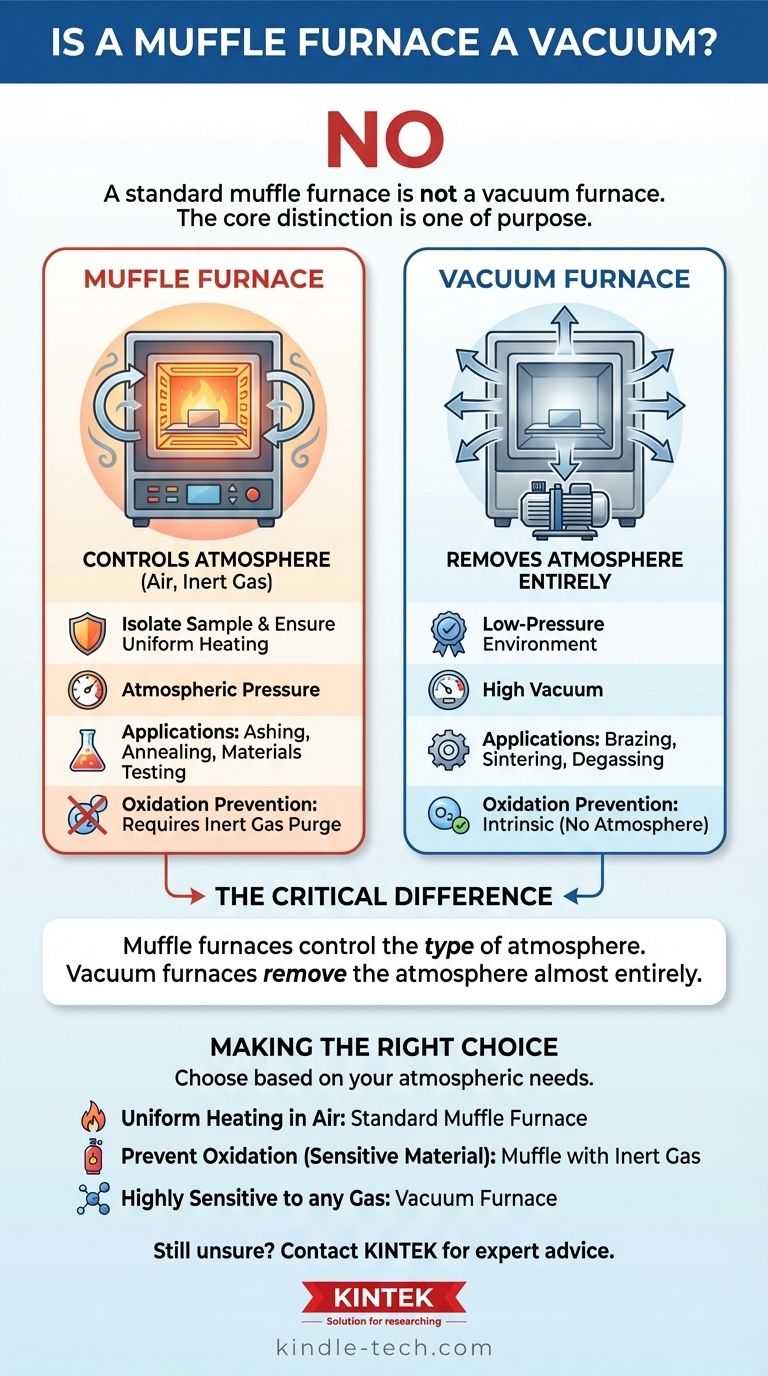
No, a standard muffle furnace is not a vacuum furnace. While a muffle furnace features a sealed chamber, its primary purpose is to provide a controlled, high-temperature environment by isolating the sample from the heating elements and any potential contaminants, not to create a vacuum. It is designed to operate at or near atmospheric pressure.
The core distinction is one of purpose. A muffle furnace's sealed chamber is designed to control the type of atmosphere (e.g., air or an inert gas), whereas a vacuum furnace is designed to remove the atmosphere almost entirely.

The Role of the Muffle Chamber
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its chamber—the "muffle." Understanding its function clarifies why it isn't a vacuum system.
To Isolate the Sample from Contamination
The original purpose of the muffle was to separate the material being heated from the flames and combustion byproducts of a fuel-fired heat source.
Modern electric muffle furnaces don't have combustion byproducts. However, the principle of isolation remains critical for preventing spalling from the heating elements or insulation from contaminating the sample.
To Ensure Uniform Heating
The muffle, made of heat-resistant refractory material, is positioned between the heating elements and the sample.
This setup prevents direct exposure to the intense heat of the elements, allowing heat to radiate and convect more evenly throughout the chamber. The result is a more homogenous temperature treatment for the entire workpiece.
To Enable Atmospheric Control
A muffle furnace's chamber is designed to be well-sealed. The references note features like double-layer door seals and multi-point locking mechanisms.
This "airtight" design is not for holding a vacuum. Instead, it allows a user to control the gaseous environment. You can operate it with ambient air, or you can purge the air and introduce a specific atmosphere, such as an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, to prevent oxidation.
Muffle Furnace vs. Vacuum Furnace: Key Distinctions
Confusing the two is common, but their engineering and applications are fundamentally different.
Primary Function
A muffle furnace controls the purity and type of gas surrounding a sample at atmospheric pressure.
A vacuum furnace removes gas to create a low-pressure environment, minimizing or eliminating interaction between the sample and any atmosphere.
Core Applications
Muffle furnaces are ideal for processes like ashing, tempering, annealing, and materials testing where the main goal is uniform heating and preventing contamination from the furnace itself.
Vacuum furnaces are essential for processes like brazing, sintering, and degassing, where any reaction with atmospheric gases (especially oxygen) would be detrimental to the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnace types involves understanding critical trade-offs in capability and complexity.
The Limits of a Muffle Furnace
A standard muffle furnace operated in air will not prevent oxidation. To achieve an oxygen-free environment, it must be equipped with ports to purge the chamber and maintain a positive pressure with an inert gas.
Even with an inert gas purge, it cannot achieve the near-complete absence of gas molecules that a vacuum furnace provides.
The "Airtight" Misconception
The seals on a muffle furnace are designed to prevent room air from leaking in and the controlled atmosphere from leaking out at atmospheric pressure.
They are not engineered to withstand the significant pressure differential required to maintain a high vacuum. A vacuum furnace requires a much more robust chamber, specialized seals, and powerful vacuum pumps, making it a more complex and expensive system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your application dictates the right tool. Base your decision on the atmospheric conditions your process requires.
- If your primary focus is uniform high-temperature heating in air (e.g., ashing, binder burnout, some ceramic firings): A standard muffle furnace is the correct and most cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is to prevent oxidation of a sensitive material (e.g., heat treating certain steels): A muffle furnace with inert gas purging capabilities is a viable option.
- If your primary focus is a process that is highly sensitive to any atmospheric gas (e.g., brazing reactive metals, advanced sintering): A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable, as it is the only way to effectively remove the atmosphere.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace comes down to understanding the critical difference between controlling an atmosphere and removing it entirely.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Controls atmosphere type (air, inert gas) | Removes atmosphere entirely |
| Operating Pressure | At or near atmospheric pressure | High vacuum environment |
| Key Application | Ashing, annealing, materials testing | Brazing, sintering, degassing |
| Oxidation Prevention | With inert gas purging | Intrinsic (no atmosphere) |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your specific process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Our team can help you determine the ideal heating solution—whether it's a standard muffle furnace, a gas-purge model, or a high-vacuum system—to ensure optimal results for your materials and applications.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How long should a furnace take to raise the temperature? Key Factors for Optimal Heating Speed
- What is muffle in muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- What are the different types of ashing analysis? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What is the use of muffle oven in laboratory? For Clean, High-Temperature Material Processing



















