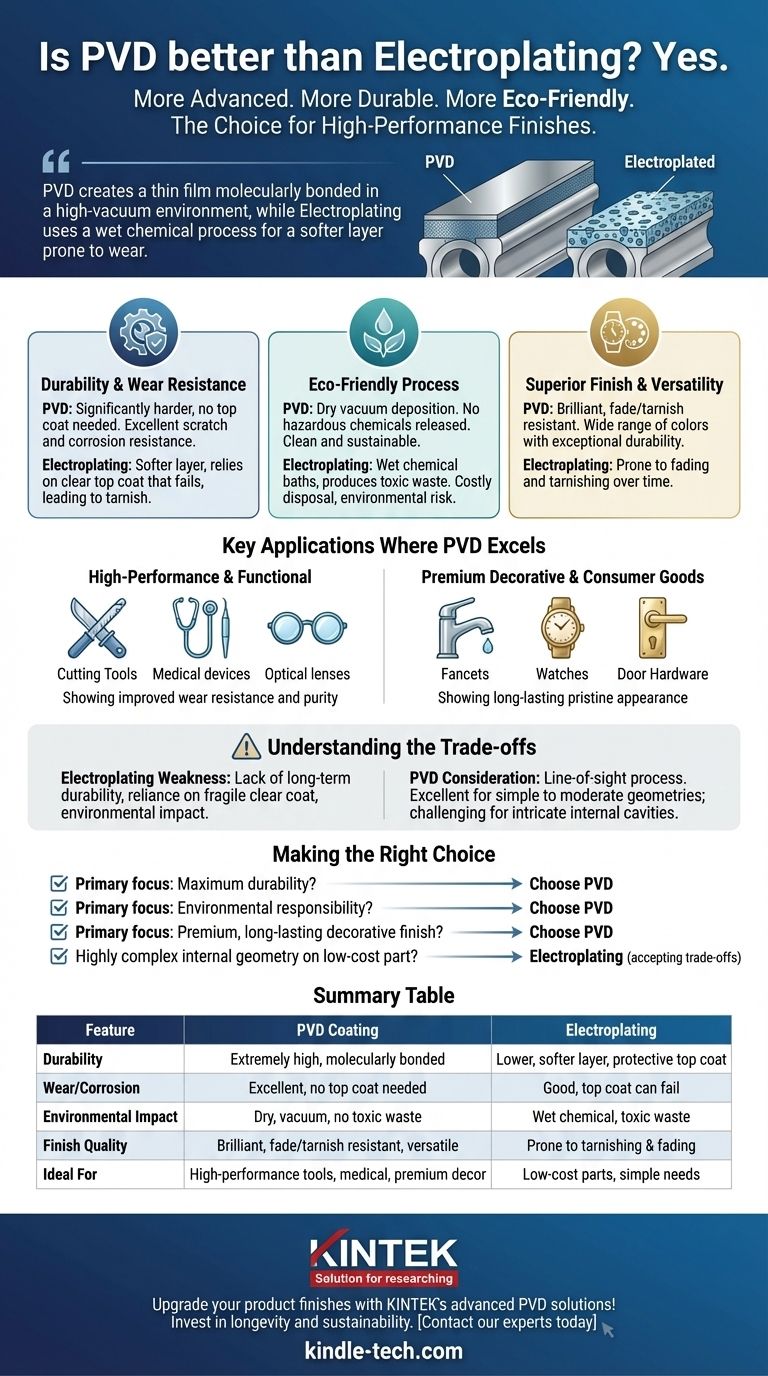
For most modern applications, yes. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a more advanced and robust coating process compared to traditional electroplating. PVD offers superior durability, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, and it is a significantly more environmentally friendly process, making it the preferred choice for high-performance and premium decorative finishes.
The core difference is not just the final coating, but the process itself. PVD creates a thin film that is molecularly bonded to the surface in a high-vacuum environment, while electroplating uses a wet chemical process to deposit a softer layer that is more prone to wear and tarnishing.

Why PVD Outperforms Electroplating
The Matter of Durability and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are significantly harder and more resistant to corrosion than electroplated finishes. This is because the PVD process creates an extremely dense, bonded layer on the surface of the part.
Unlike many electroplated finishes on materials like brass or nickel, PVD does not require a clear top coat. This is critical, as the clear coat on an electroplated item is often the first point of failure, degrading over time and leading to tarnishing and corrosion.
The inherent hardness of PVD coatings also reduces friction and improves oxidation resistance, extending the life of the component.
A Cleaner, More Environmentally Friendly Process
Electroplating is a wet chemical process that involves submerging parts in baths containing hazardous chemicals. This process generates toxic waste that requires careful and costly disposal.
PVD, in contrast, is a dry vacuum deposition method. It does not release harmful chemicals into the environment, making it a much cleaner and more sustainable technology.
Superior Finish and Aesthetic Versatility
PVD provides a brilliant, durable finish that is highly resistant to the fading and tarnishing that plagues many electroplated products.
Furthermore, the PVD process allows for a wide range of colors and finishes, all while maintaining exceptional durability. This makes it ideal for both functional applications and high-end decorative pieces where appearance is paramount.
Key Applications Where PVD Excels
High-Performance and Functional Coatings
The purity, hardness, and thinness of PVD coatings make them essential for applications where performance is non-negotiable.
This includes cutting tools, molds, and dies, which benefit from improved wear resistance. It is also used in medical devices, optical lenses, and semiconductor components where durability and cleanliness are crucial.
Premium Decorative and Consumer Goods
For products that must withstand daily use while maintaining a pristine appearance, PVD is the superior choice.
It is frequently used for faucets, door hardware, watches, and other items where the finish must resist scratches, cleaning chemicals, and tarnishing for the life of the product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Inherent Weakness of Electroplating
The primary drawback of electroplating is its lack of long-term durability. The coating is softer and relies on a protective clear coat that can easily be compromised, leading to failure.
Its reliance on hazardous materials also makes it an increasingly undesirable process from both a regulatory and environmental perspective.
The Main Consideration for PVD
While superior in nearly every performance metric, the PVD process has practical considerations. It is a line-of-sight process, meaning the coating material travels in a straight line to the substrate.
This makes it exceptionally good for coating surfaces with simple to moderately complex geometries. However, coating the inside of very long, narrow tubes or extremely intricate internal cavities can be more challenging than with an immersion process like electroplating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum durability, wear resistance, and longevity: Choose PVD. Its molecularly bonded finish is unmatched for resisting scratches, corrosion, and tarnish.
- If your primary focus is environmental responsibility and process cleanliness: Choose PVD. It is a dry, non-polluting process, unlike the chemical baths required for electroplating.
- If your primary focus is a premium, long-lasting decorative finish: Choose PVD. It provides a brilliant finish that will not fade or tarnish and is available in a wide variety of colors.
- If you are coating a highly complex internal geometry on a low-cost, low-performance part: Electroplating might be technically feasible, but you must accept the significant trade-offs in durability and environmental impact.
Ultimately, choosing PVD is an investment in superior performance, longevity, and environmental responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extremely high, molecularly bonded | Lower, softer layer with protective top coat |
| Wear/Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, no top coat needed | Good, but top coat can fail |
| Environmental Impact | Dry, vacuum process, no hazardous waste | Wet chemical process, produces toxic waste |
| Finish Quality | Brilliant, fade and tarnish-resistant, versatile colors | Prone to tarnishing and fading over time |
| Ideal For | High-performance tools, medical devices, premium decor | Low-cost parts with simple durability needs |
Upgrade your product finishes with KINTEK's advanced PVD solutions!
As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTEK understands the critical need for durable, high-performance coatings. Our PVD coating technology delivers unmatched wear resistance, corrosion protection, and aesthetic versatility for your most demanding applications—all through an environmentally responsible process.
Whether you're developing medical devices, precision tools, or premium consumer goods, investing in PVD means investing in longevity and sustainability.
Contact our experts today to explore how KINTEK's PVD coatings can enhance your product's performance and value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance



















