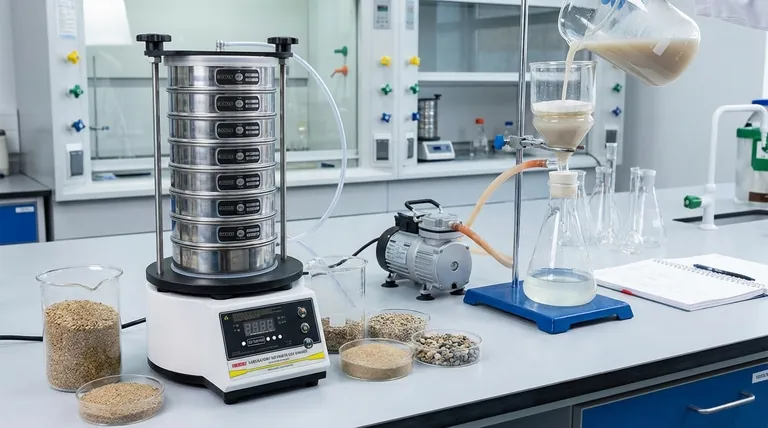
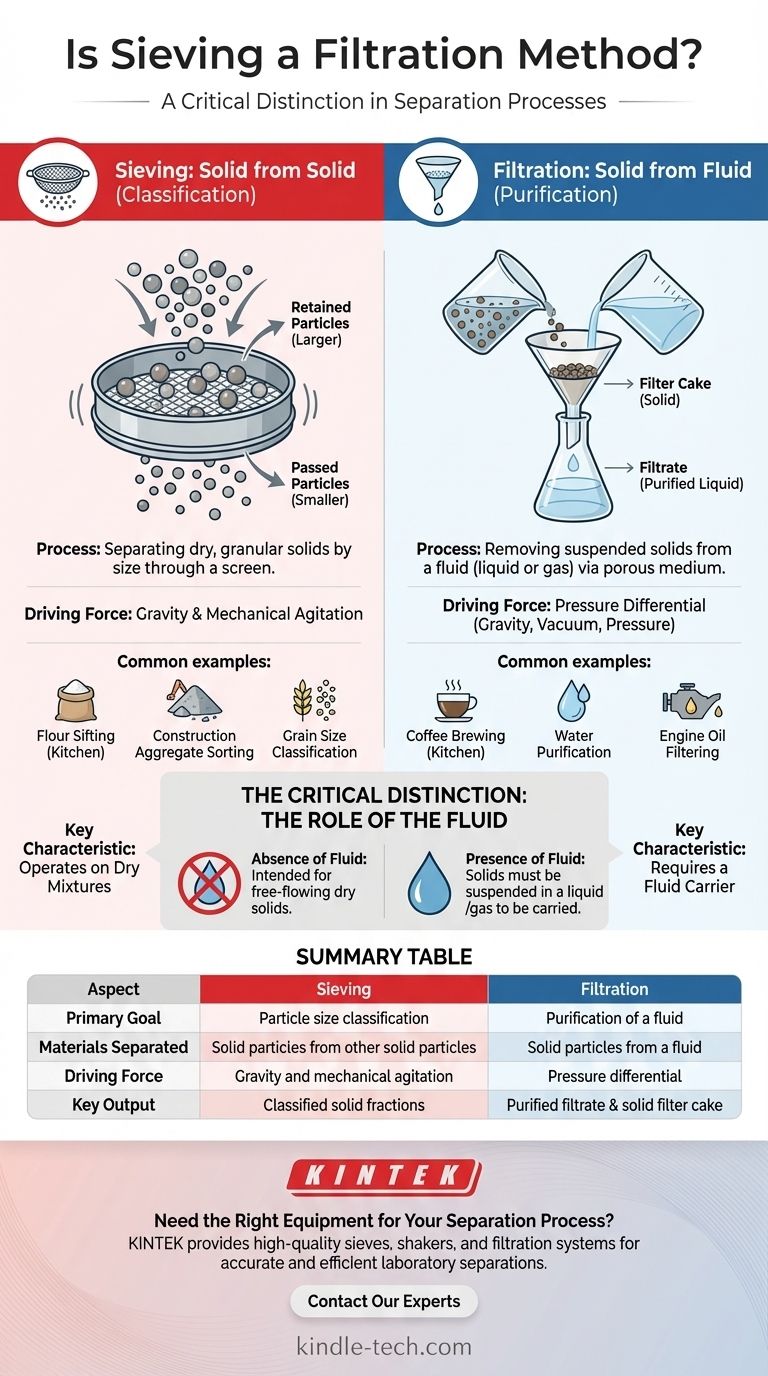
While sieving can be seen as a very specific type of filtration, it is more accurate and useful to define them as distinct processes. Both involve passing a material through a screen-like medium to achieve separation, but they differ fundamentally in what they are designed to separate. The key distinction lies in the state of the materials involved.
Filtration is the process of separating solid particles from a fluid (a liquid or gas) by passing the mixture through a filter medium. Sieving, on the other hand, is a method of separating solid particles from other solid particles based purely on their size.

What Defines Filtration?
Filtration is a ubiquitous process in science and industry, centered on the removal of solids from a fluid stream.
The Core Principle: Solid from Fluid
The essential components of filtration are a solid, a fluid in which it is suspended, and a filter medium. The fluid passes through the porous medium, while the solid particles, being larger than the pores, are retained.
The liquid that passes through is called the filtrate, and the solid material trapped on the filter is the filter cake.
The Driving Force
Filtration is typically driven by a pressure differential. This can be as simple as gravity (like in a drip coffee maker) or enhanced by applying pressure to the input side or a vacuum to the output side to speed up the process.
Common Examples
Familiar examples include using a coffee filter to separate coffee grounds from water, water purifiers that remove sediment and microorganisms, and engine oil filters that trap contaminants.
What Defines Sieving?
Sieving, also known as sifting, is a mechanical separation technique focused entirely on the physical size of dry, granular particles.
The Core Principle: Solid from Solid
Sieving involves passing a mixture of granular solids through a screen or mesh with uniform openings. Particles smaller than the openings pass through, while larger particles are retained.
The primary goal is not purification but classification—sorting a mixture into two or more groups based on particle size.
The Driving Force
The driving force in sieving is typically a combination of gravity and mechanical agitation. Shaking or vibrating the sieve ensures that all particles come into contact with the screen, allowing for an efficient separation.
Common Examples
Common examples include sifting flour in a kitchen to remove lumps, separating different sizes of sand and gravel at a construction site, and grain processing to sort seeds by size.
The Critical Distinction: The Role of the Fluid
The presence or absence of a fluid carrier is the definitive line separating these two techniques.
Filtration Requires a Fluid
In filtration, the solids being separated are suspended within a liquid or gas. The process is impossible without this fluid phase to carry the particles to the filter medium and pass through as the filtrate.
Sieving Operates on Dry Mixtures
Sieving is fundamentally designed for dry, free-flowing granular materials. Introducing a liquid would fundamentally change the process, causing particles to stick together and clog the sieve mesh.
Where the Lines Can Blur
A technique called wet sieving exists, where a liquid (usually water) is used to help wash fine particles through the sieve. However, the objective remains particle size classification, not solid-liquid separation, making it a specialized form of sieving rather than true filtration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the distinction is critical for selecting the correct equipment and designing an effective separation process.
- If your primary focus is purifying a liquid or gas by removing contaminants: You are performing filtration and need a filter medium designed to trap suspended solids.
- If your primary focus is sorting a dry mixture of particles into different size groups: You are performing sieving and need one or more sieves with specific mesh sizes.
- If your primary focus is collecting a solid product from a chemical reaction slurry: You are performing filtration, likely using vacuum assistance to efficiently separate the solid from the liquid.
Mastering the language of separation starts with recognizing this fundamental difference in purpose and state of matter.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Sieving | Filtration |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Particle size classification | Purification of a fluid |
| Materials Separated | Solid particles from other solid particles | Solid particles from a fluid (liquid/gas) |
| Driving Force | Gravity and mechanical agitation | Pressure differential (gravity, vacuum, or pressure) |
| Key Output | Classified solid fractions | Purified filtrate and/or solid filter cake |
Need the Right Equipment for Your Separation Process?
Whether your goal is precise particle size analysis with sieving or efficient solid-liquid separation with filtration, KINTEK has the solution. We specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including a full range of sieves, shakers, and filtration systems, to ensure accuracy and efficiency in your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and let us help you select the perfect equipment for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Dry Three-Dimensional Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















