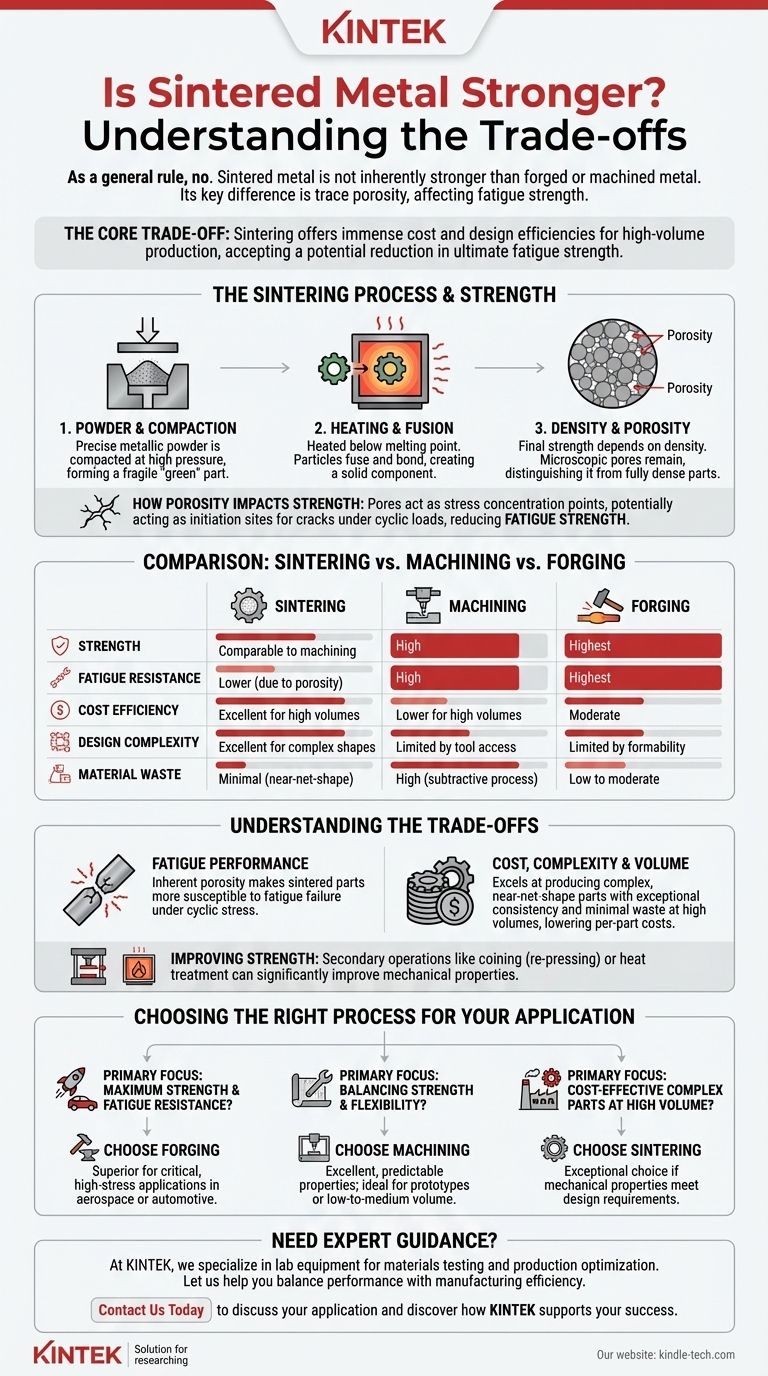
As a general rule, sintered metal is not inherently stronger than metal parts produced through forging or machining from wrought stock. However, a well-executed sintering process can produce components with mechanical strength that is comparable to, and sometimes sufficient to replace, their machined equivalents. The primary difference lies in the trace porosity that remains after the sintering process.
The choice to use sintering is not about achieving superior strength, but about leveraging its immense cost and design efficiencies for high-volume production. The core trade-off is accepting a potential reduction in ultimate fatigue strength in exchange for significant manufacturing advantages.

What Determines the Strength of Sintered Metal?
To understand the strength of a sintered part, you must first understand the process. It is fundamentally different from traditional subtractive (machining) or formative (forging) methods.
The Sintering Process in Brief
Sintering begins with a precise metallic powder. This powder is compacted under high pressure in a die to create a "green" part that has the desired shape but is fragile.
This green part is then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature just below the metal's melting point. The heat causes the individual particles to fuse and bond together, creating a solid, functional component.
The Critical Role of Density and Porosity
The strength of a sintered part is directly related to its final density. A higher-density part has less internal void space, known as porosity.
Because the particles are fused rather than melted and cast, microscopic pores will almost always remain. While a high-quality process minimizes this, porosity is the key factor that distinguishes a sintered part's strength from a fully dense wrought or forged part.
How Porosity Impacts Strength
These microscopic pores can act as stress concentration points. When the part is put under load, especially repeated cyclic loads, these points can become initiation sites for cracks, potentially reducing the part's overall fatigue strength.
How Sintering Compares to Other Methods
The strength of sintered metal is best understood in direct comparison to the most common alternatives.
Sintering vs. Machining
Machining starts with a solid bar or block of wrought metal, which is already fully dense and has a uniform grain structure. The process simply removes material to achieve the final shape.
A high-density sintered part can achieve tensile strength very close to that of a machined part made from a similar alloy. However, due to porosity, it may not match the fatigue performance.
Sintering vs. Forging
Forging subjects a solid piece of metal to extreme pressure, physically deforming it into shape. This process refines and aligns the metal's grain structure, eliminating voids and producing the highest possible strength and fatigue resistance.
Sintered parts cannot match the strength of a forged component. Forging remains the superior method for creating parts that must withstand the most extreme stress and cyclic loading.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Efficiency
If sintering doesn't produce the strongest parts, its widespread use points to other significant advantages. The decision to use it is an engineering trade-off.
The Weak Point: Fatigue Performance
As noted, the inherent porosity of sintered parts makes them more susceptible to fatigue failure than forged or even machined components. This makes sintering less suitable for highly critical applications where cyclic stress is the primary mode of failure.
The Strong Point: Cost and Complexity
Sintering excels at producing complex, near-net-shape parts at very high volumes with exceptional consistency and minimal material waste.
Forming a complex gear, for example, via sintering requires very little finishing work. Machining the same gear would be time-consuming and generate significant scrap, while forging it might not be able to achieve the same geometric intricacy. This efficiency translates directly into lower per-part costs.
Improving Sintered Part Strength
The gap in strength can be narrowed. Secondary operations like coining (re-pressing the part to increase density) or heat treatment can significantly improve the mechanical properties of a sintered component, making them competitive for a wider range of applications.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
Selecting the correct manufacturing method depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and your business goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: Forging is the superior choice, especially for critical, high-stress applications in aerospace or automotive drivetrains.
- If your primary focus is balancing good strength with design flexibility: Machining from solid stock provides excellent, predictable properties and is ideal for prototypes or low-to-medium volume production.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex parts at high volume: Sintering is an exceptional choice, provided its mechanical properties meet the design requirements for the application.
By understanding this balance of properties and economics, you can select the manufacturing process that delivers the precise performance and value your project requires.
Summary Table:
| Property | Sintering | Machining | Forging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Comparable to machining | High | Highest |
| Fatigue Resistance | Lower (due to porosity) | High | Highest |
| Cost Efficiency | Excellent for high volumes | Lower for high volumes | Moderate |
| Design Complexity | Excellent for complex shapes | Limited by tool access | Limited by formability |
| Material Waste | Minimal (near-net-shape) | High (subtractive process) | Low to moderate |
Need help selecting the right metal fabrication process for your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert guidance and high-quality lab equipment for materials testing and production optimization. Whether you're evaluating sintering for high-volume parts or require solutions for strength testing, our team can help you balance performance with manufacturing efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can support your success in materials development and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size
- Why is cold working better than hot working? A Guide to Choosing the Right Metal Forming Process
- What is cold isostatic pressing mold material? Essential Elastomers for Uniform Density
- How big is the isostatic pressing market? A Deep Dive into the $1.2B+ Advanced Manufacturing Enabler
- What is the process of isostatic graphite? A Guide to High-Performance, Uniform Material Creation



















