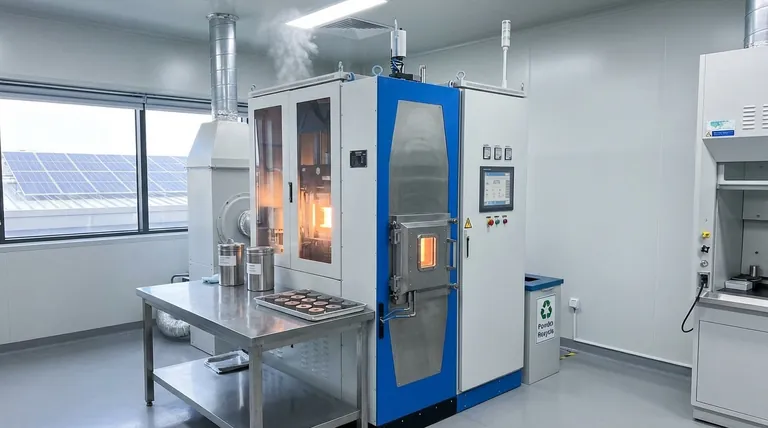
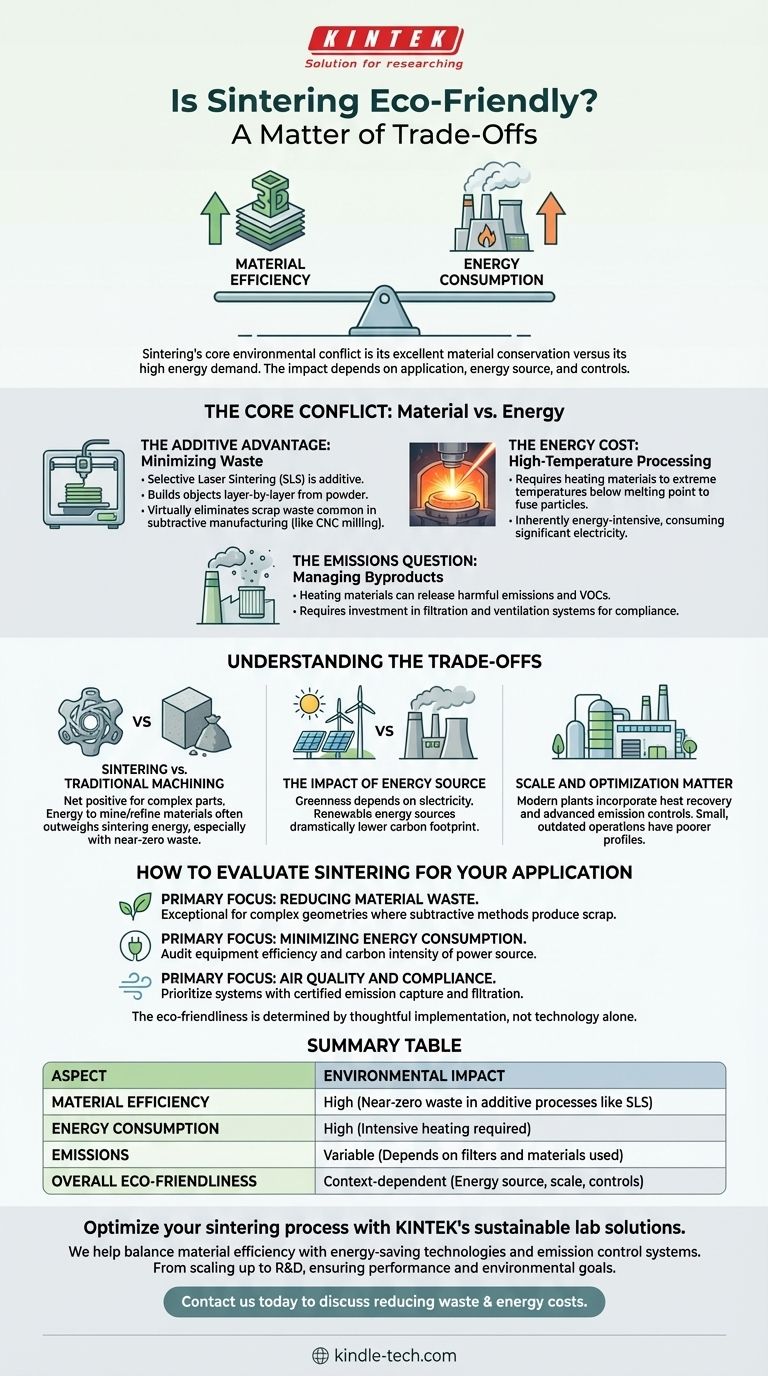
The environmental friendliness of sintering is a matter of trade-offs. While the process offers significant advantages in material efficiency, particularly in its additive manufacturing forms, this benefit is weighed against its substantial energy consumption and the potential for harmful emissions.
Sintering's core environmental conflict is its excellent material conservation versus its high energy demand. The process is not inherently "green" or "harmful"; its true impact depends heavily on the specific application, the energy source, and the environmental controls in place.

The Core Conflict: Material vs. Energy
Sintering's environmental profile is defined by two opposing factors. On one hand, it is a champion of material efficiency. On the other, it is a significant consumer of energy.
The Additive Advantage: Minimizing Waste
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), a modern form of the technology, is an additive manufacturing process. It builds objects layer-by-layer from a powder bed.
This method uses only the material needed for the part itself, virtually eliminating the scrap waste common in subtractive manufacturing (like CNC milling), where a part is carved from a larger block.
The Energy Cost: High-Temperature Processing
The fundamental mechanism of sintering involves heating materials to extreme temperatures, just below their melting point, to fuse particles together.
This process is inherently energy-intensive. It requires powerful industrial furnaces or lasers that consume a significant amount of electricity to maintain these high temperatures for extended periods.
The Emissions Question: Managing Byproducts
Heating powdered materials, especially polymers or metals containing binders, can release harmful emissions and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
This has led to government regulations on air quality around sintering operations, which necessitates investment in filtration and ventilation systems to mitigate environmental impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Viewing sintering in isolation is misleading. Its environmental impact must be weighed against the alternatives and the specifics of the operation.
Sintering vs. Traditional Machining
Compared to subtractive machining, sintering can be a net positive for complex parts. The energy and resources required to mine, refine, and ship raw material often outweigh the energy used during a highly efficient sintering run, especially when factoring in near-zero material waste.
The Impact of Energy Source
The "greenness" of the electricity used is a critical variable. A sintering facility powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind will have a dramatically lower carbon footprint than one powered by fossil fuels.
Scale and Optimization Matter
Modern, large-scale sintering plants often incorporate heat recovery systems and advanced emission controls that significantly reduce their overall environmental impact. A small, inefficient, or outdated operation will have a much poorer profile.
How to Evaluate Sintering for Your Application
To make an informed decision, you must assess the process based on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is reducing material waste: Sintering is an exceptional choice, particularly for complex geometries where subtractive methods would produce significant scrap.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy consumption: You must carefully audit the energy efficiency of the specific equipment and the carbon intensity of its power source.
- If your primary focus is air quality and compliance: Prioritize systems with certified, state-of-the-art emission capture and filtration technologies.
Ultimately, the eco-friendliness of a sintering process is determined not by the technology alone, but by the thoughtful and responsible way it is implemented.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | High (Near-zero waste in additive processes like SLS) |
| Energy Consumption | High (Intensive heating required) |
| Emissions | Variable (Depends on filters and materials used) |
| Overall Eco-Friendliness | Context-dependent (Energy source, scale, controls) |
Optimize your sintering process with KINTEK's sustainable lab solutions.
As a specialist in laboratory equipment and consumables, KINTEK helps you balance material efficiency with energy-saving technologies and emission control systems. Whether you're scaling up production or refining R&D protocols, our expertise ensures your sintering operations meet both performance and environmental goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can reduce waste, lower energy costs, and ensure compliance for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is sample preparation important in analysis? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What are the lab safety rules for heating substances? Essential Protocols to Prevent Accidents
- What is the problem in pyrolysis? The Key Challenges to Commercial Viability
- What is the application and principle of centrifugation? Mastering Sample Separation for Your Lab
- Why is nickel alloy chosen for molten CaCl2-CaF2-CaO systems? Protect Your High-Temperature Processes
- What is the effect of sintering on hardness? Maximize Material Strength & Durability
- What are the safety rules for all heating process in the laboratory? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is the demand for synthetic diamonds? Rising Popularity for Ethical & Affordable Gems



















