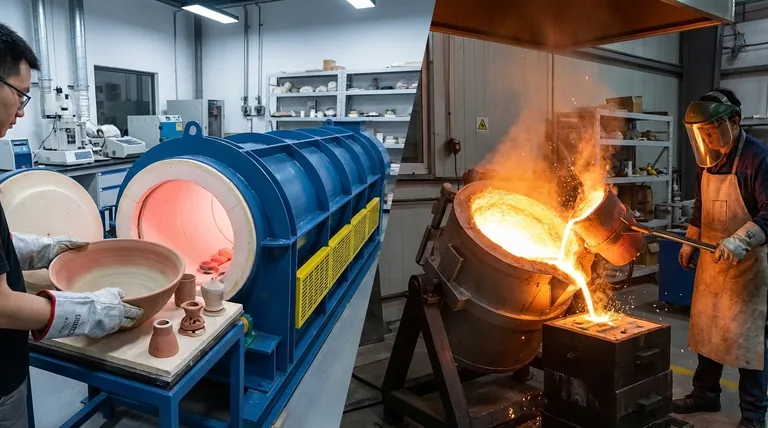
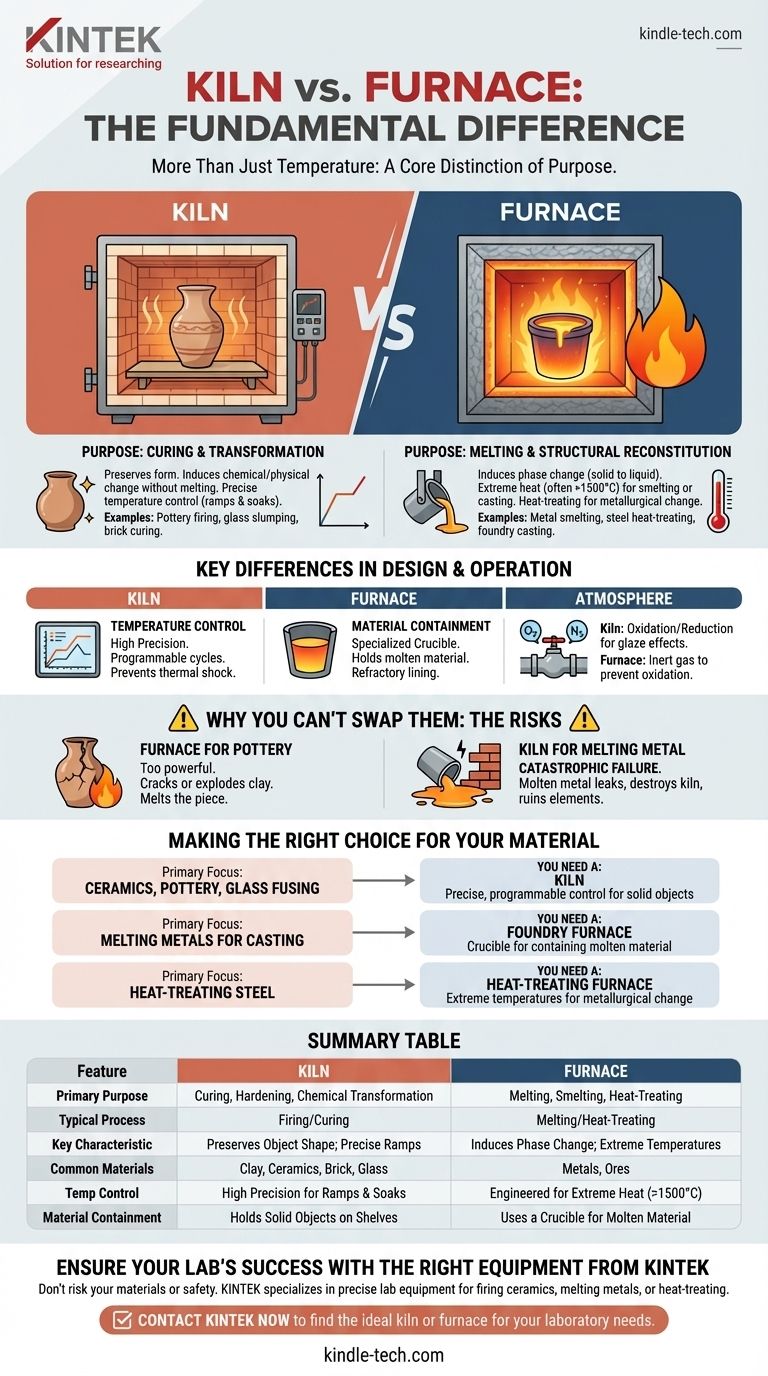
Yes, there is a fundamental difference between a kiln and a furnace that goes beyond just temperature. A kiln is a type of oven that hardens or chemically alters a material without changing its essential shape, as in the firing of pottery. A furnace, in contrast, is typically used for processes that involve melting or fundamentally changing a material's structure, such as smelting metal ore or heat-treating steel.
The core distinction is one of purpose. A kiln is designed for curing and transformation while preserving an object's form. A furnace is designed for melting and structural reconstitution at extreme temperatures.

The Core Functional Distinction: Process vs. Phase Change
Understanding the intended process for each device is the clearest way to distinguish between them. Their designs are highly specialized for these different tasks.
The Role of a Kiln: Driving Chemical Change
A kiln's primary function is to apply heat in a controlled manner to induce a permanent chemical or physical change. This is often called firing or curing.
The goal is not to melt the material but to harden it, remove moisture, or cause components to fuse together on a microscopic level. The object's overall shape is meant to remain intact throughout the process.
Common materials processed in a kiln include clay, bricks, ceramics, and some types of glass during slumping or fusing.
The Role of a Furnace: Inducing Phase and Structural Change
A furnace is built for processes that require much higher energy, often to change a material's state of matter from solid to liquid (phase change).
This includes smelting, where ore is heated to extract molten metal, and casting, where metal is melted to be poured into a mold.
Furnaces are also used for heat-treating, where a metal like steel is heated to rearrange its crystalline structure, thereby altering its properties like hardness or ductility.
Key Differences in Design and Operation
The different purposes of kilns and furnaces lead to critical differences in their construction and how they are operated.
Temperature Range and Control
While both can reach very high temperatures, furnaces are generally engineered to achieve the extreme melting points of metals, often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F).
Kilns, especially for ceramics, are valued for their precise temperature control. They can be programmed for complex schedules with specific heating rates (ramps) and holding times (soaks), which are critical for preventing thermal shock that would crack the ware.
Containing the Material
A kiln is designed to hold solid objects. Its interior is often lined with soft, porous firebrick that is an excellent insulator but would be destroyed by contact with molten material.
A furnace for melting metals must have a crucible or a hearth made of highly refractory materials (like graphite or silicon carbide) specifically designed to contain a liquid at extreme temperatures.
Atmosphere
Both kilns and furnaces may use atmosphere control, but for different reasons. In pottery, an oxygen-starved (reduction) atmosphere can be introduced to create dramatic and unique glaze effects.
In an industrial furnace, a specific atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) is often used to prevent the oxidation and contamination of molten metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why You Can't Swap Them
Using the wrong piece of equipment is not just inefficient; it is often destructive and dangerous. Understanding their limitations is key.
The Risk of Using a Furnace for Pottery
A furnace typically lacks the fine-grained temperature control needed for ceramics. Its raw power could easily heat the clay too quickly, causing it to crack or explode. At its highest temperatures, it would simply melt the ceramic piece into a puddle.
The Critical Risk of Melting Metal in a Kiln
Attempting to melt metal in a standard pottery kiln is a catastrophic failure waiting to happen. The molten metal will leak out of its container and destroy the soft firebrick floor and walls. It will also likely short out and ruin the electrical heating elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your choice depends entirely on the material you are working with and the transformation you wish to achieve.
- If your primary focus is ceramics, pottery, or glass fusing: You need a kiln for its precise, programmable temperature control and its design for firing solid objects.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for casting: You need a foundry furnace equipped with a crucible capable of safely containing molten material.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating steel (annealing, hardening, or tempering): You need a heat-treating furnace that can reach and hold the specific high temperatures required for metallurgical transformation.
Choosing the correct tool is the first and most critical step to ensuring the safety and success of your project.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Kiln | Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Curing, hardening, or chemical transformation (e.g., firing pottery) | Melting, smelting, or heat-treating (e.g., casting metal) |
| Typical Process | Firing/Curing | Melting/Heat-Treating |
| Key Characteristic | Preserves object shape; precise temperature ramps | Induces phase change; extreme temperatures |
| Common Materials | Clay, ceramics, brick, glass | Metals, ores |
| Temperature Control | High precision for ramps and soaks | Engineered for extreme heat (>1500°C common) |
| Material Containment | Holds solid objects on shelves | Uses a crucible to hold molten material |
Ensure Your Lab's Success with the Right Equipment from KINTEK
Choosing between a kiln and a furnace is critical for the safety and quality of your work. Using the wrong equipment can lead to project failure or even dangerous accidents.
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need. Whether you are firing ceramics, melting metals for research, or heat-treating materials, we have the right kiln or furnace for your application. Our experts can help you select the perfect tool with the precise temperature control and safety features your laboratory requires.
Don't risk your materials or safety—contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation.
✅ Contact KINTEK Now to find the ideal kiln or furnace for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















