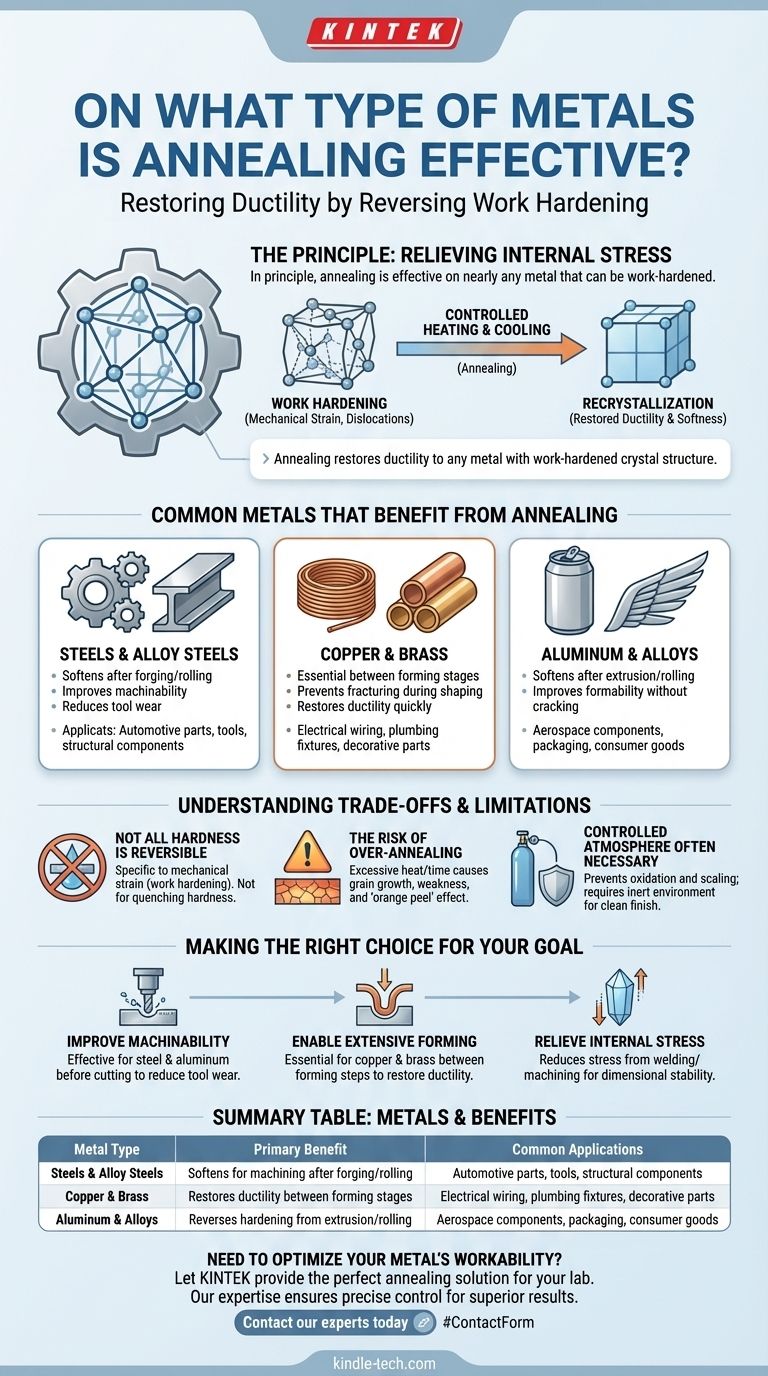
In principle, annealing is effective on nearly any metal that can be work-hardened. This includes the most common industrial metals such as steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. The process works by reversing the effects of mechanical stress, making the metal softer, more ductile, and significantly easier to shape or machine.
Annealing is not about a specific list of metals but a metallurgical process that restores ductility. Any metal whose crystal structure has been hardened by mechanical work (a process known as cold working) can have that hardness relieved and its workability restored through a controlled heating and cooling cycle.

The Principle Behind Annealing: Relieving Internal Stress
To understand which metals benefit from annealing, you must first understand why they become hard. The process is a direct response to a phenomenon called work hardening.
What is Work Hardening?
When a metal is bent, stretched, or formed at room temperature, its internal crystal structure becomes distorted. This creates a tangle of defects known as dislocations.
These dislocations impede further changes to the crystal structure, which we perceive as an increase in hardness and strength. However, this also makes the material more brittle and prone to cracking under further stress.
How Annealing Reverses Hardening
Annealing uses thermal energy to systematically undo the effects of work hardening. The process allows the metal's atoms to rearrange themselves into a more orderly state.
This controlled heating enables recrystallization, where new, strain-free crystal grains form. This effectively erases the dislocations, restoring the metal's original softness and ductility.
Common Metals That Benefit from Annealing
While the principle is widely applicable, annealing is particularly crucial for several key groups of industrial metals.
Steels and Alloy Steels
Steel is one of the most commonly annealed materials. After processes like forging or rolling, steel becomes too hard for effective machining. Annealing softens it, reducing tool wear and making it suitable for subsequent manufacturing steps.
Copper and Brass
Copper and its alloys, like brass, work-harden very quickly. For any process that requires significant shaping, such as drawing wire or forming complex parts, annealing is essential. It is often performed between forming stages to prevent the material from fracturing.
Aluminum and Its Alloys
Aluminum is frequently annealed to soften it after it has been hardened by processes like rolling or extrusion. This treatment improves its ductility, making it ready for further forming operations without the risk of cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, annealing is a precise process with important considerations. It is not a universal solution for all types of hardness.
Not All Hardness is Reversible
Annealing specifically counteracts hardness caused by mechanical strain (work hardening). It does not soften metals that have been hardened through other methods, such as the quenching and tempering used in heat-treatable steels.
The Risk of Over-Annealing
Heating a metal for too long or at a temperature that is too high can cause excessive crystal grain growth. This can make the material weak and brittle, and it may result in a poor surface finish known as an "orange peel" effect after forming.
Controlled Atmosphere is Often Necessary
Heating metals in the open air can cause oxidation and scaling on the surface, which may be undesirable. For applications requiring a clean finish, annealing must be performed in a controlled, inert atmosphere to protect the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to anneal depends entirely on the material's condition and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is to improve machinability: Annealing is highly effective for softening hard materials like steel and aluminum before cutting, which significantly reduces tool wear.
- If your primary focus is to enable extensive forming: For metals like copper and brass that harden quickly, annealing between forming steps is essential to restore ductility and prevent cracking.
- If your primary focus is to relieve internal stress: Annealing reduces the internal stresses that can build up from processes like welding or heavy machining, improving the dimensional stability and longevity of the part.
Ultimately, understanding annealing empowers you to precisely control a material's properties, turning a hard, brittle metal into one that is perfectly suited for your fabrication needs.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Primary Benefit of Annealing | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Steels & Alloy Steels | Softens for machining after forging/rolling | Automotive parts, tools, structural components |
| Copper & Brass | Restores ductility between forming stages | Electrical wiring, plumbing fixtures, decorative parts |
| Aluminum & Alloys | Reverses hardening from extrusion/rolling | Aerospace components, packaging, consumer goods |
Need to optimize your metal's workability? Let KINTEK provide the perfect annealing solution for your lab. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you achieve precise temperature control and uniform heating for superior results. Whether you're working with steel, aluminum, copper, or brass, we have the right tools to enhance your material's ductility and machinability. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation



















