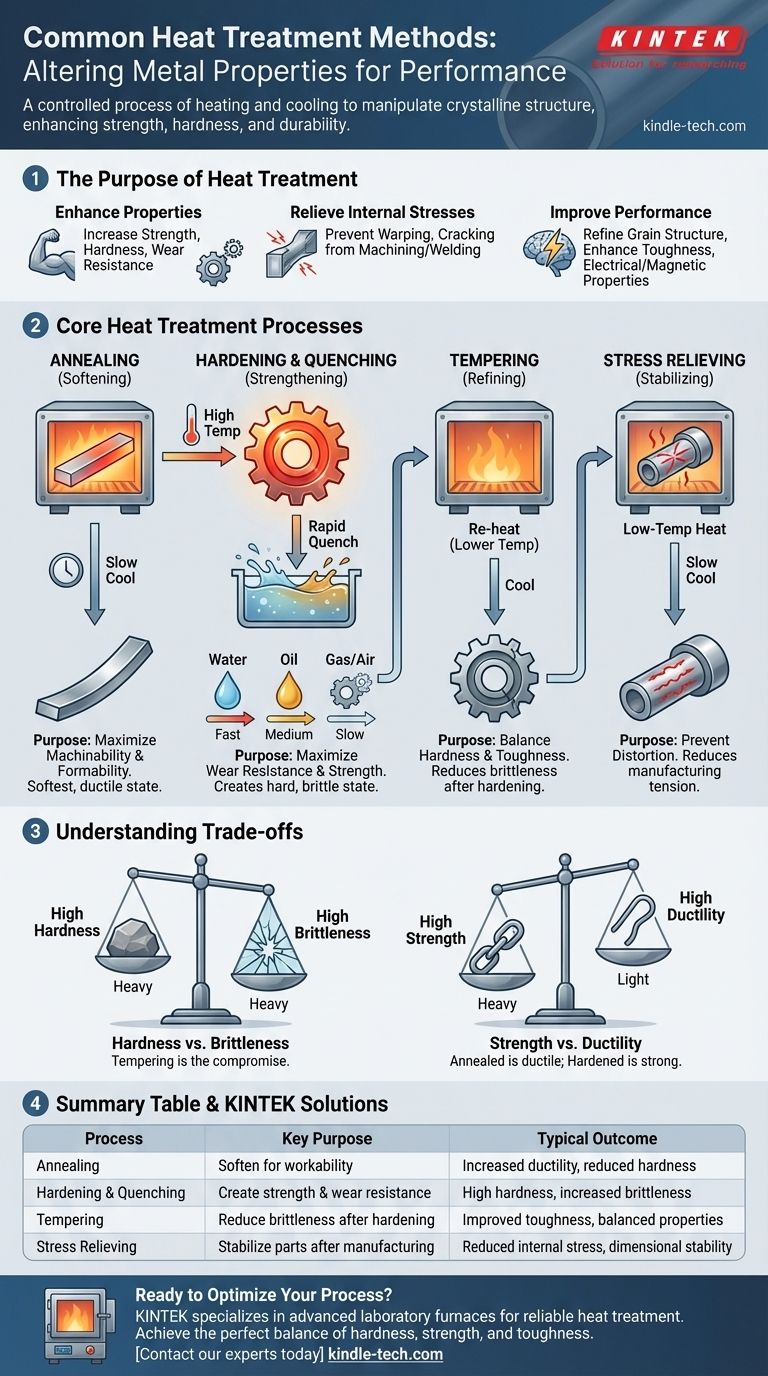
At its core, heat treatment is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling metals to intentionally alter their physical and mechanical properties. The most common methods include annealing, hardening, quenching, and stress relieving, each designed to achieve a specific outcome by manipulating the material's internal crystalline structure.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a toolbox of thermal processes. The choice of method depends entirely on the desired end-state of the material—whether that's making it softer for machining, harder for wear resistance, or more stable for long-term use.

The Purpose of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is a fundamental step in manufacturing used to unlock the full potential of a material, particularly steels. The primary goal is to change a material's properties in a predictable and beneficial way.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The most common reason for heat treatment is to modify mechanical characteristics. This includes increasing strength, hardness, and wear resistance for demanding applications or increasing ductility and softness to make a material easier to form or machine.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, and heavy machining introduce internal stresses into a material. These stresses can cause warping or cracking over time. Stress relieving is a low-temperature heat treatment that reduces this internal tension without significantly changing other properties, making the part more dimensionally stable.
Improving Material Performance
Beyond simple strength, heat treatment can refine a material’s grain structure. This refinement can improve toughness (resistance to fracture), and in some alloys, enhance electrical and magnetic properties for specialized applications.
A Breakdown of Core Heat Treatment Processes
While there are many specialized treatments, most fall into a few fundamental categories defined by their temperature cycles and cooling rates.
Annealing: Softening for Workability
Annealing is a process that involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it very slowly. This slow cooling allows the internal structure to reset into its softest, most ductile state.
The primary purpose of annealing is to make a material easier to work with. It is often performed to allow for further cold working, machining, or to prepare a material for subsequent hardening processes.
Hardening: Creating Strength and Wear Resistance
Hardening involves heating a metal to a high temperature, holding it there to ensure the desired structural change occurs, and then cooling it rapidly. This rapid cooling, known as quenching, locks the material's structure in a very hard but brittle state.
This process is used for parts that require high strength and resistance to wear and abrasion, such as gears, cutting tools, and bearings.
Quenching: The Critical Cooling Step
Quenching is not a standalone treatment but the rapid cooling phase of the hardening process. The speed of cooling is the most critical variable, and it is controlled by the quenching medium.
Common methods include:
- Brine or Water Quenching: Provides the fastest cooling rate, but can increase the risk of distortion or cracking.
- Oil Quenching: A slower, less severe quench than water, offering a good balance of hardness and reduced distortion.
- Gas or Air Quenching: The slowest quench methods, often performed in a controlled atmosphere with nitrogen or argon to prevent surface oxidation. This is typically used for high-alloy steels that don't require extreme cooling rates.
Tempering: Refining Hardness and Reducing Brittleness
A part that has been hardened and quenched is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary, lower-temperature heat treatment that is performed after hardening.
It reduces some of the extreme hardness and brittleness, while significantly increasing the material's toughness. By adjusting the tempering temperature, engineers can precisely dial in the final balance of hardness and toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single property can be maximized without impacting others. Understanding these trade-offs is key to effective material selection and treatment.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
This is the most fundamental trade-off in steel heat treatment. As you increase a material's hardness through quenching, you invariably increase its brittleness, making it more susceptible to shattering under impact. Tempering is the essential compromise, sacrificing a small amount of peak hardness to gain a large amount of toughness.
Strength vs. Ductility
Generally, as a material's strength and hardness increase, its ductility (the ability to bend or deform without fracturing) decreases. An annealed component is highly ductile but weak, while a fully hardened component is very strong but will crack rather than bend.
Performance vs. Process Complexity
Achieving superior, highly consistent results often requires more complex processes. Heat treating in a controlled inert gas atmosphere (using argon or nitrogen) prevents oxidation and results in a clean surface, but it is more costly than treating in open air. The choice depends on the final application's requirements and budget.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment must be directly linked to the component's intended function.
- If your primary focus is maximum machinability or formability: Annealing is the correct process to soften the material and make it easy to work with.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and hardness: Hardening and quenching are necessary, followed by a low-temperature temper to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is stabilizing a part after welding or heavy machining: Stress relieving is the ideal choice to prevent future distortion without altering the core strength.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high strength and good toughness: The combination of hardening, quenching, and a carefully selected tempering temperature is the most common path.
By understanding these fundamental processes, you gain control over the final performance of your material.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Purpose | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften material for workability | Increased ductility, reduced hardness |
| Hardening & Quenching | Create strength and wear resistance | High hardness, increased brittleness |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness after hardening | Improved toughness, balanced properties |
| Stress Relieving | Stabilize parts after manufacturing | Reduced internal stress, dimensional stability |
Ready to Optimize Your Heat Treatment Processes?
Understanding the theory is the first step. Achieving consistent, high-quality results requires precise control and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces and consumables designed for reliable heat treatment, from precise annealing to controlled atmosphere quenching.
Whether you're developing new alloys or ensuring the quality of manufactured components, our solutions help you achieve the perfect balance of hardness, strength, and toughness.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your material performance and process reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What affects the rate of melting? Master the Key Factors for Precise Control
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it work? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab
- What temperature causes melting? Debinding vs. Melting in Metal Fabrication
- How do you make biochar in a muffle furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Pyrolysis
- What precautions should be taken while heating and cooling the crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Safety



















