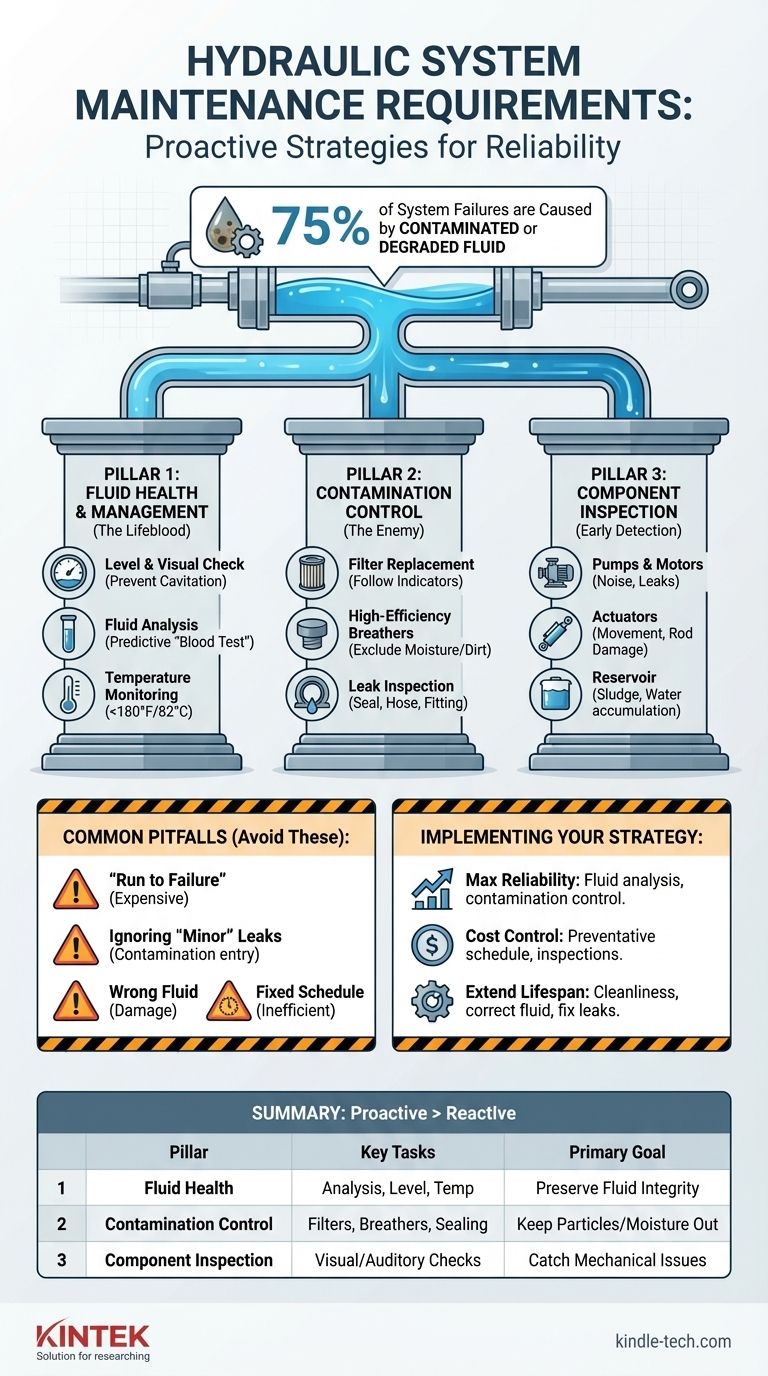
At its core, effective hydraulic system maintenance revolves around three key activities: managing the hydraulic fluid, controlling contamination, and inspecting core components. These requirements range from simple daily visual checks for leaks and fluid levels to more involved periodic tasks like replacing filters and analyzing fluid samples to prevent system failure.
The central goal of hydraulic maintenance is not just to fix what's broken, but to proactively preserve the health of the hydraulic fluid. Since contaminated or degraded fluid is the leading cause of over 75% of system failures, a strategy focused on fluid cleanliness is the most effective way to ensure reliability and longevity.

The Three Pillars of Hydraulic Maintenance
A robust maintenance program is built on three foundational pillars. Focusing your efforts here will address the most common failure points and deliver the greatest return in system uptime.
Pillar 1: Fluid Health and Management
Think of hydraulic fluid as the lifeblood of your system. Its condition dictates the performance and lifespan of every component.
Fluid Level and Visual Check The simplest and most frequent task is checking the fluid level in the reservoir. Low fluid levels can cause the pump to cavitate (draw in air), leading to rapid damage and system overheating.
Fluid Quality (The "Blood Test") Regular fluid sampling and analysis is the single most effective predictive maintenance task you can perform. This analysis measures contamination levels, water content, viscosity, and additive depletion, giving you a precise picture of the fluid's health and enabling you to change it based on condition, not just hours.
Operating Temperature Consistently check the system's operating temperature. Excessive heat (typically above 180°F or 82°C) rapidly degrades the fluid, damages seals, and reduces system efficiency. High temperatures are a symptom that requires investigation.
Pillar 2: Contamination Control
Contaminants are the primary enemy of a hydraulic system. Particles as small as 5 microns—invisible to the naked eye—can damage the precise tolerances in pumps, valves, and motors.
Filters Filters are your primary defense. Regularly inspect filter condition indicators, which signal when a filter is clogged and needs replacement. Adhere to a strict schedule for changing filters, as a clogged filter in bypass mode offers no protection.
Breathers The reservoir must "breathe" as fluid levels change. Standard breather caps can allow airborne moisture and dirt to enter the system. Upgrading to high-efficiency desiccant breathers, which dry and filter incoming air, is a high-value improvement.
Seals, Hoses, and Fittings Inspect all external seals (on cylinders, pumps, motors) and all hoses and fittings for leaks. A leak is not just a loss of fluid; it is a potential entry point for dirt and moisture when the system is off.
Pillar 3: System Component Inspection
While fluid is the priority, regular inspection of the hardware is crucial for catching issues before they become catastrophic.
Pumps and Motors Listen for changes in operational noise. Whining or knocking can indicate cavitation, aeration, or impending mechanical failure. Check for leaks around the pump or motor shaft seals.
Actuators (Cylinders and Motors) Observe actuators in operation. Jerky or slow movement can indicate internal leakage or air in the system. Check cylinder rods for scoring or damage, which can tear seals and introduce contamination.
Reservoir The reservoir should be periodically checked for sludge and water accumulation at the bottom. A clean reservoir is essential for a clean system.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Even with a plan, certain misconceptions can undermine your efforts and lead to costly downtime.
The "Run to Failure" Fallacy
This reactive approach is exceptionally expensive. A simple pump failure can send a catastrophic wave of contamination throughout the entire system, requiring a complete flush and potentially damaging other expensive components like valves and actuators.
Ignoring "Minor" Leaks
A small, slow leak is often dismissed as a nuisance. However, it is a clear indicator of a failing seal or loose fitting. More importantly, it is a pathway for contamination to enter the system. Fixing small leaks promptly is a critical preventative measure.
Using the Wrong Fluid
Using a hydraulic fluid that does not meet the manufacturer's specifications for viscosity and additive package is a critical error. The wrong fluid can lead to improper lubrication, overheating, and premature wear on all components.
Changing Fluid on a Fixed Schedule Alone
While better than nothing, changing fluid based only on run hours can be wasteful or risky. If the system is clean and runs cool, the fluid may last much longer than the schedule suggests. If it runs hot or in a dirty environment, it may need to be changed sooner. Fluid analysis is the only way to know for sure.
Implementing an Effective Maintenance Program
Your maintenance strategy should align directly with your operational goals. Use these guidelines to tailor your approach.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and uptime: Prioritize a rigorous fluid analysis program and invest in high-efficiency contamination control, such as desiccant breathers and offline filtration.
- If your primary focus is cost control: Implement a strict preventative maintenance schedule for filter changes and component inspections to avoid the high cost of unplanned, catastrophic failures.
- If your primary focus is extending equipment lifespan: Emphasize system cleanliness above all else. Ensure you are always using the correct, high-quality fluid and that all "minor" leaks are fixed immediately.
Ultimately, shifting your mindset from reactive repair to proactive system health is the key to managing a successful hydraulic maintenance program.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Pillar | Key Tasks | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Health | Level checks, fluid analysis, temperature monitoring | Preserve fluid integrity to prevent 75% of system failures |
| Contamination Control | Filter replacement, breather maintenance, leak sealing | Keep particles and moisture out of the system |
| Component Inspection | Visual and auditory checks of pumps, actuators, reservoir | Catch mechanical issues before they cause catastrophic damage |
Ensure your hydraulic systems operate with maximum reliability and uptime. A proactive maintenance plan is the most effective way to prevent the high costs of unplanned downtime and component failure. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for effective fluid analysis and contamination control. Let our experts help you build a tailored maintenance strategy. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's hydraulic system needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes



















