In essence, optical coatings are exceptionally thin, engineered layers of material applied to an optical surface, like a lens or mirror, to precisely control how it interacts with light. By adding one or more of these microscopic films, we can dramatically alter the reflection, transmission, and absorption properties of the underlying component, turning a simple piece of glass into a high-performance instrument.
The core function of an optical coating is to manipulate light waves at a surface through a principle called thin-film interference. This allows engineers to eliminate unwanted reflections, create highly reflective mirrors, or filter out specific wavelengths of light with incredible precision.

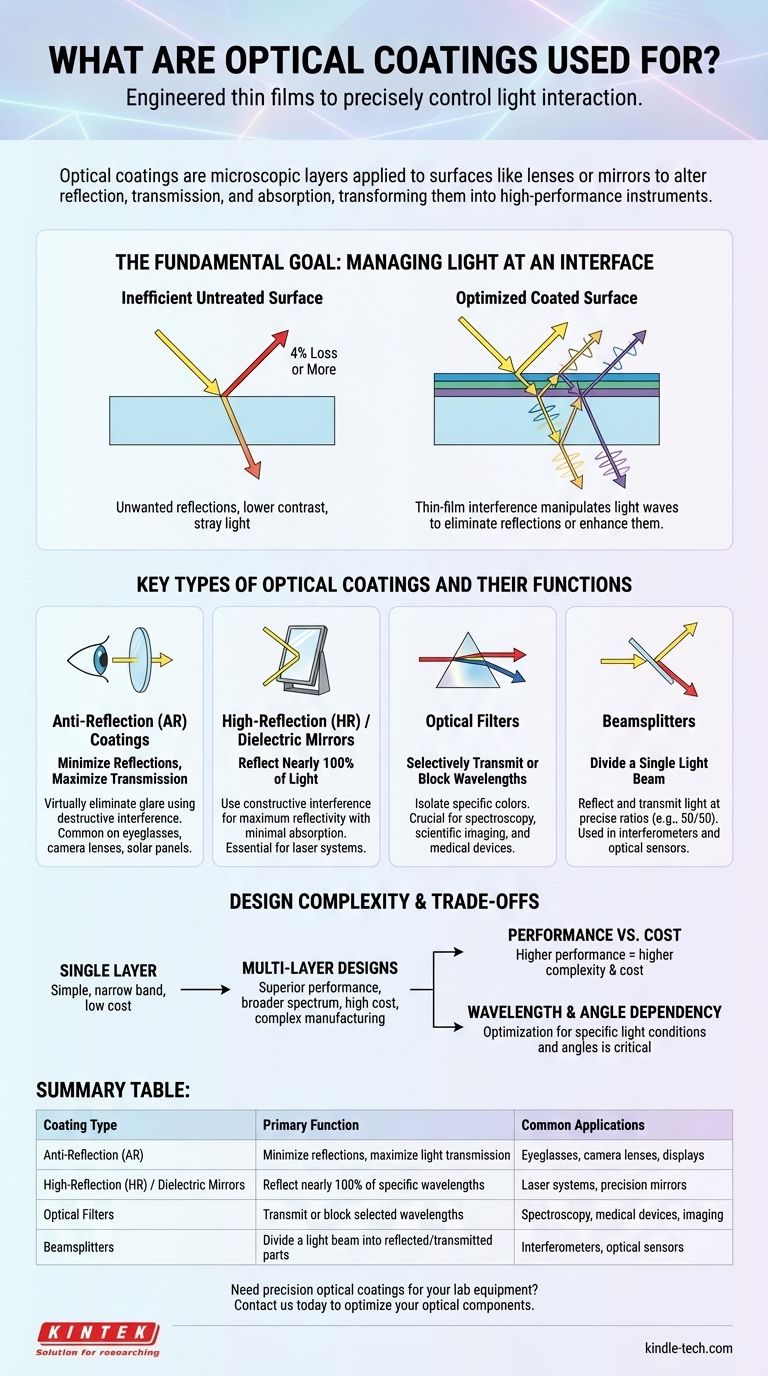
The Fundamental Goal: Managing Light at an Interface
Why Untreated Surfaces are Inefficient
When light travels from one medium to another—such as from air into a glass lens—a portion of that light inevitably reflects off the surface. For a standard glass surface, this can be a 4% loss or more.
In a complex system with many lenses, like a camera or microscope, this cumulative loss degrades image contrast and brightness, creating stray light and ghost images.
The Principle of Thin-Film Interference
Optical coatings work by introducing new reflective surfaces. When light hits a coated lens, some light reflects from the top of the coating, and some reflects from the bottom (at the coating-glass interface).
These two reflected light waves then interact, or "interfere," with one another.
How Interference is Controlled
By carefully controlling the thickness and refractive index of the coating material, we can dictate the nature of this interference.
We can design the coating so the reflected waves cancel each other out (destructive interference) or so they reinforce each other (constructive interference), depending on the desired outcome.
Key Types of Optical Coatings and Their Functions
Anti-Reflection (AR) Coatings
The most common type of coating, AR coatings, use destructive interference to virtually eliminate reflections. This maximizes the amount of light that passes through the optic.
You find them everywhere: on eyeglasses, camera lenses, solar panels, and high-definition displays where maximum light transmission and minimal glare are critical.
High-Reflection (HR) / Dielectric Mirrors
The opposite of an AR coating, an HR coating uses constructive interference to create a surface that reflects nearly 100% of light at specific wavelengths.
These are not like household mirrors made of metal. Dielectric mirrors are essential for applications requiring maximum reflectivity with minimal light absorption, such as in laser systems.
Optical Filters
Filter coatings are designed to selectively transmit certain wavelengths (colors) of light while blocking others.
This includes band-pass filters that only allow a narrow range of colors through, long-pass filters that block shorter wavelengths, and short-pass filters that block longer ones. They are fundamental to scientific instruments, spectroscopy, and medical devices.
Beamsplitters
A beamsplitter coating is engineered to divide a single beam of light into two. It does this by reflecting a specific percentage of the light and transmitting the rest.
Common ratios are 50/50 or 70/30 (Reflection/Transmission) and are crucial for interferometers and certain types of optical sensors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Complexity
The Power of Multi-Layer Designs
A single coating layer offers limited performance over a narrow band of wavelengths. True high-performance coatings are almost always composed of multiple layers.
As noted in advanced optical design, stacking dozens of layers with varying thicknesses and refractive indices allows engineers to achieve superior performance across a much broader spectrum of light and at different angles of incidence.
Performance vs. Cost
The complexity of a coating design directly impacts its cost. A simple single-layer magnesium fluoride AR coating is inexpensive.
A multi-layer, broadband AR coating that must also be highly durable requires a more complex manufacturing process (like ion-beam sputtering) and is therefore significantly more expensive.
Wavelength and Angle Dependency
No coating is perfect for all conditions. A coating designed to be anti-reflective for visible light may be highly reflective in the infrared spectrum.
Similarly, a coating optimized for light hitting a surface straight-on will perform differently as the angle of incidence changes. This is a critical design constraint.
Matching the Coating to the Application
Choosing the right coating begins with defining its primary function within the optical system.
- If your primary focus is maximizing clarity and light throughput: You need an Anti-Reflection (AR) coating, likely a multi-layer broadband design for applications like camera lenses or display screens.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly efficient mirror: You need a High-Reflection (HR) coating, often a dielectric stack for applications like laser systems where absorption must be minimized.
- If your primary focus is isolating specific colors or wavelengths: You need an optical filter coating, such as a band-pass or edge filter for scientific imaging or spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is dividing a single light source: You need a beamsplitter coating designed for a precise reflection-to-transmission ratio for your specific instrumentation.
Ultimately, selecting the right optical coating transforms a standard component into a precision tool engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-Reflection (AR) | Minimize reflections, maximize light transmission | Eyeglasses, camera lenses, displays |
| High-Reflection (HR) / Dielectric Mirrors | Reflect nearly 100% of specific wavelengths | Laser systems, precision mirrors |
| Optical Filters | Transmit or block selected wavelengths | Spectroscopy, medical devices, imaging |
| Beamsplitters | Divide a light beam into reflected/transmitted parts | Interferometers, optical sensors |
Need precision optical coatings for your lab equipment? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including custom optical coatings tailored for spectroscopy, laser systems, and scientific instruments. Our coatings enhance light control, improve accuracy, and boost the efficiency of your laboratory setups. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your optical components for superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Temperature Measurement Double-Sided Coated Germanium Ge Lens
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What physical conditions does an HPHT press provide for BDD synthesis? Achieve Extreme 5 GPa & 1800 K Conditions
- What is the purpose of adding a boron source in CVD diamond growth? Master P-Type Semiconductor Conductivity
- What is the role of an HFCVD reactor in synthesizing boron-doped diamond? Expert Guide to Diamond Gas Activation
- Why are non-active BDD anodes selected for wastewater treatment? Achieve Total Pollutant Mineralization











