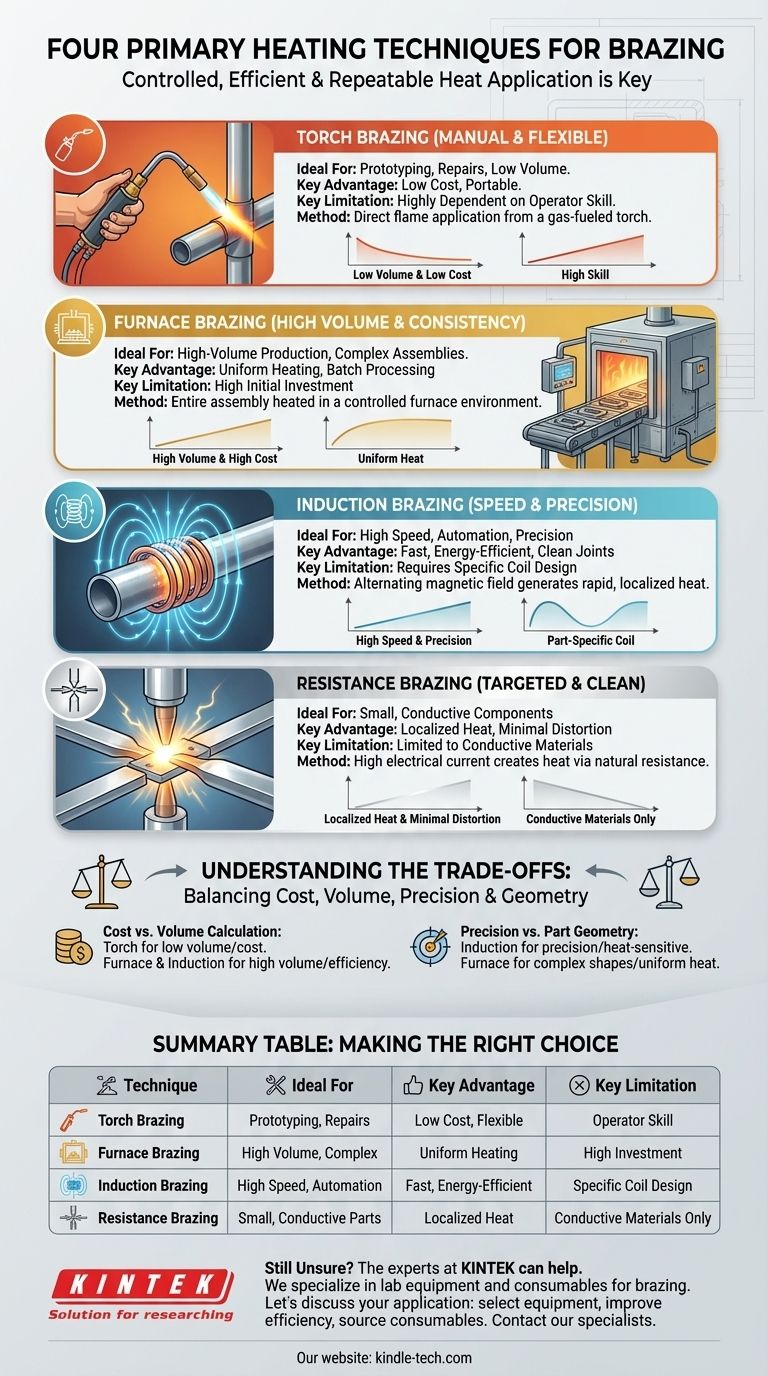
While several methods exist, the four most common and distinct heating techniques for brazing are torch brazing, furnace brazing, induction brazing, and resistance brazing. Each method applies heat differently, making them suitable for specific materials, production volumes, and joint configurations.
The core challenge in brazing isn't just reaching the filler metal's melting point, but applying heat in a controlled, efficient, and repeatable way. The "best" technique is entirely dependent on the specific requirements of the application, including production volume, joint complexity, and material properties.

The Four Primary Heating Techniques for Brazing
Brazing requires heating a base metal to a temperature that will melt a filler metal, but not the base metal itself. The way this heat is delivered defines the technique and its ideal use case.
Torch Brazing (Manual & Flexible)
This is the most common method for manual brazing and repairs. It involves using a gas-fueled torch (such as oxy-acetylene) to apply a direct flame to the parts being joined.
The primary advantage of torch brazing is its low initial cost and portability. However, it is highly dependent on operator skill to achieve consistent heating and avoid overheating the base materials.
Furnace Brazing (High Volume & Consistency)
In furnace brazing, the entire assembly is placed inside a furnace and heated to the brazing temperature. These furnaces can be gas or electrically heated and often use a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
This method is ideal for high-volume production of small to medium-sized assemblies. It ensures uniform heating, making it perfect for complex parts with multiple joints that need to be brazed simultaneously.
Induction Brazing (Speed & Precision)
Induction brazing uses an alternating magnetic field generated by an induction coil. This field induces electrical currents within the metal parts, which generates heat rapidly and precisely at the joint area.
This technique is extremely fast, energy-efficient, and highly controllable, making it a popular choice for automated production lines. It excels at creating strong, clean joints with minimal heat affecting the rest of the component.
Resistance Brazing (Targeted & Clean)
Resistance brazing generates heat by passing a high electrical current through the joint via electrodes. The natural electrical resistance of the components causes heat to build up precisely at the point of contact.
This method is very fast and localized, making it suitable for joining small, electrically conductive components where minimal heat transfer to surrounding areas is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right heating technique involves balancing cost, volume, precision, and the specific geometry of your parts. There is no single "best" method, only the most appropriate one for the job.
The Cost vs. Volume Calculation
Torch brazing has a very low initial equipment cost, making it perfect for one-off jobs or low-volume prototyping.
Furnace and induction systems represent a significant capital investment. However, for mass production, their speed and automation result in a much lower cost per part, justifying the initial expense.
Precision vs. Part Geometry
Induction heating offers unparalleled precision, heating only the immediate joint area. This is ideal for heat-sensitive components but requires a coil designed for a specific part geometry.
Furnace brazing heats the entire assembly, which removes the geometric limitations of an induction coil and is great for complex shapes. However, it means the entire part is subjected to high temperatures.
The Role of Operator Skill
The quality of a torch-brazed joint is almost entirely dependent on the skill of the operator. It is a manual art that requires significant training and experience.
In contrast, furnace, induction, and resistance brazing are easily automated processes. Once the parameters are set, they produce highly consistent and repeatable results with minimal operator intervention.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct heating method is a critical decision that impacts quality, speed, and cost. Use the following as a guide to match the technique to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is prototyping, repairs, or low-volume work: Torch brazing offers the best combination of low cost and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex assemblies: Furnace brazing provides unmatched consistency and the ability to braze multiple joints at once.
- If your primary focus is speed, automation, and precise heat control: Induction brazing is the most efficient and repeatable method for high-volume manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is joining small, conductive parts with minimal heat distortion: Resistance brazing provides extremely fast and localized heating for specific applications.
Ultimately, the most effective brazing strategy comes from matching the heating technique's unique strengths to your specific engineering and production requirements.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Ideal For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Prototyping, Repairs, Low Volume | Low cost, Flexible | Operator skill-dependent |
| Furnace Brazing | High Volume, Complex Assemblies | Uniform heating, Batch processing | High initial investment |
| Induction Brazing | High Speed, Automation, Precision | Fast, Energy-efficient, Clean joints | Requires specific coil design |
| Resistance Brazing | Small, Conductive Components | Localized heat, Minimal distortion | Limited to conductive materials |
Still Unsure Which Brazing Technique is Right for Your Project?
Choosing the correct heating method is critical for achieving strong, consistent, and cost-effective brazed joints. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific brazing and manufacturing challenges.
We can help you:
- Select the optimal equipment for your production volume and part geometry.
- Improve process efficiency and joint quality.
- Source reliable consumables to ensure successful results.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our brazing specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints



















