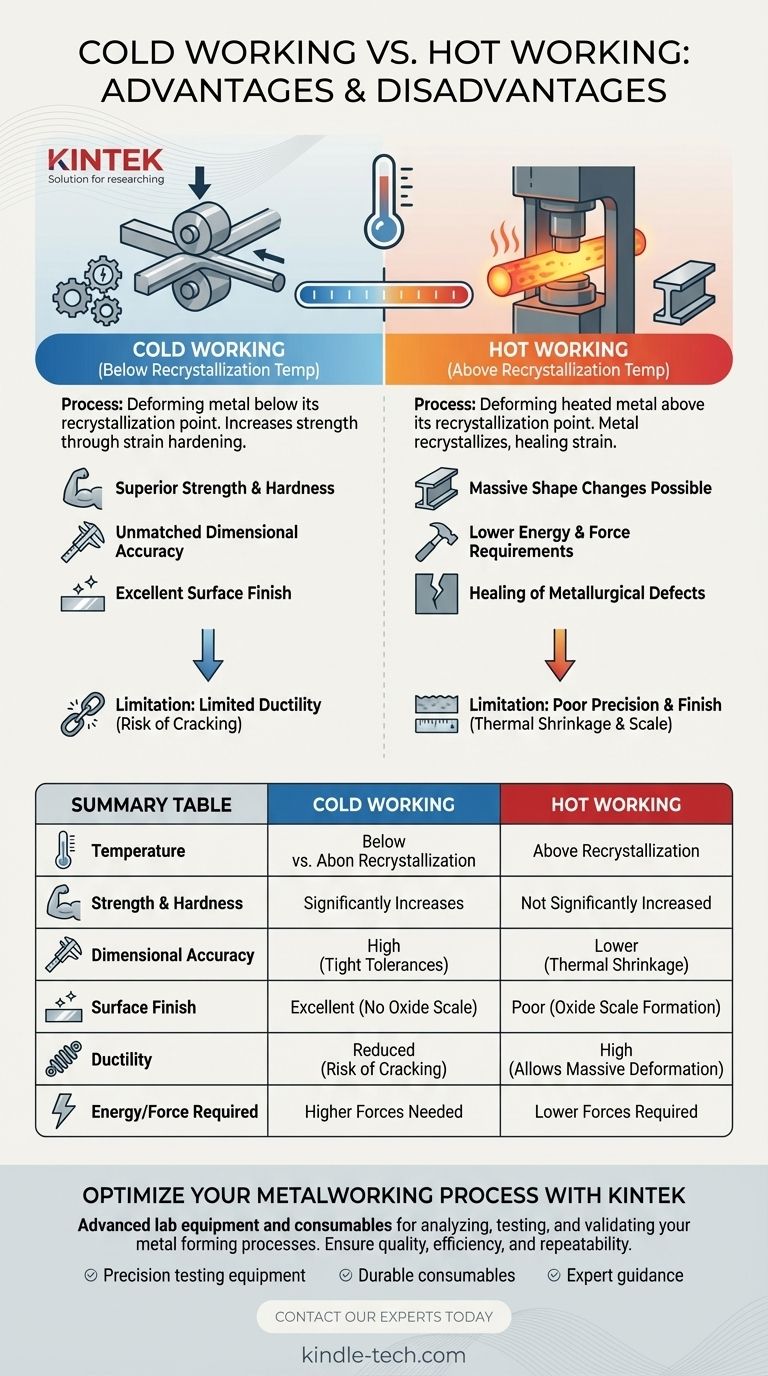
In metalworking, the choice between cold and hot working is a foundational decision that dictates a component's final properties, precision, and cost. Cold working produces a stronger, more accurate part with a better surface finish, but is limited in its shaping ability. Conversely, hot working allows for massive changes in shape and is more economical for large deformations, but sacrifices dimensional precision and surface quality.
The decision is not about which process is "better," but which one aligns with your project's primary driver: strength and precision (cold working) versus large-scale formability (hot working). The key is understanding that temperature is the lever controlling the trade-off between a material's strength and its ductility.

What Defines "Cold" vs. "Hot" Working?
The distinction between these two processes is not based on everyday temperature but on a specific metallurgical threshold unique to each metal alloy.
The Recrystallization Temperature: The Scientific Boundary
The critical factor is the recrystallization temperature. This is the temperature at which a deformed metal can form new, strain-free grains, effectively healing the internal damage caused by deformation.
Hot working occurs above this temperature, while cold working occurs below it. This is why lead can be hot-worked at room temperature, while steel requires temperatures over 1000°C.
Hot Working: Deforming Above Recrystallization
In hot working, the metal is heated until it is soft and highly ductile. As forces are applied, the microscopic crystal grains deform but immediately recrystallize, erasing the strain.
This process is analogous to kneading warm dough. You can stretch and shape it extensively because it remains soft and pliable, and it doesn't get progressively harder to work with.
Cold Working: Deforming Below Recrystallization
In cold working, the metal is shaped at or near room temperature. The crystal grains are deformed, stretched, and distorted, but they do not recrystallize.
This creates internal stress and an entanglement of microscopic defects called dislocations. This phenomenon, known as strain hardening or work hardening, is like bending a paperclip back and forth—it gets progressively stronger and stiffer until it breaks.
The Core Advantages of Cold Working
Engineers choose cold working when the final mechanical properties and precision are paramount.
Superior Strength and Hardness
By preventing recrystallization, cold working locks in the effects of strain hardening. This process significantly increases the material's tensile strength and hardness.
Unmatched Dimensional Accuracy
Because the part is not heated and cooled, there are no issues with thermal expansion or contraction. This allows for the production of parts with very tight tolerances and high repeatability.
Excellent Surface Finish
Cold working does not produce an oxide layer (scale) on the metal's surface. The resulting part is clean and smooth, often eliminating the need for secondary machining or polishing operations.
The Core Advantages of Hot Working
Hot working is the process of choice for large-scale manufacturing and creating complex shapes from bulk material.
Massive Shape Changes are Possible
The extreme ductility and low flow stress of a heated metal allow for enormous deformations without the risk of fracture. This is how massive products like structural I-beams and railway tracks are formed.
Lower Energy and Force Requirements
A hot billet of metal is significantly easier to deform than a cold one. This means the machinery used—like rolling mills and forging presses—can be less powerful, reducing operational and capital costs.
Healing of Metallurgical Defects
The high temperatures and compressive forces of hot working can weld shut internal voids and porosity from the initial casting process. This improves the material's internal soundness and toughness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Neither process is a universal solution. The choice involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs.
Cold Working's Achilles' Heel: Limited Ductility
The same strain hardening that increases strength also drastically reduces ductility. A cold-worked material becomes more brittle, limiting how much it can be shaped before it cracks. This restricts the complexity of parts that can be made.
Hot Working's Downside: Poor Precision and Finish
As a hot-worked part cools, it shrinks unpredictably, making tight dimensional control nearly impossible. Furthermore, the high temperatures cause an oxide scale to form on the surface, resulting in a rough finish that typically requires removal.
The Cost Equation: More Than Meets the Eye
Hot working requires significant energy to run furnaces, but the machinery forces are lower. Cold working requires more powerful and robust equipment but can save money by eliminating the need for secondary finishing operations. The most cost-effective solution depends entirely on the part's geometry, material, and required production volume.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material selection and end-goal dictate the correct process. The most effective path is the one that directly addresses your primary design constraint.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and a precise finish: Choose cold working for components like high-strength bolts, precision shafts, and drawn wires.
- If your primary focus is creating large or complex shapes economically: Choose hot working for structural components like I-beams, railway tracks, and large open-die forgings.
- If you need a balance of properties: Consider a hybrid approach where initial shaping is done via hot working, followed by a final cold working pass (cold finishing) to achieve the desired dimensional accuracy and strength.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the manufacturing process that most efficiently achieves your design intent.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Cold Working | Hot Working |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Below recrystallization temperature | Above recrystallization temperature |
| Strength & Hardness | Significantly increases | Not significantly increased |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High (tight tolerances) | Lower (due to thermal shrinkage) |
| Surface Finish | Excellent (no oxide scale) | Poor (oxide scale formation) |
| Ductility | Reduced (risk of cracking) | High (allows massive deformation) |
| Energy/Force Required | Higher forces needed | Lower forces required |
| Ideal For | Precision parts, bolts, shafts | Large structural components, I-beams |
Optimize Your Metalworking Process with KINTEK
Choosing between cold and hot working is critical for achieving the desired material properties and precision in your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary to analyze, test, and validate your metal forming processes. Whether you're working on high-strength precision parts or large-scale structural shapes, our solutions help you ensure quality, efficiency, and repeatability.
Let us support your laboratory needs with:
- Precision testing equipment for material property analysis.
- Durable consumables for consistent results.
- Expert guidance to align your process with project goals.
Ready to enhance your metalworking outcomes? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can empower your lab's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) contribute to the fabrication of HE-O-MIEC and LLZTO? Expert Densification Guide
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Preferred for Sulfide Solid Electrolytes? Maximize Your Ionic Conductivity
- What is the role of a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) in C-PSC lamination? Enhance Solar Efficiency Without Heat
- What advantages does CIP equipment offer for W-TiC composites? Achieve High-Density, Defect-Free Materials
- How does a cold isostatic press (CIP) address YAG ceramic density? Achieve Uniform High-Density Green Bodies











